Guest Post: Correcting the Diversity Skills Disconnect Using LSSSE Data
 Guest Post: Correcting the Diversity Skills Disconnect Using LSSSE Data
Guest Post: Correcting the Diversity Skills Disconnect Using LSSSE Data
Nicole P. Dyszlewski
Head of Reference, Instruction, & Engagement
Roger Williams University School of Law
There is a disconnect within legal academia about diversity, inclusion, racism, sexism, equality, power, and social justice issues in law. There is a disconnect between faculty attitudes about the value of teaching diversity skills and the actual inclusion of diversity skills in law school doctrinal classes. This disconnect has existed for years. It exists in the hallways and the cafeterias, but it looms largest over law school classrooms. The disconnect has taken on a new urgency in the year since the murder of George Floyd (and countless other Black victims of police violence), since a year’s worth of historic protests against anti-Black violence, and since the demands made by student groups at many of our schools to change the status quo. Today I want to share some of my own experiences with this disconnect, talk about how LSSSE data can be used to inform our institutions about the disconnect, and introduce a book I have been working on in the last few years to help provide resources for those who want to teach 1L students about the roles that diversity, equity, and social justice play in shaping and practicing the law.
I have very rarely heard a law professor say that teaching about social justice, equity, and the needs of a diverse society is not important or not a good fit for the law school curriculum. While these naysayers exist, they seem to be very few in number. Most law professors I have encountered in person, in my networks, on law Twitter, or through their scholarship seem to think these issues are relevant if not critical in law. In fact, the council of the ABA's Section of Legal Education and Admissions to the Bar recently approved a revision to law school accreditation standards which would require schools to “provide training and education to law students on bias, cross-cultural competency, and racism: (1) at the start of the program of legal education, and(2) at least once again before graduation.” (See the current Notice and Comment).
 Despite wide agreement among faculty that these topics are critical in the law school curriculum, I have also observed a NIMBY-ism. I have heard faculty from several schools explain that there is too much content to cover in the semester and they can’t possibly add diversity issues to their class. I have heard professors say that diversity, racism, sexism, social justice, and similar issues don’t naturally come up in the class they teach so it wouldn’t make sense to add them. I have heard professors say they will not use any hypos or examples which confront these issues because they feel that the discussion would be too difficult to manage and take away from the “real” learning. While many of us agree that these topics are critical to the law school curriculum, fewer faculty find them critical to their own classes and their own teaching practice. There is a disconnect here between what we espouse and what we do.
Despite wide agreement among faculty that these topics are critical in the law school curriculum, I have also observed a NIMBY-ism. I have heard faculty from several schools explain that there is too much content to cover in the semester and they can’t possibly add diversity issues to their class. I have heard professors say that diversity, racism, sexism, social justice, and similar issues don’t naturally come up in the class they teach so it wouldn’t make sense to add them. I have heard professors say they will not use any hypos or examples which confront these issues because they feel that the discussion would be too difficult to manage and take away from the “real” learning. While many of us agree that these topics are critical to the law school curriculum, fewer faculty find them critical to their own classes and their own teaching practice. There is a disconnect here between what we espouse and what we do.
It is our students, particularly our students from marginalized and underrepresented communities, who are paying the price for this disconnect. As LSSSE Director Meera Deo stated in a recent report, “what the data unequivocally show, is that those who are most affected by policies involving diversity—the very students who are underrepresented, marginalized, and non-traditional participants in legal education—are the least satisfied with diversity efforts on campuses nationwide.”
There isn’t much data on the prominence of diversity or social justice within most law schools’ curricula. Even if at an individual level we are successful at teaching diversity and diversity skills in our classrooms, how mainstream is this practice? Is it effective? Some schools may include questions on diversity, diversity skills, and inclusion in annual faculty activity reports or end of the semester student evaluations. Some (Many? Most?) schools do not. In 2020, LSSSE introduced a set of supplemental questions focused on diversity and inclusion. At my own institution we are waiting for this year’s supplemental LSSSE data to begin analyzing it to inform us on the student perspectives of diversity in the curriculum. We have also been in discussions about how to supplement the LSSSE data with additional surveys of students’ perspectives.
The LSSSE Diversity and Inclusiveness supplemental module includes questions about how much the student feels that their coursework has emphasized developing the skills necessary to work effectively with people from various backgrounds, learning about other cultures, discussing issues of equity or privilege, respecting the expression of diverse ideas, and recognizing your own cultural norms and biases. This data is integral to assessing your institution, your curriculum, and also your institution’s commitment to diversity. Engaging with the LSSSE data on diversity and inclusion is one place for law schools to start. LSSSE Director Deo cautions, “while institutions have been touting a commitment to equality with broad diversity statements and written policies supporting equal opportunities, traditional insiders see these words as doing the work while underrepresented students pay the price for ongoing inequities.”
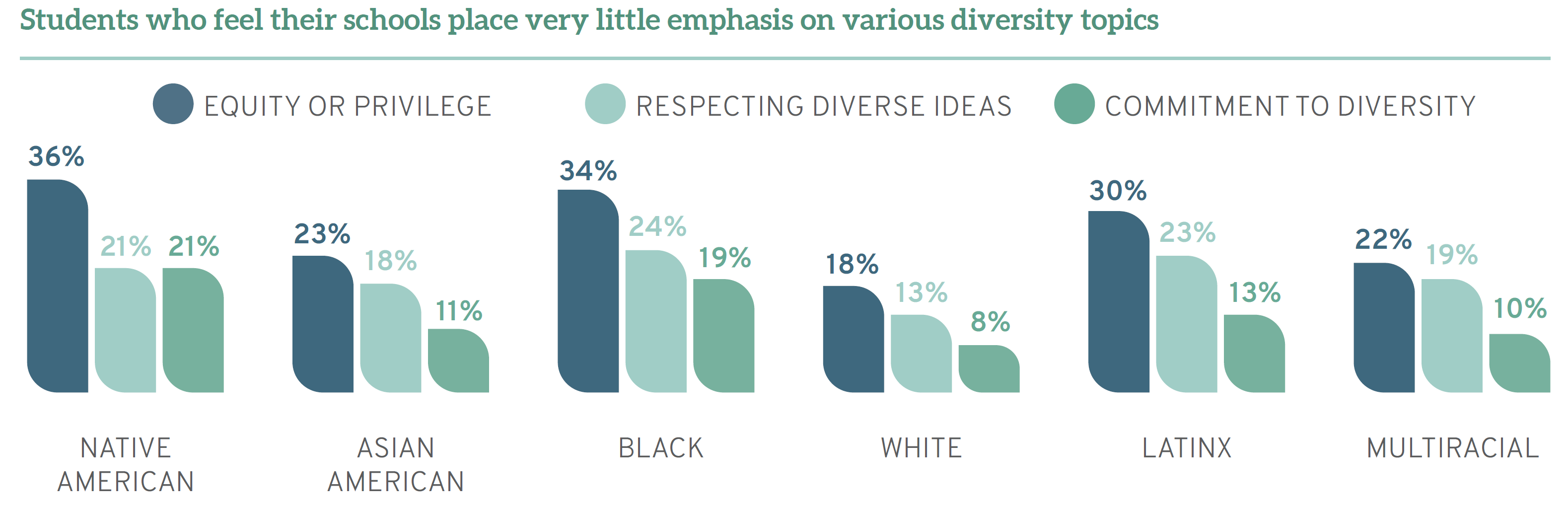
Over the last year dozens of law schools have re-focused their diversity and inclusion efforts, planning, programming, and assessment. At my institution we have been in discussions throughout the Spring semester as we plan to use this forthcoming data to assess an item in our strategic plan for diversity and inclusion in which we vowed to “[a]ddress inequality and social justice issues in courses across the curriculum, identify teaching materials that facilitate consideration of those issues, and provide students the opportunity, where appropriate, to evaluate faculty members on the effectiveness of their efforts.” For this assessment, the LSSSE data will be one tool in our toolbox.
Another step law schools must take is to fully integrate diversity and diversity skills into the foundational curriculum. Kimberly M. Mutcherson, Co-Dean & Professor of Law at Rutgers Law School, gets right to the heart of the matter in her Foreword to LSSSE’s 2020 Annual Report, Diversity and Exclusion, calling on law schools “to re-visit their curricula and note how they fail to adequately grapple with law as a tool of oppression (past and present).”
A few years ago, a group of colleagues and I began a project to solicit and compile practical resources for professors who are trying to rework the curriculum in the way Dean Mutcherson describes. This spring, we published a book titled Integrating Doctrine and Diversity: Inclusion and Equity in the Law School Classroom. It is a collection of essays with practical advice, written by faculty for faculty, on specific ways to integrate diversity, equity, and inclusion into the first year law school curriculum. It contains essays, organized by 1L class topics, on both pedagogical approaches and case studies. The essays contain thoughtful, meaningful engagement from faculty who’ve reflected consciously on how to address diversity in the classroom. The book also contains a cross-curricular chapter addressing these issues from a broader perspective. The book is a response to students who are seeking more from their classes, but it is also a response to the faculty who want to change but need guidance and inspiration on how to begin.
As legal education considers the wisdom in revising our accreditation standards, and as we enjoy our summer of writing and preparing for fall classes, I would ask that we consider the next steps towards diversifying our curricula and fixing the disconnect between our teaching and our institutional goals. Let this be the summer of reviewing LSSSE data, auditing our syllabi for diverse voices, supplementing our casebooks with readings that seek to decolonize the law, re-considering our pedagogical practices, and making room for the lived experiences of our students in our classrooms.
Guest Post: Understanding the Nuances: Diversity Among Asian American Pacific Islanders
 Understanding the Nuances: Diversity Among Asian American Pacific Islanders
Understanding the Nuances: Diversity Among Asian American Pacific Islanders
Vinay Harpalani
Henry Weihofen Professor & Associate Professor of Law
University of New Mexico School of Law
Asian American Pacific Islander (AAPI) Heritage Month recognizes the collective contributions of all AAPIs, but it is also an opportunity to move beyond the collective and highlight the nuanced differences between various AAPI groups. Lumping together all of these groups, without appreciation for their unique histories, experiences, and challenges, can obscure important differences, which in turn reinforces stereotypes. For example, although the “model minority” stereotype depicts AAPIs as high academic achievers from relatively privileged socioeconomic backgrounds, this is only accurate for a subset of the AAPI population. Higher education institutions in particular should highlight the vast diversity among AAPIs, as these institutions place a special value on understanding diversity and are also places where the model minority stereotype is propagated. Yet, when reporting applicant and enrollment data and other metrics, higher education institutions often simply classify their students as AAPI or even just “Asian.” And “Asian” as a singular label is particularly problematic, because it not only obscures differences between AAPI groups, but also conflates the different experiences of new immigrants and international students with those of second- and later generations of Asian Americans. Failure to distinguish these groups exacerbates another stereotype of AAPIs: that we are “perpetual foreigners”—always associated with their ancestral nations rather than with the U.S. Higher education institutions should thus disaggregate their data on AAPI students and be more nuanced in their assessments.
