Artificial intelligence (AI) is the ability of machines to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as reasoning, learning, or decision making. AI has been applied to various domains, including law, where it can assist in research, drafting, analysis, or prediction. However, the use of AI in the law is certainly not without controversy, particularly given the high-profile and embarrassing incidents in which lawyers who had not properly vetted their AI bot’s research included AI hallucinations in court filings.
Institutions of higher education are currently grappling with the question of whether artificial intelligence is an essential tool of the future workforce or a means by which students may attempt to bypass their own educational enrichment and critical thinking skill development. We wanted to know how often JD students are currently using AI in their law school coursework. In 2024, LSSSE added the following question:
How often do you use AI (ChatGPT or similar technology) to help prepare for class or complete class assignments, projects, exams, or papers?
- Never
- Sometimes
- Often
- Very often
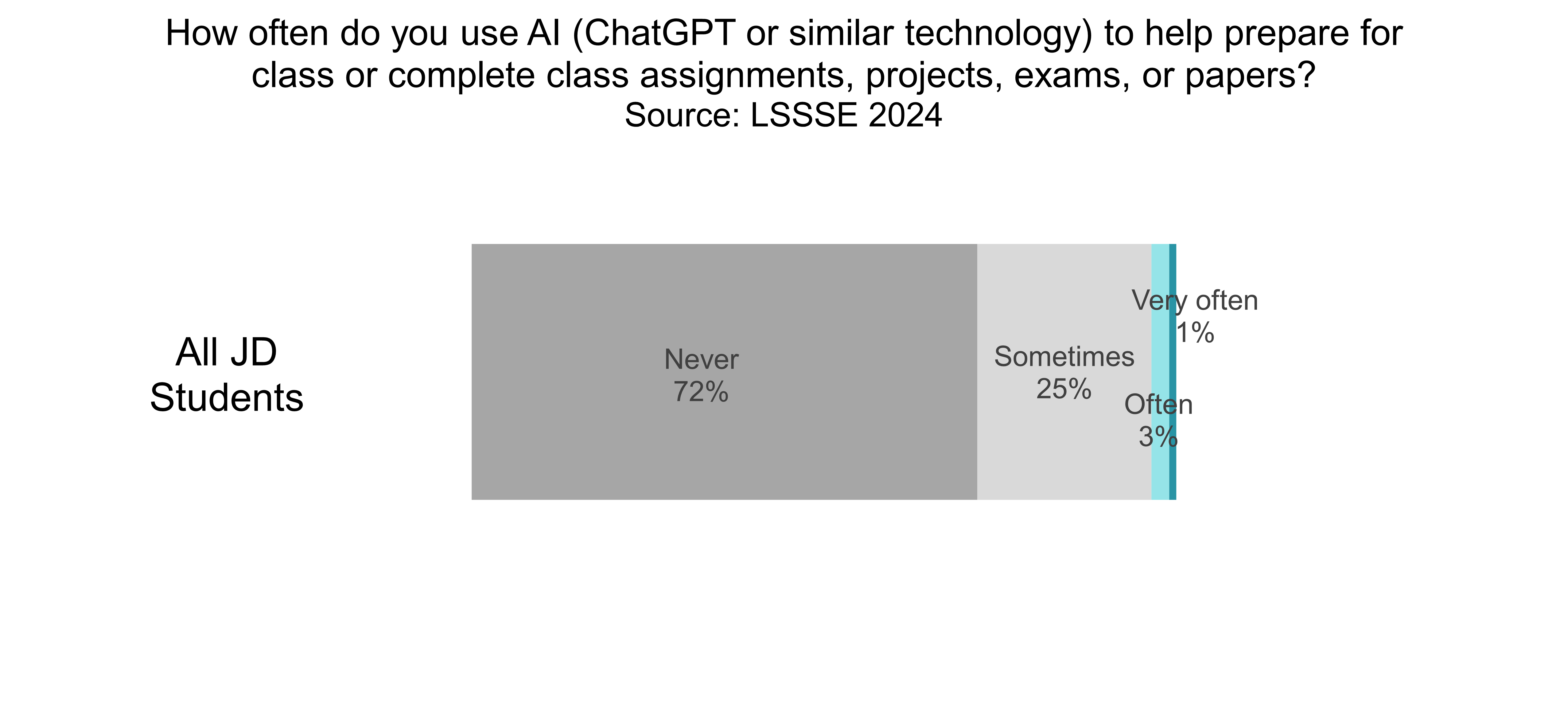
Our analysis shows that most law students are not currently using AI in their coursework at all. Almost three-quarters (72%) never use AI to prepare for class or complete assignments. A quarter of law students (25%) sometimes use AI in their coursework, and only 4% use it often or very often.