But therein lies the challenging part. There is no consensus on how to classify various AAPI groups or on which groups should be included together. Sometimes, people from different geographic areas of Asia are separated into smaller regional groups. East Asian Americans trace their ancestry to China, Korea, Japan, Mongolia, or Taiwan, while Southeast Asian Americans are descended from Thailand, Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, Myanmar, Malaysia, Singapore, the Philippines, Indonesia, Brunei, or Timor Leste. South Asian (“Desi”) Americans trace their roots to India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bhutan, Afghanistan, or the Maldives Islands. Pacific Islanders are descended from Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia—three major island groups in the Pacific Ocean—and are sometimes classified separately from Asian Americans altogether. And although South Asian Americans are formally classified with as Asian Americans, many people do not think of them as such. AAPI student organizations on college campuses illustrate this well, as they can emphasize national, ethnic, or collective identities. In addition to AAPI, other terms include “Asian American”, “Asian Pacific American” (APA), “Asian/Pacific Islander” (API), Asian Pacific Islander Desi American (APIDA), and “Asian American Native Hawaiian Pacific Islander” (AANHPI).
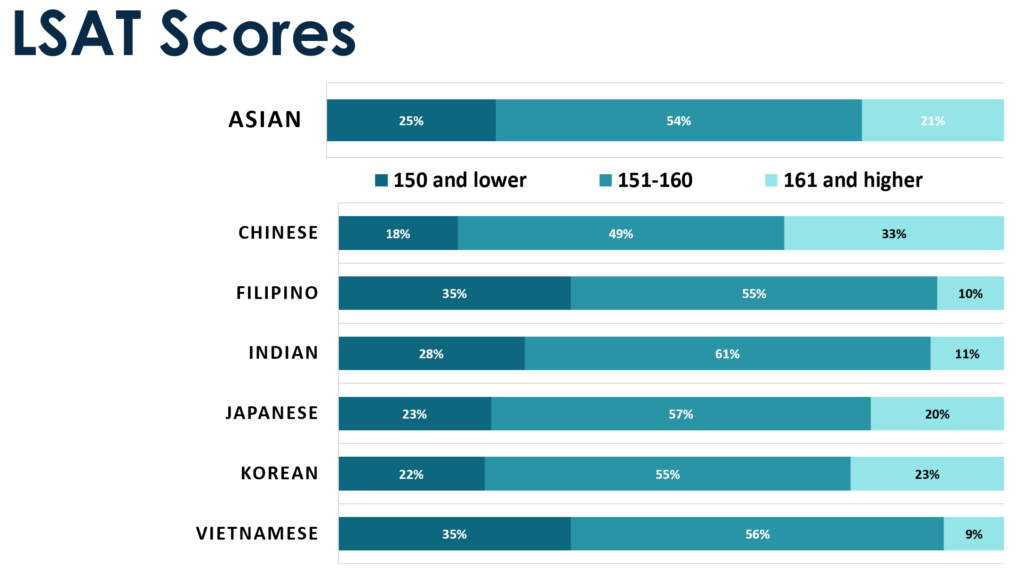
While the broad regional groupings may sometimes be appropriate, grouping by ethnicity or nation of ancestry may better capture the nuances—especially for relatively recent immigrants who left their homelands under particular circumstances, or for international students from particular countries. The Law School Survey of Student Engagement (LSSSE) collects data on diversity among AAPI law students, including differences between domestic and international students. Among its many metrics, LSSSE has disaggregated data on AAPI groups by their nation of ancestry. In its 2016 survey, LSSSE asked AAPI respondents about their ethnicity, and it analyzed this data in its 2017 report on AAPI law students. Overall, 1,147 respondents identified as AAPI: 7% of the total LSSSE pool. Six subgroups comprised at least 5% of the AAPI pool: Chinese (23%); Korean (19%); Asian Indian (18%); Japanese (8%); Filipino (8%); and Vietnamese (5%).

LSSSE’s analysis showed significant differences between these groups. For example, while 81% of Asian Indian American students in the sample had at least one parent with a bachelor’s degree, only 41% of Vietnamese American students did. And although AAPIs generally are stereotyped as high-achieving students, there were also differences in LSAT performance: 33% of Chinese American students in the sample scored 161 (83rd percentile) or higher, whereas only 9% of Vietnamese American students did. These differences may well be related to the immigration histories of these groups. Many Asian Indian and Chinese immigrants to the U.S. came via the occupational preferences of the Immigration Act of 1965, which favored those from educated, professional backgrounds. Conversely, many Vietnamese immigrants came as refugees after the Vietnam War and did not have the same resources. LSSSE’s data also indicate that compared to other AAPI groups, Vietnamese American students were more likely to be working in non-law related jobs, working more than 8 hours per week, and more likely to be providing care to others in their household while they were in law school.
The differences between international and domestic students can also be significant. Students born and/or raised in the U.S. are often socialized very differently than those born and raised in their ancestral nations, and these two groups often have different backgrounds, outlooks, and experiences. Rather than grouping together all students descended of a particular ethnicity, it is informative to distinguish between international and domestic students for each ethnicity. This may be challenging in some circumstances, given the small samples for some ethnicities. In LSSSE’s 2016 survey, 50% of students of Chinese descent were international students, while only 1% of Filipino students were, and proportions of other AAPI subgroups identifying as international students varied widely: 24% Korean; 14% Asian Indian; 8% Vietnamese; and 7% Japanese. Depending on the questions being explored, it may be prudent to focus only on domestic students for some analyses and only on international students for others, and it may be necessary to combine the two for some purposes.
When analyzing the demographics and the academic and social experiences of AAPI students, higher education institutions should follow LSSSE’s lead and disaggregate different groups, and also distinguish between international and domestic students. There is no single, ideal way to classify all of the groups: that will depend on the question and analysis at hand. But paying attention to the nuances will help to dispel the stereotypes that AAPIs are “model minorities” and “perpetual foreigners”—stereotypes that lump different AAPI groups together. And while we can and should celebrate the heritage and contributions of AAPIs as a whole, understanding the nuanced differences between groups is what will truly address the challenges faced by various AAPI communities.
Law Student Leisure Time, 2004-2020
Law students need time to rest and recharge. Amidst questions about how much time law students spend working, preparing for class, commuting, and participating in extracurricular activities, LSSSE also asks about time spent on leisure activities such as reading, relaxing and socializing, and exercising. Here, we look at trends in leisure activities from 2004 to 2020.
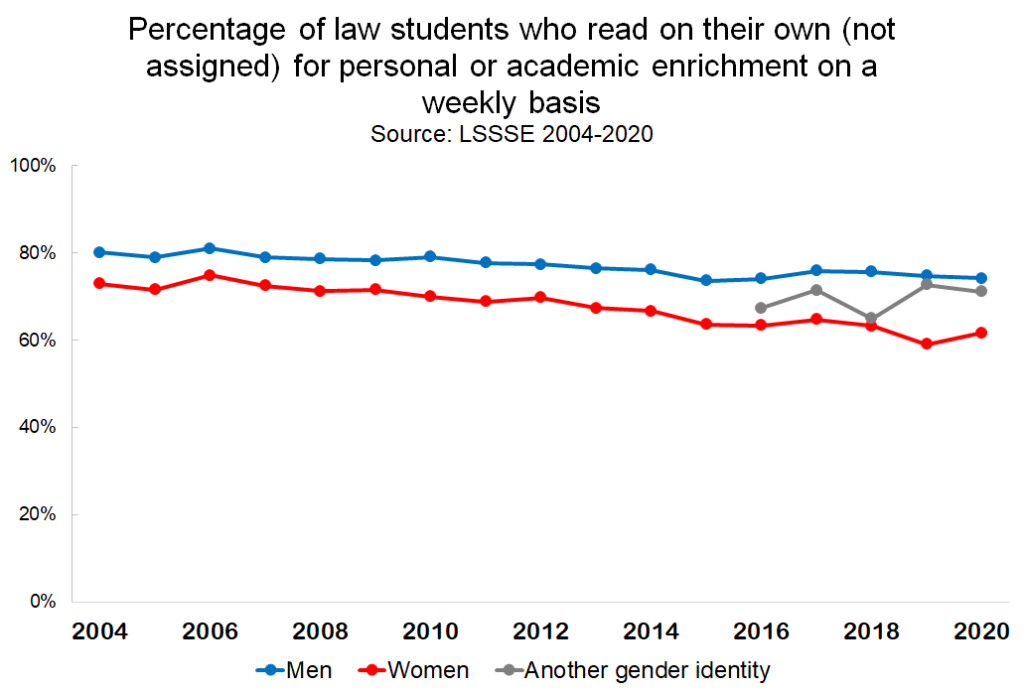
Most law students read on their own for personal or academic enrichment for at least one hour per week. However, the percentage of students who spend time on non-assigned reading has decreased gradually over the last decade and a half. Across every year studied, more men than women spend time reading for personal enrichment, and the gap has widened in the last few years. In 2004, 80% of men and 73% of women read on their own for at least an hour per week. In 2020, those numbers were 74% of men and only 62% of women.
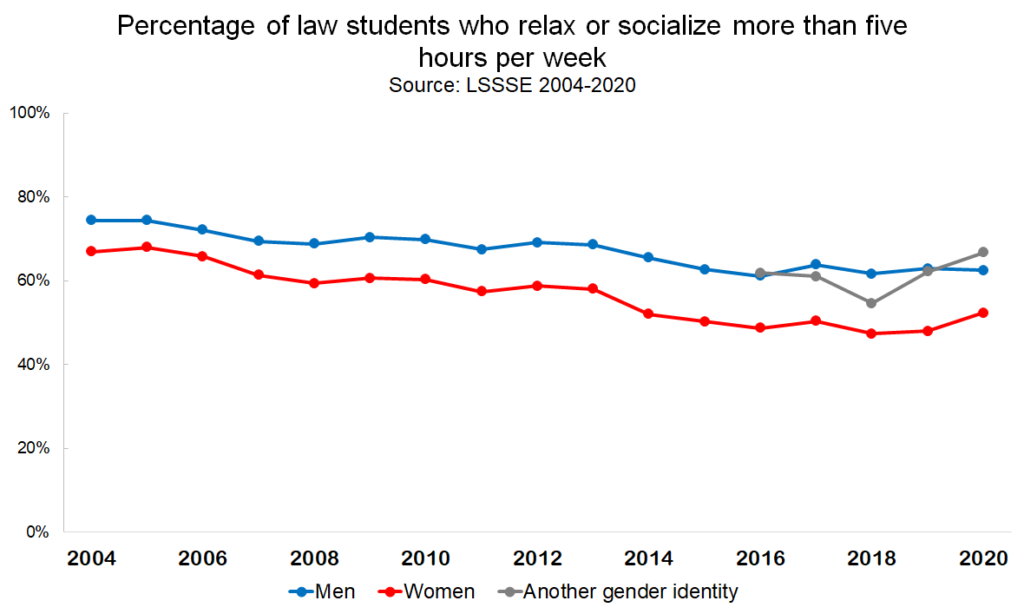
These trends toward a) decreasing time spent on leisure and b) more men than women engaging in leisure activities also hold true for time spent relaxing and socializing. The percentage of law students who relax or socialize for more than five hours per week (which is about an hour per day) has decreased from 71% in 2004 to 56% in 2020. Female law students are less likely to have time to relax. About half of female law students (48%) spent fewer than five hours per week relaxing and socializing in 2020, compared to only 37% of their male counterparts.
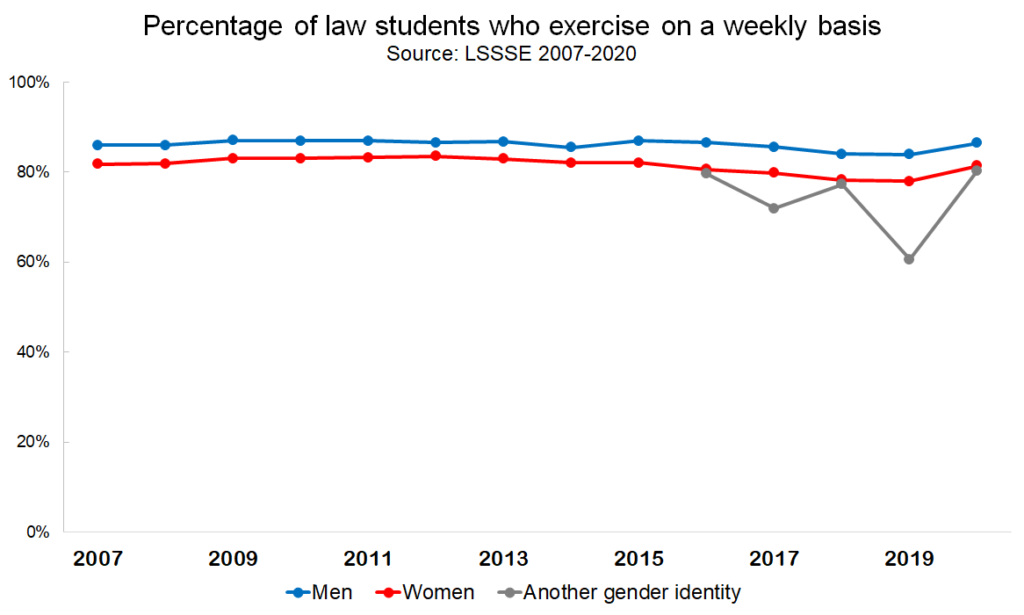
Fortunately, law students continue to make time for physical activity. Slightly more than eighty percent of law students exercise on at least a weekly basis, a number that has remained fairly constant since 2007, when the question was first added to the survey. Again, men are more likely than women to make time for exercise, although the disparity is not as great as it is for relaxing/socializing and for reading. This may suggest that when law students of all genders need a break from the sedentary work of reading and studying, they turn to physical activity to blow off some steam.
Guest Post: Assessment: How to Do It and How LSSSE Can Help
 Assessment: How to Do It and How LSSSE Can Help
Assessment: How to Do It and How LSSSE Can Help
Emily Grant
Professor of Law
Washburn University School of Law
Psst. Have you heard? The American Bar Association (ABA) wants law schools to do assessment.
Of course you’ve heard. We all heard the call to assessment even before the relevant ABA standards (301, 302, 314, and 315) took effect in 2016.
Unlike some, however, I’ve drunk the assessment-flavored Kool-Aid, I’ve got the assessment tattoo,[1] and I’m bringing my flashlight back into the cave to help others with the assessment process. And luckily for all of us, LSSSE can play an important role in institutional assessment activities.
First up, what is assessment? At the most basic level, assessment is evaluation. It is the process of collecting data about student learning and using that data to improve teaching, learning, and indeed the full functioning of a law school.[2]
To that end, the ABA has mandated that a law school must establish a program of legal education and identify specific learning outcomes, or goals, that it is seeking to achieve (Standard 301). Those learning outcomes should include, at the very least, the topics listed in Standard 302, including the knowledge, skills, and values that law school graduates are to possess. The law school should use both formative and summative assessment methods[3] when evaluating students (Standard 314). And Standard 315 brings it all together: the law school administration and faculty “shall conduct ongoing evaluation” of the school and should use the results of that evaluation to make decisions about the future.

The process is designed to help law schools ensure that they, as institutions, are accomplishing their goals and that their students are taking away the things that are most important, as defined by each law school. Within the broad guidelines of the ABA noted above, law schools can prioritize certain knowledge, skills, and values—a social justice mission, for example, or specific professional competencies important to the institution. The assessment process can then expose weaknesses in the curriculum that might allow the important learning outcomes to fall through the cracks, and law schools can adjust accordingly. But the assessment process is also an opportunity for law schools to gather empirical evidence about their strengths and to continue and encourage curricular growth in those areas the students are learning and incorporating well.[4]
The assessment process needs to happen across various levels: institutions, programs or departments, and individual courses. The steps in the assessment process will generally be the same:
- Create student learning outcomes and ensure that the curriculum aligns with the outcomes.
- Design and administer assessment instruments to measure student achievement of those outcomes.
- Review and analyze data that assessment instruments produce.
- Make changes based on the data to improve student learning.
- Repeat the process to evaluate impact of the changes and whether they made any difference in student learning.
Assessment is a cyclical process; it’s iterative in that the data leads to information which can lead to changes in curriculum and instruction which produces new data to analyze. Institutions that merely gather data in spreadsheets will wind up being data rich but information poor. Instead, law schools must use the data “to determine whether they are delivering an effective educational program.”[5] The assessment process is meaningful only when schools use the data “to improve [themselves], to change the curriculum, to change teaching and learning methods, and even to change the assessment methods themselves.”[6]
LSSSE has been a model of effective data-use and frankly, serves as an entire warehouse of granular and big-picture data that law schools can access as part of the assessment process. For example, many law schools have already identified learning outcomes in areas such as knowledge of the law, effective research and writing, oral presentation skills, critical thinking, problem-solving, and professional ethics.
Check out the following questions on the LSSSE survey:
To what extent has your experience at your law school contributed to your knowledge, skills, and personal development in the following areas?
- Acquiring a broad legal education
- Acquiring job or work-related knowledge and skills
- Writing clearly and effectively
- Speaking clearly and effectively
- Thinking critically and analytically
- Using technology
- Developing legal research skills
- Working effectively with others
- Learning effectively on your own
- Understanding yourself
- Understanding people of other racial and ethnic backgrounds
- Solving complex real-world problems
- Developing clearer career goals
- Developing a personal code of values and ethics
- Contributing to the welfare of your community
- Developing a deepened sense of spirituality
That question alone is goldmine of information for law schools to methodically and quantitatively get feedback on the efficacy of the curriculum.
In total, about 60 items in the LSSSE survey map to the ABA standards and interpretations. All participating law schools receive an accreditation report, which could serve as another source of relevant data.
One of my professional roles is Co-Director of the Institute for Law Teaching and Learning, an organization of law school professors across the country (and beyond!) dedicated to improving… well… law teaching and learning. Because we recognize the value of the assessment process in strengthening legal education, we have recently released a comprehensive book discussing the assessment process in detail: Assessment of Teaching and Learning: A Comprehensive Guidebook for Law Schools by Kelly Terry, Gerald F. Hess, Emily Grant, Sandra Simpson (Carolina Academic Press 2021).
In the book, we explain that assessment in law schools can be viewed as a prism. Contained within the prism are principles and practices that apply to various aspects of legal education, including institutional assessment, programmatic assessment, and course-level assessment of student learning, as well as assessment of teaching effectiveness. The book is structured to be a resource in all of those areas. Specifically, it provides a thorough overview of the assessment process generally, and it includes a chapter about how to build a culture of assessment throughout the institution. Next, the book turns to the specifics of assessing student learning in a variety of contexts: at the institutional level, at the course level, and in the context of other programs in the law school, including experiential learning, legal writing, centers and concentrations, co-curricular activities, and non-academic units. Finally, the book focuses the assessment lens on teaching, with a discussion of the fundamentals and suggestions for both summative and formative assessment of teaching performance.
Using data from reliable and trusted sources, such as LSSSE, is important for law schools as they work to evaluate the effectiveness of their curricula. Data from LSSSE can be a valuable resource for law schools as they prepare for review by the ABA Accreditation process. In particular, LSSSE data can be central to a law school’s self-study and strategic planning process by providing focus and opportunities for follow-up. Moreover, LSSSE results are actionable; that is, they point to aspects of student and institutional performance that law schools can do something about. And that, after all, is the entire purpose of the assessment process.
----
[1] Not really, but how nerdy would that be?!
[2] Barbara E. Walvoord, Assessment Clear and Simple: A Practical Guide for Institutions, Departments, and General Education 2 (2010).
[3] Formative assessment is feedback provided during the course with the goal of improving students learning. Summative assessment evaluates student learning at the end of a particular course.
[4] Lori E. Shaw & Victoria L. VanZandt, Student Learning Outcomes and Law School Assessment: A Practical Guide to Measuring Institutional Effectiveness 32 (2015).
[5] Roy Stuckey et al., Best Practices for Legal Education: A Vision and a Road Map 272 (2007).
[6] Id. at 273.
Writing Papers in Law School
Writing assignments are useful tools for challenging students to put complex thoughts into understandable language. The amount of writing required in law school can vary across courses, years, and schools. Students also sometimes have different reactions to their writing experiences. Here, we estimate how many pages students wrote during the 2019-2020 school year and show how the number of pages written is related to perceived gains in writing abilities.