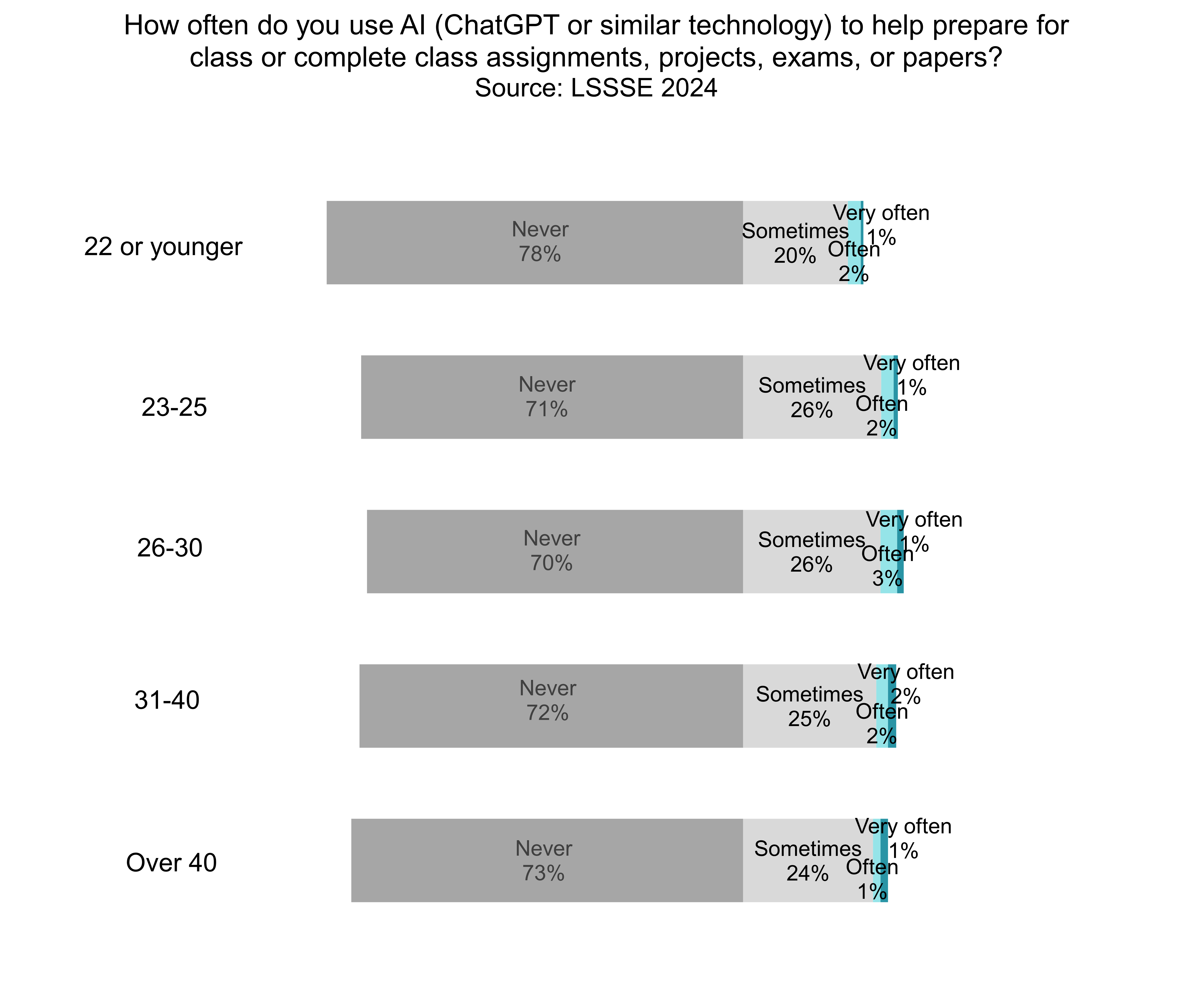
There are only slight generational differences in AI usage, with students in the 23-30 age group a perhaps a tiny bit more likely to use AI than other students. Interestingly, law students who are 22 or younger are the least likely age group to use AI for class preparation or assignments, with only 22% doing so at least sometimes.