Law students report on their writing assignments with three LSSSE questions:

Universal Background Checks: This would require a background check for all individuals seeking to purchase firearms, regardless of the source of the firearm. This would help to keep guns out of the hands of individuals argumentative essay on gun control with a criminal history or history of mental illness.
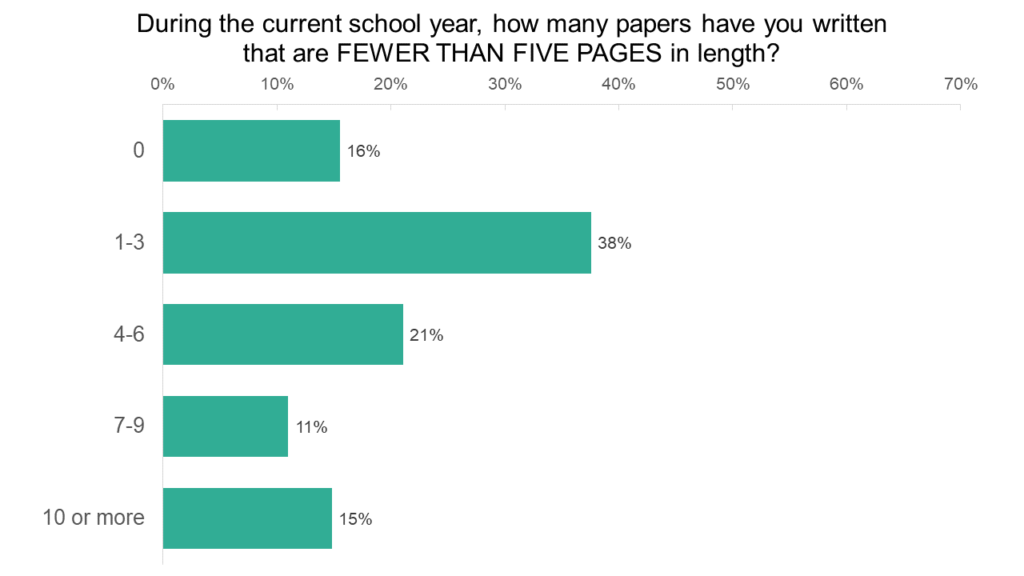
Shorter papers (fewer than five pages in length) are quite common law school. Only 16% of respondents did not write any short papers. Most students (59%) wrote between one and six short papers, although 15% of students wrote ten or more.
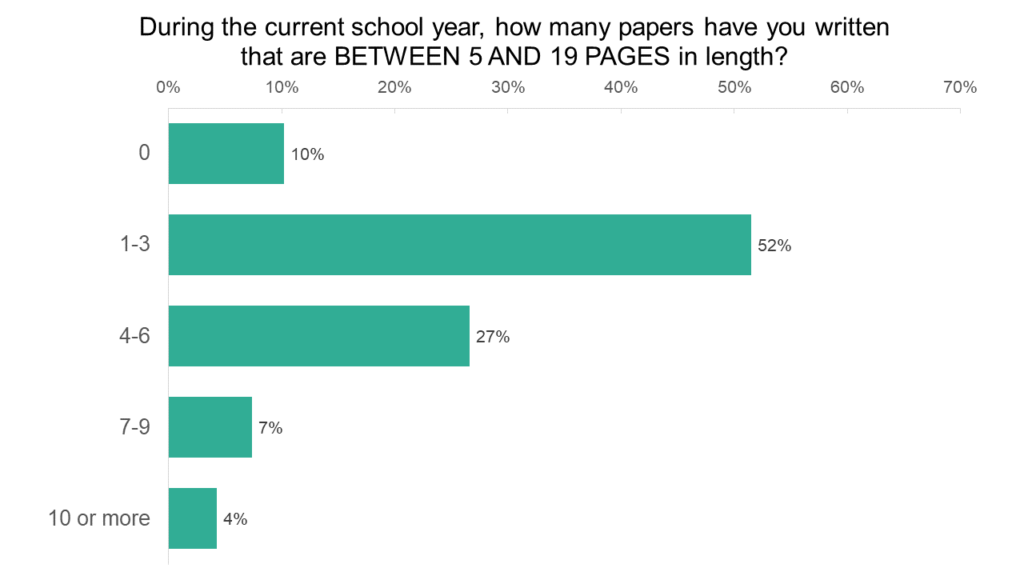
Medium-length papers (5-19 pages) are another staple of law school. Slightly more than half of law students (52%) wrote one to three papers of this length during the previous school year, and another quarter (27%) wrote four to six papers of this length. Only 10% of students did not write a medium-length paper in the previous year.
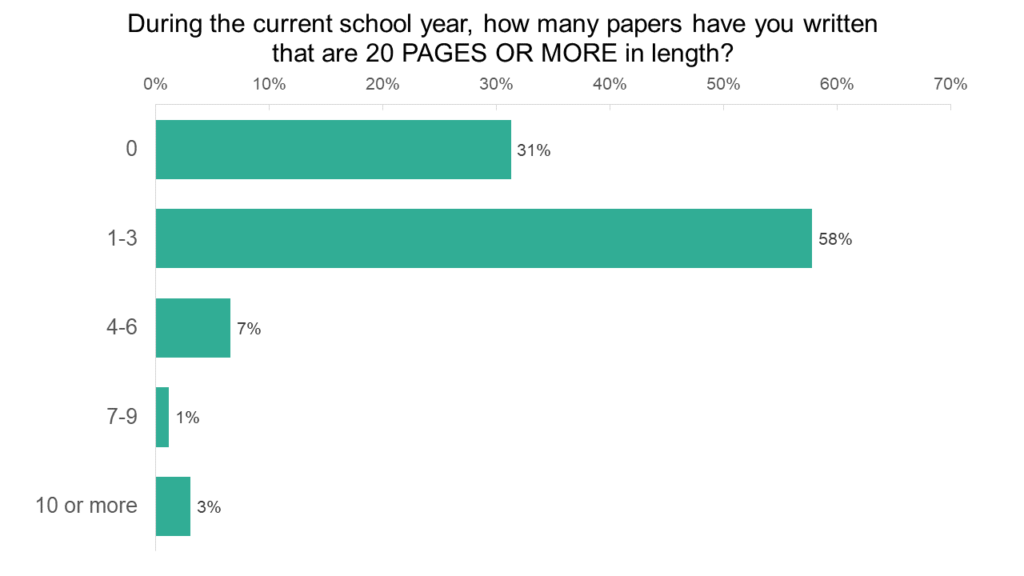
Long papers (20+ pages) are somewhat less common. About 31% of students did not write any long papers during the previous school year, although more than half of students (58%) wrote between one and three long papers.
We can also use information from these three writing questions to create a very rough estimate of the total number of pages each student wrote for class assignments over the past year. Law students tended to write between 26 and 100 pages total. This range accounts for about 60% of law students. Over a quarter (27%) of law students fell specifically into the 51-75 page range. But nearly one in five law students (19%) wrote over 125 pages in the previous school year.
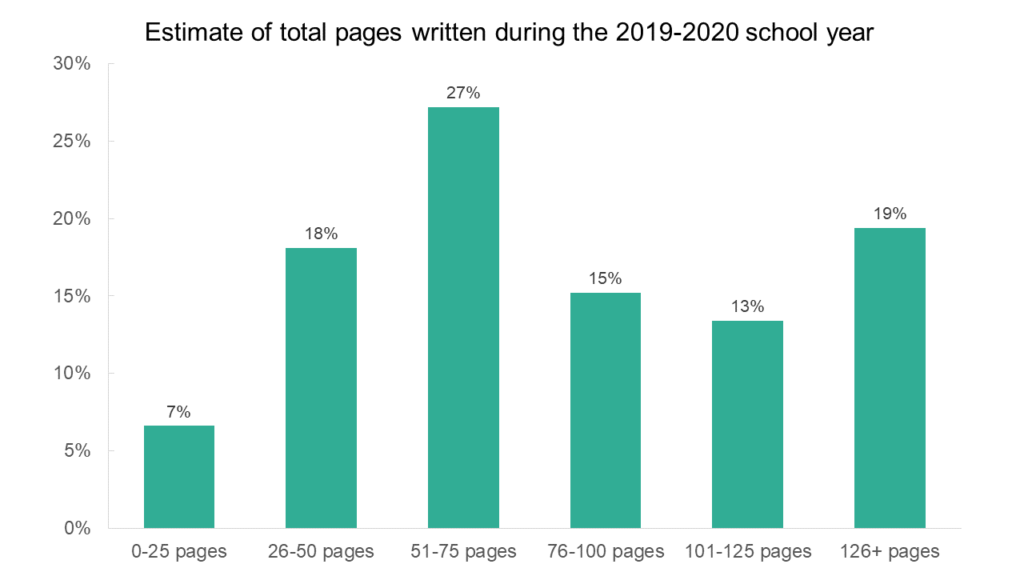
Part of the purpose of writing assignments is to assess how students are assimilating and analyzing information. Another purpose is to enhance students’ writing abilities. In a separate section of the survey, LSSSE asks about the degree to which law school has contributed to the development of the student’s writing ability. Interestingly, when we correlate students’ responses to this question with the number of pages of writing they did over the course of the year, we see a gradual increase that plateaus at around 76-100 pages. That is, in general, students who write more pages of text believe that law school has helped them become better writers but only to a certain point. Beyond about a hundred pages of writing (combined across all their classes), students are not more likely to say that their experience at law school has contributed to their ability to write clearly and effectively.
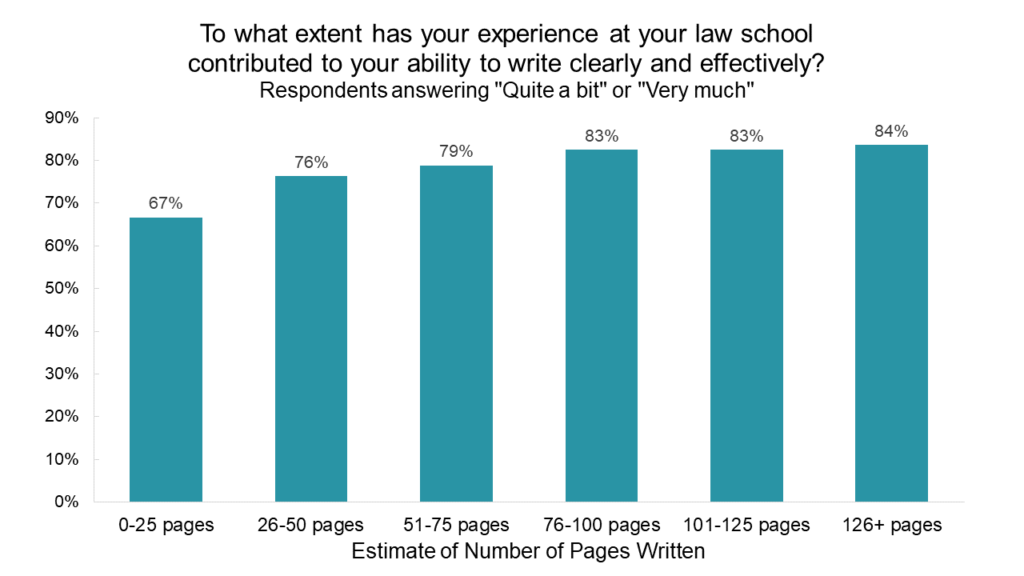
Law school provides consistent opportunities for students to hone their writing and reasoning skills. Most law students write a handful of short- and medium-length papers each year. Students generally feel that law school contributes to their ability to write clearly and effectively, including those students who only wrote 25 or fewer pages in the previous year. However, students who wrote more (up to around 100 pages) tend to respond more favorably to the writing skill development question than students who wrote less.
Guest Post: Moving Legal Education to the Fourth Dimension
 Guest Post: Moving Legal Education to the Fourth Dimension
Guest Post: Moving Legal Education to the Fourth Dimension
Deborah Jones Merritt
Distinguished University Professor
John Deaver Drinko-Baker & Hostetler Chair in Law
Much of law school is two-dimensional, confined to the written pages of statutes, regulations, and appellate decisions. Clients appear in our classroom hypotheticals and final exams, but they are cardboard figures designed to illustrate a point or test a legal concept. These cut-out clients lack the backstories, personalities, and secrets that three-dimensional clients embody. Nor do these cardboard clients change their circumstances or modify their goals, as real clients do. While law school is two-dimensional, law practice spreads over all four dimensions of space and time.
How do new lawyers jump from two dimensions to four? Research I conducted with Logan Cornett, Director of Research at IAALS (the Institute for the Advancement of the American Legal System), suggests that the transition is difficult. Our research team conducted 50 focus groups with new lawyers and their supervisors to explore this transition. Our groups spanned 18 locations nationwide and included 200 demographically diverse lawyers. In addition to their demographic diversity, our focus group members represented a wide range of employment contexts: federal, state, and local government; nonprofits; firms of all sizes, and solo offices. They also worked in more than 50 distinct practice areas, ranging from animal rights to workers compensation.
These focus groups generated more than 1500 pages of transcribed comments, which we analyzed using standard tools of qualitative research. NVivo software helped us organize and code the data; we then followed the principles of grounded theory to draw insights directly from the data. The results overwhelmingly support four conclusions: (1) More than half of new lawyers engage directly with clients during their first year, often as early as the first week. (2) Many of these lawyers also take primary responsibility for client matters. (3) Although some employers offer careful supervision and training, many do not. Instead, many new lawyers operate solo—even when they receive a paycheck from an employer. (4) To practice effectively under these circumstances, new lawyers must possess twelve foundational competencies or “building blocks.”
We discuss these twelve building blocks at length in our report, Building a Better Bar: The Twelve Building Blocks of Minimum Competence. For quick reference, the blocks are:
- The ability to act professionally and in accordance with the rules of professional conduct
- An understanding of legal processes and sources of law
- An understanding of threshold concepts in many subjects
- The ability to interpret legal materials
- The ability to interact effectively with clients
- The ability to identify legal issues
- The ability to conduct research
- The ability to communicate as a lawyer
- The ability to see the “big picture” of client matters
- The ability to manage a law-related workload responsibly
- The ability to cope with the stresses of legal practice
- The ability to pursue self-directed learning
Even a quick glance suggests that many of these building blocks are three- and four-dimensional, rather than two-dimensional. New lawyers must act professionally, not just know the written rules of professional conduct. They must also counsel clients who live multi-faceted lives and who change their goals over time. Understanding legal processes, seeing the big picture of client matters, managing workloads, communicating as a lawyer, and coping with the stresses of legal practice are all three- and four-dimensional tasks.
Law schools have made significant progress in teaching students to navigate the complex dimensions of law practice: Clinics and other experiential offerings have expanded over the last 20 years. In LSSSE’s most recent survey, two-thirds of law students reported that their legal education helped them either “very much” or “quite a bit” to acquire job-related knowledge and skills. Sixty percent expressed similar appreciation of law school’s contribution to learning how to solve “complex real-world problems.”
But the LSSSE survey also points to areas of needed improvement. Only about half of respondents believed that law school had helped them “very much” or “quite a bit” in understanding people of other racial and ethnic backgrounds, developing clear career goals, shaping a personal code of values and ethics, or working effectively with others. Although phrased differently than our twelve building blocks, these competencies relate to the complex skills we identified in our research.
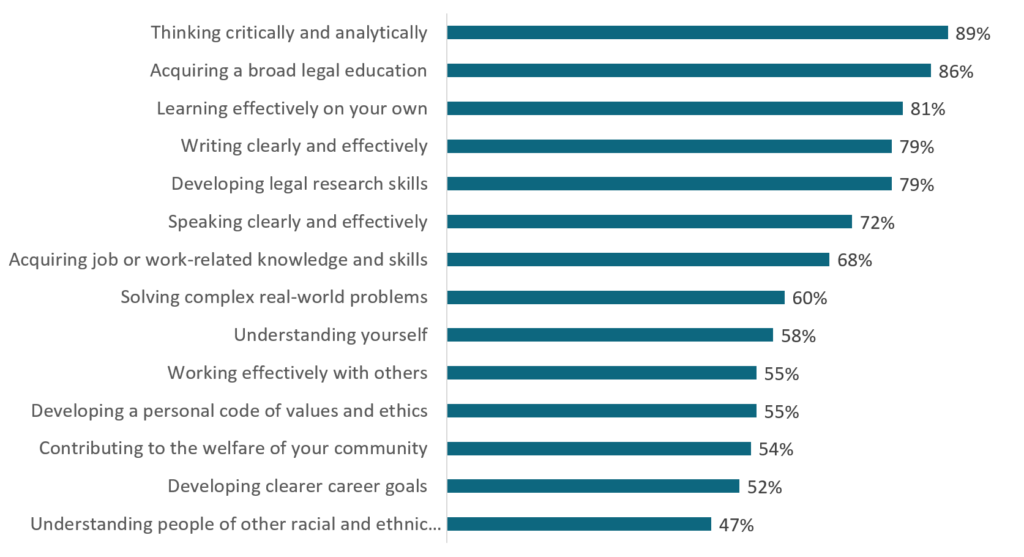
Once the LSSSE respondents enter practice, moreover, they may be less sanguine about their preparation. Many new lawyers in our focus groups told us that their first year of practice was a “trial by fire.” They struggled to counsel clients, develop strategies, and resolve matters with little supervision. Once on the job, they discovered that they needed more job-related skills than law school provided. Why, they asked, didn’t law school better prepare them for the full range of their work?
Legal educators often say that employers are better suited than professors to teach advanced practice skills. Law school, they argue, properly focuses on teaching basic skills (such as case analysis), threshold concepts, and detailed doctrine. But our research partially disputes that claim. New lawyers undoubtedly need the basic skills and threshold concepts that law school instills. But once they possess those competencies, employers are quite capable of teaching junior lawyers specialized doctrine. Indeed, many new lawyers practice in fields that they never studied. In contrast, employers lack both time and expertise to teach advanced skills like counseling clients, gathering relevant facts, and negotiating with adversaries.
Law school is the place to learn these complex skills. Clinicians and other skills professors know how to teach cognitive skills like counseling, fact gathering, and negotiating. They also know how to provide feedback to novices and coach them to competence. Workplaces offer opportunities to hone professional skills, but schools are the best place to learn the basics.
Some lawyers think of counseling, fact gathering, and negotiating as soft skills that can’t be taught. But there’s nothing soft or unteachable about these skills. They’re harder to teach than the skills we teach in the first-year curriculum, but they’re quite teachable. Think of these skills as the second stage of learning to think like a lawyer. First-year students learn how to analyze legal materials, synthesize those materials, and apply legal rules to hypothetical problems. Those skills lay a foundation for learning more complex skills like counseling, fact gathering, and negotiating. The latter skills require students to add multi-dimensional clients, uncertain legal processes, and shifting fact patterns to their two-dimensional analyses.
If we want our graduates to serve clients effectively, law schools must step into the fourth dimension. Before graduation, every student should learn to counsel clients, gather facts, negotiate, and perform the other multi-dimensional skills embodied in the twelve building blocks listed above. The LSSSE survey can help us continue to track progress on that essential front.
The word "impotence" is considered outdated and is rarely used in modern medical sources. It is used when more than 75% of attempts to get an erection during sexual intercourse end in failure. A more https://www.faastpharmacy.com/ accurate and modern term is "erectile dysfunction", which describes a variety of problems in bed in young and mature men.
Working While in Law School
In 2014, the American Bar Associated eliminated the standard that restricted full-time law students from working more than twenty hours per week. Certainly, studying law is an intense and demanding endeavor that may preclude having a job for many students. However, some students continue to work during law school for personal or economic reasons or to gain experience. Here, we look at trends in employment in the legal and non-legal sectors among both full-time and part-time law students.