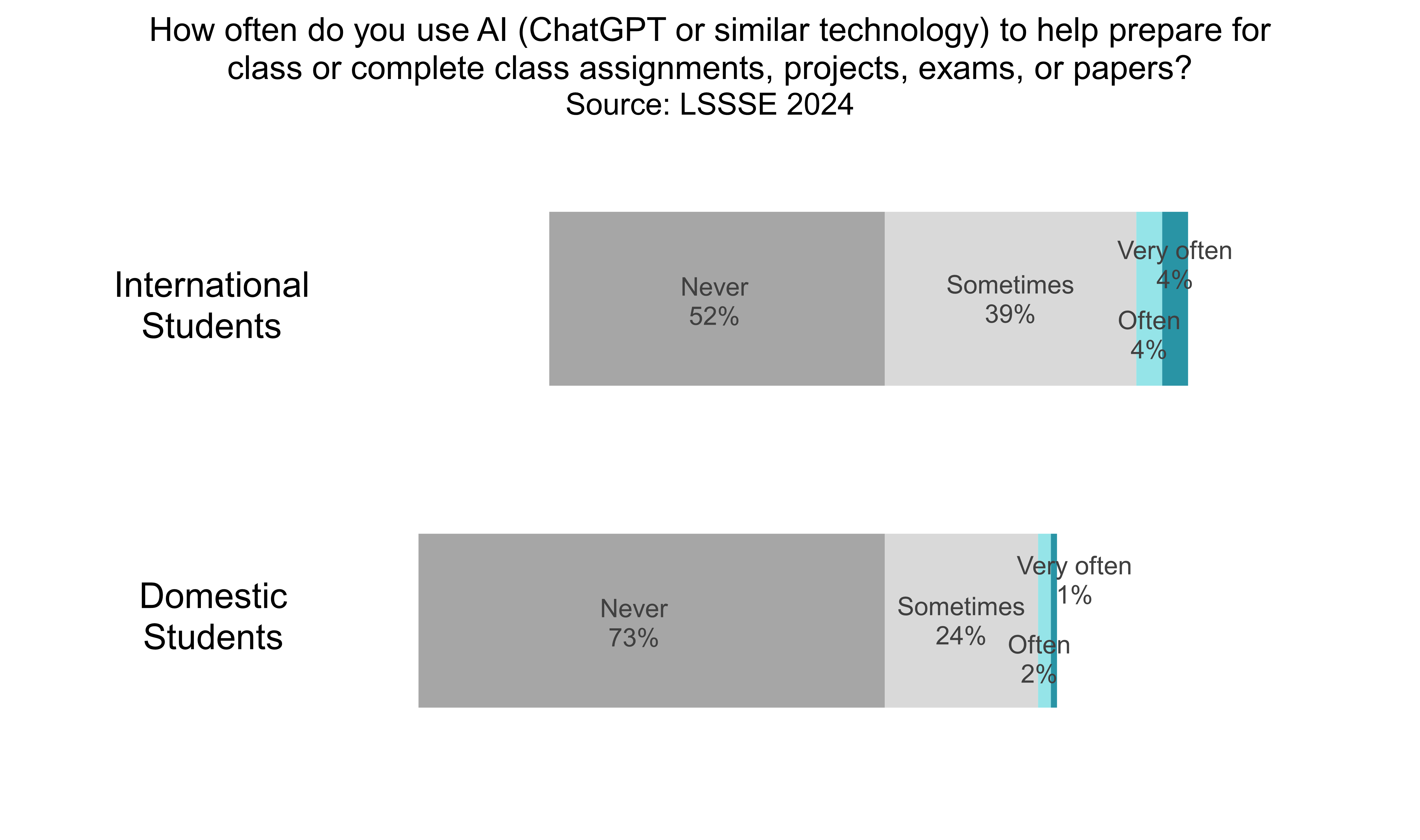
However, international law students are much more likely than domestic law students to use AI for their law school coursework. Almost half of international law students (48%) use AI at least sometimes compared to only 27% of domestic law students. This parallels a larger trend in undergraduate education in which U.S. college students are much less likely to use AI than their counterparts elsewhere in the world. International students attending U.S. law schools who speak English as a second language may be drawn to AI because of the ways it can be harnessed to support the unique needs of multilingual students, particularly in decoding complex texts. Whether AI usage for this or any other purpose is necessarily desirable remains to be seen, although it is useful to note that students are already accessing and using these tools.
AI usage among law students in the U.S. is currently quite low, with most students never using it for their coursework. There are some variations by age and nationality, particularly with international law students using AI tools at a much higher rate than domestic law students. Law schools would be wise to pay attention to both the potential benefits of AI for legal research and writing, as well as the challenges and limitations of AI in the legal domain. LSSSE will continue to track AI usage to understand the degree to which law students are using these tools in their pursuit of learning and understanding the law.