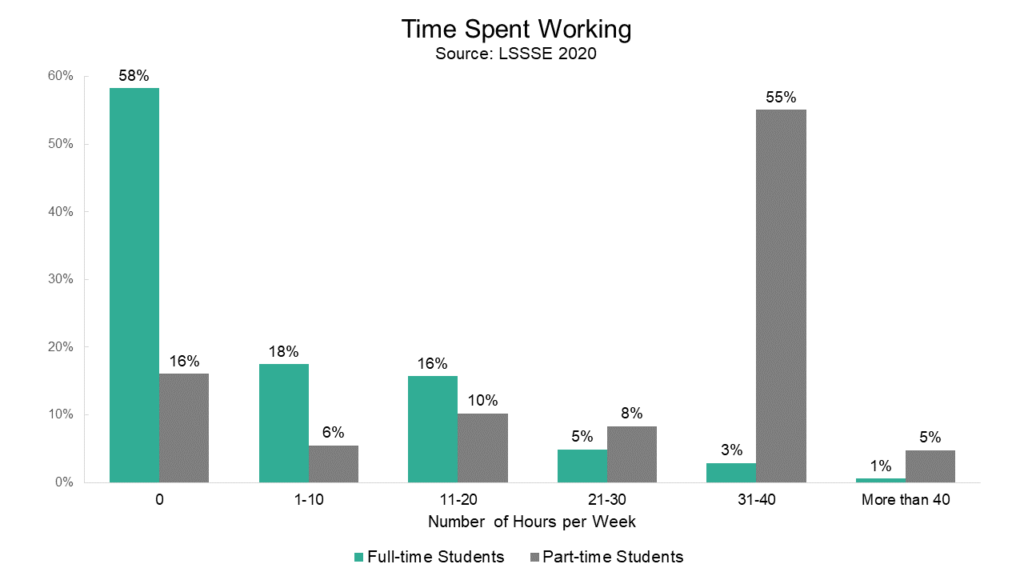
The vast majority (84%) of part-time students have a job. Full-time students are obviously less likely to work for pay, although 42% of them had jobs in 2020. Breaking the analysis down by enrollment status and class, full-time 1L students are the least likely group to have a job, with a 21% employment rate. The proportion of employed full-time students increases significantly among 2L students (52% employed) and again among 3L students (60% employed). Interestingly, part-time 3L students were somewhat less likely to be employed than their 1L, 2L, and 4L counterparts.
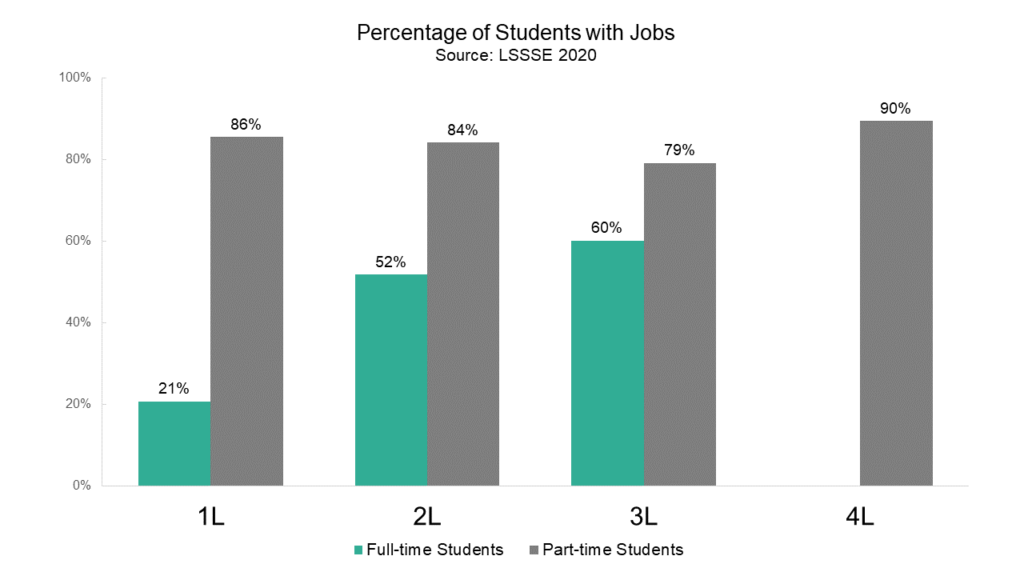
Regardless of the ABA’s abolition of work hour limitations, the vast majority of full-time students continue to work twenty hours per week or fewer. Full-time students with jobs work an average of 14 hours per week. Only about 9% of full-time students work more than twenty hours per week, and only 4% have workloads that approach or exceed full time. Conversely, part-time students with jobs work an average of 32 hours per week. Most part-time students (60%) work approximately full time or more, which we characterize as 31+ hours of work per week.
As full-time students progress through their legal studies, they are more likely to work for pay. 2L and 3L students are also much more likely to have a law-related job than their 1L counterparts. Among full-time students who work for pay, only 35% of 1L students have a law-related job, compared to 73% of 2L students and 79% of 3L students. Part-time students are more equally split among law-related and non-legal jobs, although the proportion who work in a legal job increases as students move toward graduation. Forty-four percent of part-time 1L students who work are employed in a law-related job, compared to 59% of 4L students. (Note that the proportions in the figure below do not add up to 100% since employed students may work at both law-related and nonlegal jobs.)
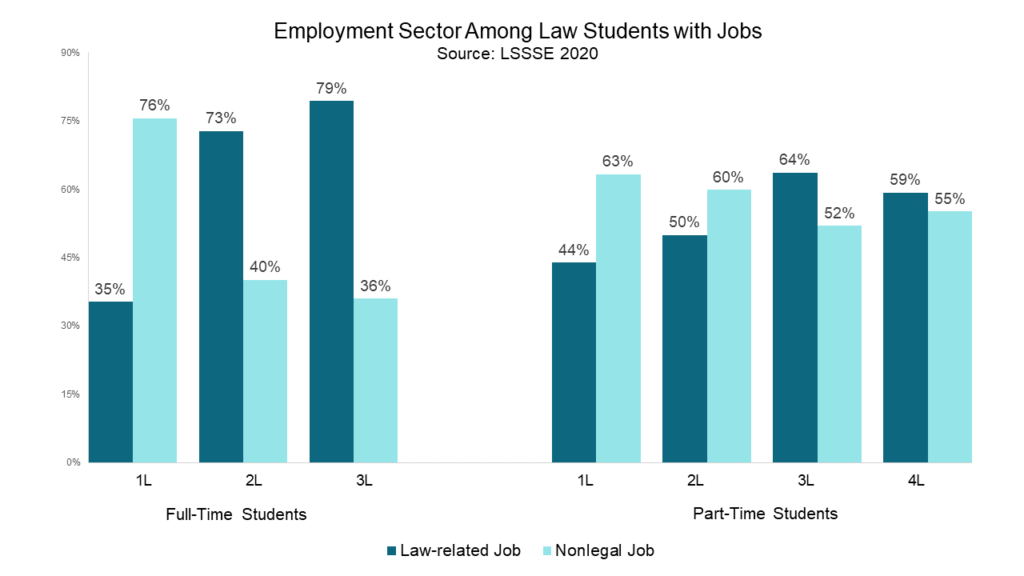
Law school remains a demanding and time-consuming activity. Although the ABA no longer explicitly forbids working full-time while also attending law school full-time, it does not appear that many students are seizing the opportunity to work long hours. This seems abundantly logical given the amount of time that full-time students spend on studying and preparing for class each week. Part-time students are, of course, more likely to have time to work each week, and they are more likely than their full-time colleagues to work in the non-legal sector. This suggests that students are managing to find ways to earn money and gain work experience while also balancing the other demands on their time, and the way they do this is influenced by their enrollment status and the amount of time they have already spent in law school.
How Many Law Students Are Following in Their Lawyer Parent’s Footsteps?
Why and how do people choose their course of study and their future career? While status, compensation, and personal values likely play an important role in choosing a career, there may also be an influence of family tradition. We used LSSSE data from 2019 and 2020 to ask how many law students have at least one lawyer parent and to see whether these students differ in appreciable ways from their classmates who were not raised by a lawyer.
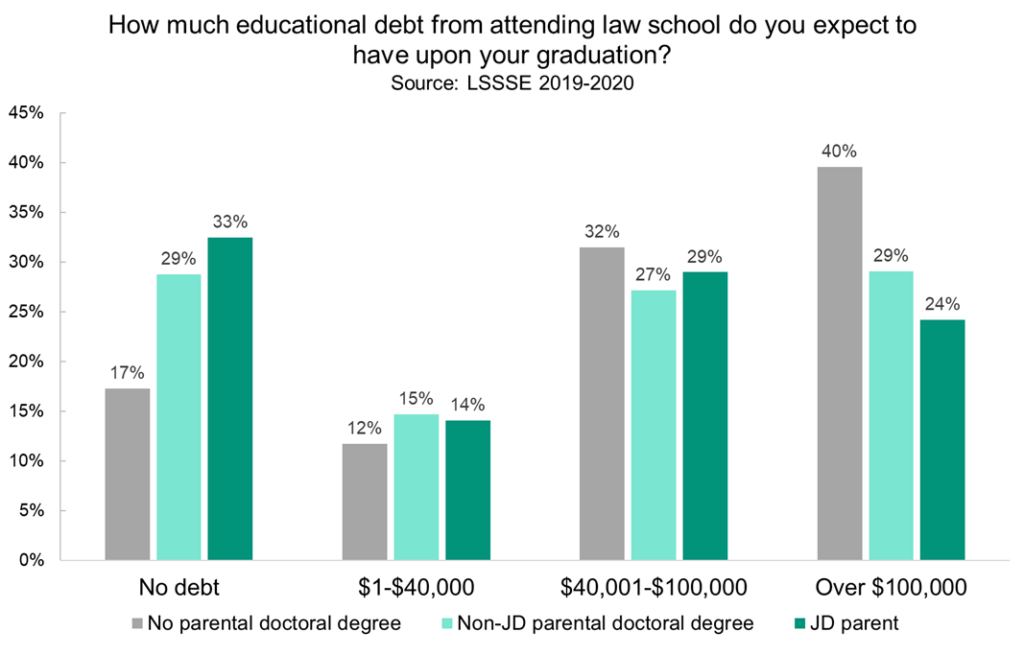
Law students tend to have educated parents. Around 73% of LSSSE respondents have at least one parent with a bachelor’s degree or higher. One in five students (20%) have at least one parent with a doctoral or professional degree (PhD, JD, MD, DDS, etc.), and among those students, just over half (53%) report that the doctoral degree is a JD. Overall, 11% of LSSSE respondents have a parent with a JD.
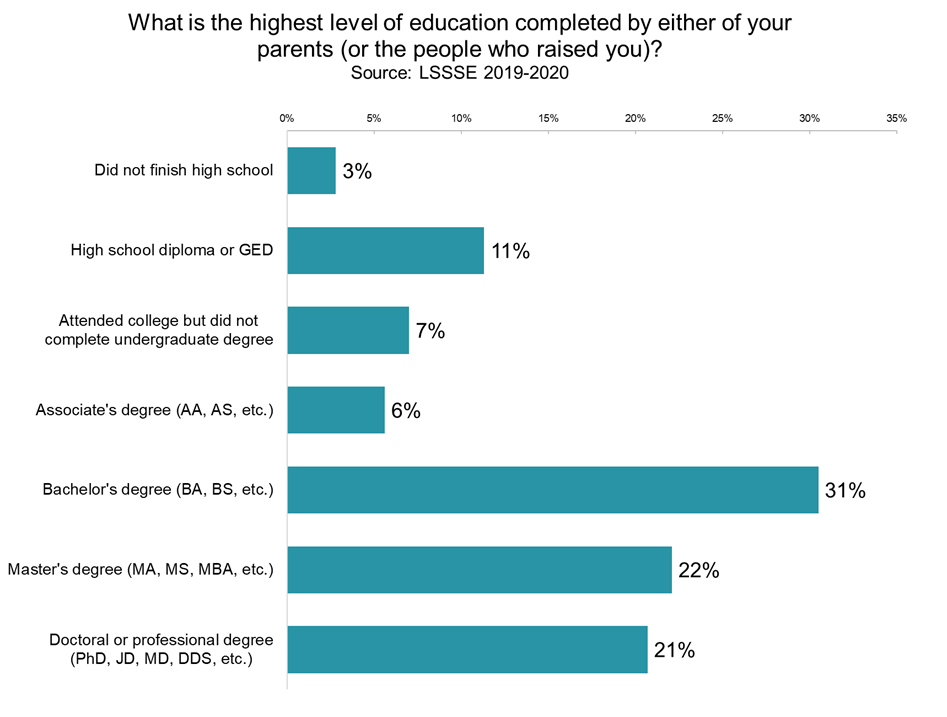
By and large, law students are satisfied with their experiences at law school, and we see minimal differences in satisfaction by parental education. If we combine “good” and “excellent” ratings, satisfaction is 84% among students who have at least one parent with a JD, 83% among students who have at least one parent with a different doctoral degree, and 81% among students whose parents do not have doctoral degrees. Students who have at least one parent with a doctoral degree may be slightly more likely to choose the highest rating (38% vs. 35% among students with non-doctorate parents).
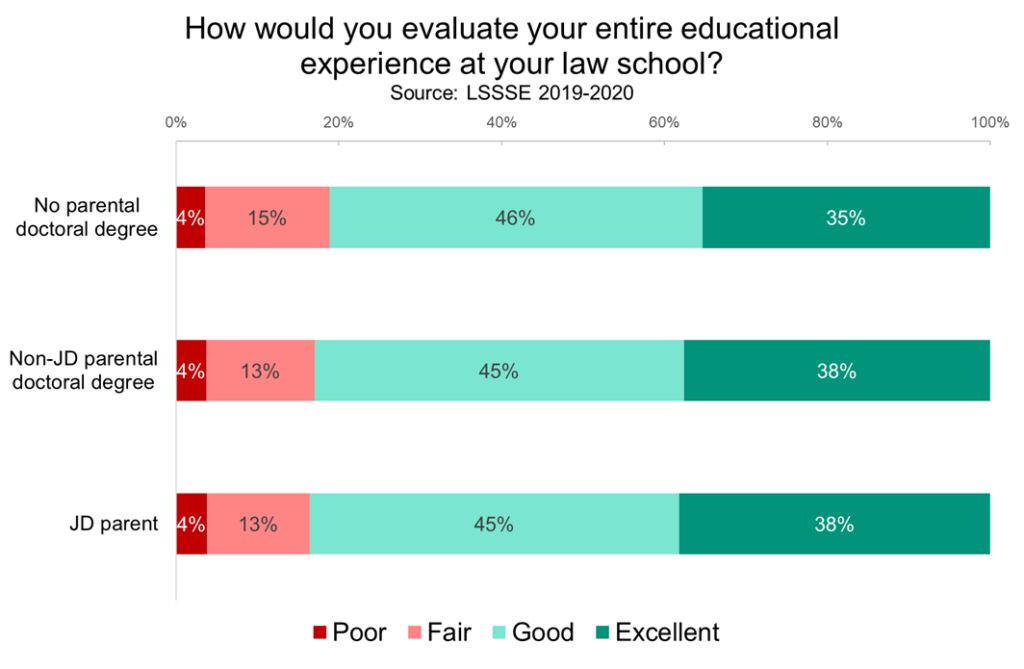
We do, however, see large differences in expected law school debt based on parental education. Students with less educated parents are much more likely to expect to owe more than $100,000 upon graduation and much less likely to graduate debt-free than their classmates with more educated parents. On some level, this may make sense, given that parental education is a strong predictor of a students’ socioeconomic status. However, it remains deeply problematic given that law school debt disadvantages students from lower income households and minimizes upward economic mobility, particularly among students of color. Interestingly, compared to their counterparts whose parents have non-JD doctoral degrees, students with JD parents are still less likely to owe over $100,000 and are more likely to graduate debt-free. If we assume socioeconomic status is roughly equivalent among parents with doctorates, then there may be some advantage to having a lawyer parent, either by increased parental investment in the students’ education or by a keener insight into navigating the process of financing a legal education.
Guest Post: Legal Education and the Illusion of Inclusion
Guest Post: Legal Education and the Illusion of Inclusion
 Shaun Ossei-Owusu
Shaun Ossei-Owusu
Presidential Assistant Professor of Law
University of Pennsylvania Carey Law School
A new semester and a potentially new political landscape are upon us. Last month law students around the country resumed coursework. Their educational pursuits are virtual, in-person, or some mix of both. No matter the format, law students continue their educational journey in an ideologically polarized pandemic society where race, class, and gender disparities are on sharp display.
Students will also be learning in a context where changes in our legal system may have direct relevance to their legal education. As is typically the case, a newly constituted Supreme Court has a diverse docket this term that might shape substantive areas of law that students take courses in, chiefly constitutional law. There will be regulatory shifts that come with new administrations. These kinds of changes will have meaning for administrative law and related areas of law: health law, environmental law, employment law, and civil rights, to name a few. COVID-19 has upended state and federal judiciary systems in ways that have still-undetermined implications for procedural courses law students take (e.g., evidence, civil procedure, criminal procedure) and access to justice issues more generally. And we know from the late Deborah Rhode’s work which communities access to justice issues tend to devastate—racial minorities, women, and other marginalized populations.
Notwithstanding future uncertainty, one thing can be said with some measure of confidence: issues of race and gender—amongst other social categories—will remain relevant inside and outside the sometimes intellectually-cordoned off walls of law schools. How these issues are integrated in the classroom, if they are at all, will affect the substantive learning of law and will either include or exclude historically marginalized groups.
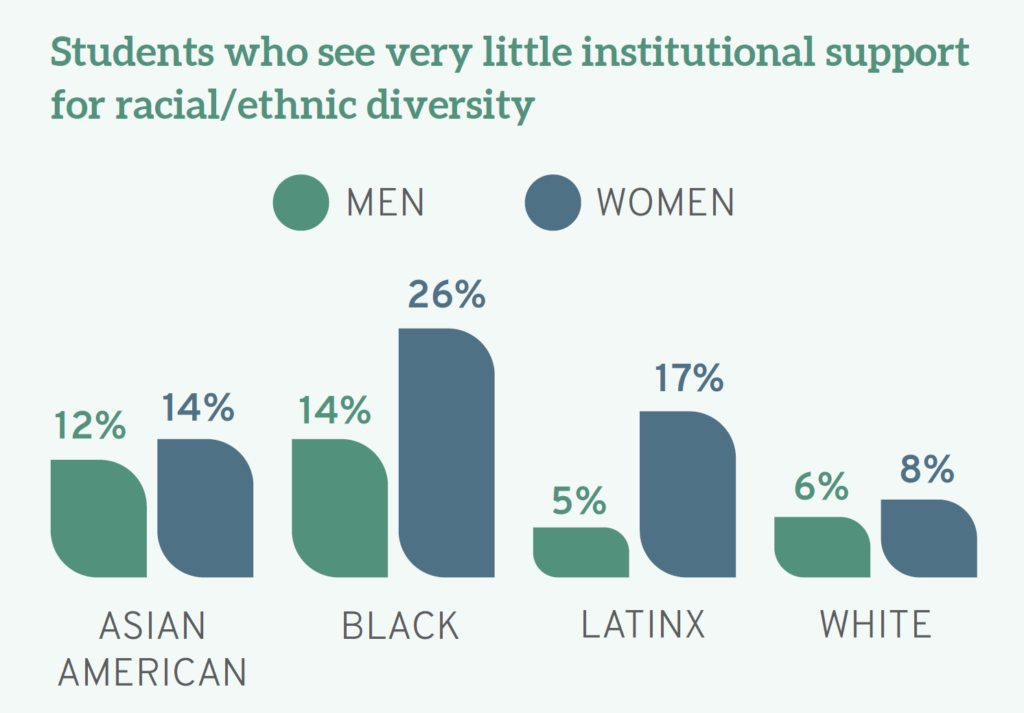
In the specific context of legal education, the results of Law School Survey of Student Engagement’s (LSSSE) Annual Survey illuminate. The Report provides a glimpse into how law schools fail to meet the aspirational goal of inclusion that often takes up primetime real estate on their websites and promotional materials. From my own read, the most jaw-dropping finding is intersectional in nature and about Black and Latinx women law students—aspiring attorneys who are often told that they do not look like lawyers when they transition to practice. 26% of Black women respondents and 17% of Latinx women respondents reported that their schools do “very little” to support racial and ethnic diversity.
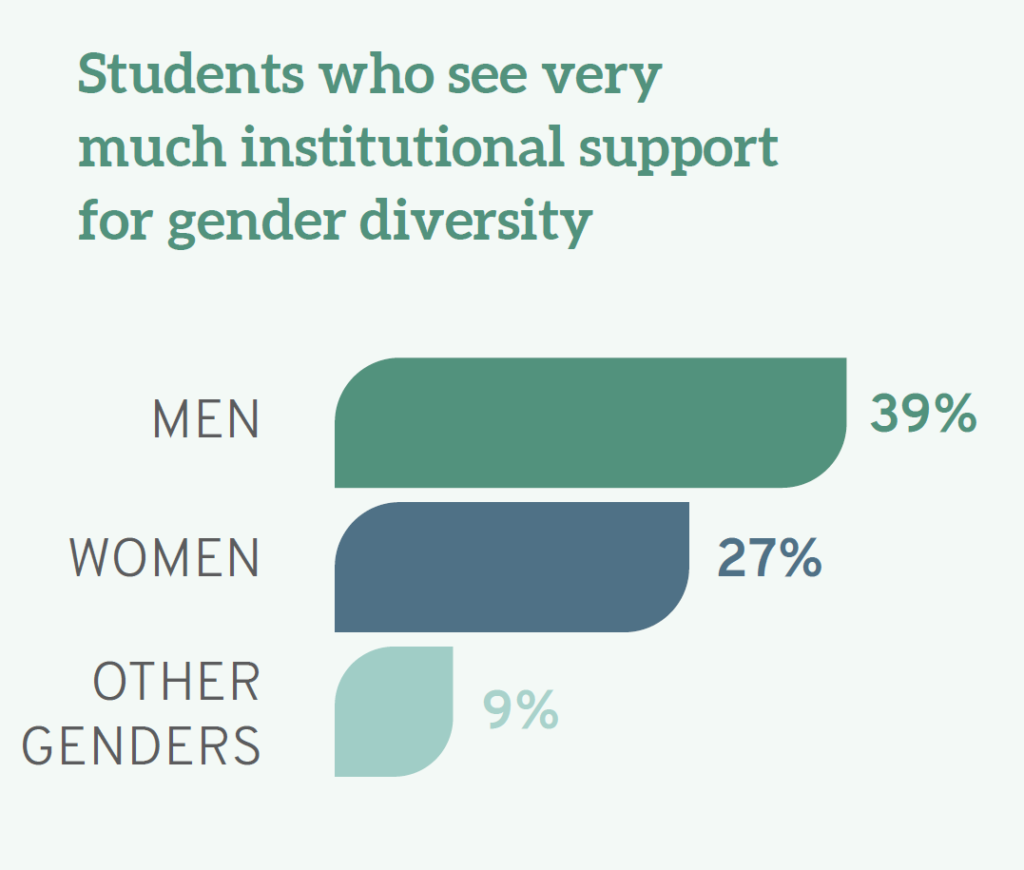
Disenchantment with the lack of support for diversity can be distilled even further. The Report notes that men varied on the issue of gender inclusivity, with 39% “very much” believing that their schools support gender diversity compared to 27% of women and 9% of individuals who identified with the “other gender” category.
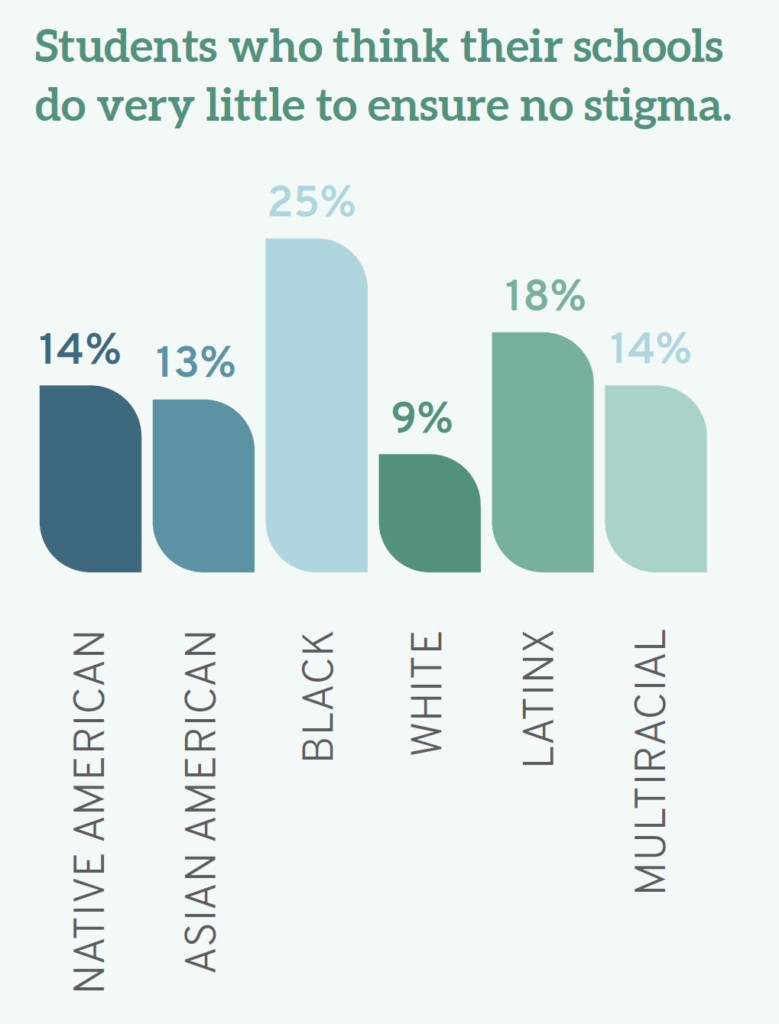
In the context of race, student views also differed, with 9% of White students, 14% of Native American students, 18% of Latinx students, and 25% of Black students believing that their schools do “very little” to ensure that students are not stigmatized based on identity.
Where sexuality and sexual orientation are concerned, 11% of heterosexual students think their schools do only “very little” to avoid identity-based stigma; conversely, 20% of gay students, 16% of lesbian students, 15% of bisexual students, and 19% of those who identify as another sexual orientation see their schools as doing “very little” in this regard. What do these findings mean for legal education and the political moment I gestured to in the beginning?
LSSSE’s data suggest that some students are dissatisfied with the six-figure education they are receiving. Put plainly, law students from backgrounds that the profession has historically excluded—women, racial minorities, LGBTQ communities, and people with disabilities in particular—do not feel part of the academic community and believe law schools are relatively disinterested in their stigmatization. In some ways, this is unsurprising, as there is a deep scholarly literature and genre of books on student disappointment with law school. Moreover, student disenchantment with legal education—which has a history of exclusion that traces back to the nativism and anti-Semitism of the early twentieth century—may in some ways be pre-determined.
The confines of the classroom, which is one of the many areas the LSSSE survey discusses, provides more insight into the inclusion-exclusion dyad. From the vantage point of some educators, law school is simply about training people to be lawyers. The most generous reading of this position suggests that social justice-like ideas like “inclusion” are too ideologically weighty to meaningfully bring in the classroom. For people who subscribe to this view, attempts at inclusion can create impossible-to-navigate landmines for professors. More skeptically, some see inclusion as an ancillary. Read in this light, the primary goal is to inculcate legal knowledge. For these professors, some things are not relevant to the practice of law and are therefore not relevant to legal education.
Such professional school-based views of legal education, vary in their reasonableness, but are held by swaths of the professoriate. Yet, there is a two-fold problem, and this is where the LSSSE survey is especially useful. First, this vision of legal education rubs up quite abrasively against the representations of law schools as bastions of inclusion. Second, this version of education, in some ways, undermines the well-touted “diversity rationale” in affirmative action jurisprudence. What does diversity mean when the subjects of diversity feel alienated?
Considering the mismatch between some students’ experiences and the stricter professional school model of legal education that some professors are beholden to, there are some options. Educators can simply be more intellectually honest about the reality that law school is a site of professionalization where inclusion principles can be trivialized. Alternatively, law schools can continue to disingenuously hitch the law school wagon to social justice rhetoric while failing to actualize inclusion as a practice. Or, in the most courageous and imaginative versions of themselves, law schools can refashion their curriculum and use developments in the legal world as opportunities to offer more inclusive learning environments.
For law schools committed to the third way, resources abound. Complaints about the need to diversify the content of law school courses have existed for decades. Scholars such as Derrick Bell and Dorothy Brown have authored casebooks that describe how race intersects with different areas of the legal curriculum, whereas feminist legal theorists, poverty researchers, scholars of law and sexuality have penned their own books, supplements, and articles that all give educational guidance on how to bring these issues into core courses, and do so in ways that are doctrinally sound. Still, some professors—many of whom have the most analytically sharp minds on their university campuses—throw their hands up in despair or continue with the same regularly scheduled program. For some of these instructors, these conversations were absent in their legal education, and they were likely not trained to incorporate these issues. Some may think it would be better to leave this work of thematic inclusion to their more expert colleagues (e.g., scholars of race, sex, class, disability) rather than wade into territory where they are sure to mess up. But throwing one's hands up in despair is increasingly a less credible course of action. The pandemic, along with the protests of 2020, have forced some people to rethink how they deliver course content, and more importantly, have made inequality a more prominent theme in our public discourse. The current socio-political moment, and the reality of pandemic pedagogy, call for curricular redesign.
Fortunately, the tools to make the classroom more inclusive are available and they are not limited to the usual courses. To be sure, law professors have written about how first-year courses like criminal law and property are inattentive to inequality in ways that produce the responses found in the LSSSE survey and have offered suggestions on how those same courses could easily be improved. But attempts to diversify and create a more inclusive curriculum are not confined to these foreseeable areas of law but can be found in more unsuspecting places like evidence, corporate law, trust and estates, and intellectual property, to name a few.
Law professors have also identified space in the curriculum for trans-substantive engagement with the kinds of questions and perspectives that demonstrate an awareness of inequality, both in legal education and in law more generally. Indeed, I, along with my colleague Karen Tani, have taken on the task of trying to simultaneously create an inclusive learning environment that rigorously addresses inequality by creating a 50-person Law and Inequality course at Penn Law. This endeavor and more meaningful engagements with diversity need not be limited to women, racial minorities, and sexual minorities. Inclusion also implicates and has meaning for the larger law student population. One of the most understated findings in the LSSSE Report is that 16 percent of white students believed law schools placed “very little” emphasis on issues of equity and privilege and do not prioritize providing students with the skills necessary to confront discrimination and harassment.
My purpose here is not to proselytize teaching a course like the one we are offering. Instead, I want to highlight how student dissatisfaction with inclusion, which the Report highlights in detailed and accessible fashion, can be situated within this critical juncture. 2021 is a unique moment where law schools can reimagine legal education in real time, and for a post-pandemic world. This will not be easy, as this is a stressful time for faculty—some of whom are in high-risk groups during the pandemic and/or have a variety of care obligations. COVID-19 has upended a lot of assumptions and forced people to change longstanding pedagogical practices. Institutions could do a lot of good by encouraging faculty reflection and supporting creative reorganization of current courses.
The LSSSE Report tells us that in many ways, law schools are failing to provide the inclusive educational spaces that they, I believe in good faith, want to offer and that students of various backgrounds actively desire. Ultimately, the teaching tools are available, the moment is ripe, and the only outstanding question is whether legal educators will make the changes necessary so that the next LSSSE survey offers more optimistic findings.
What Do 1L Students Plan to Do in Law School?
Most students complete law school in three years. With intense coursework and notoriously challenging reading loads, law students must be selective about how they allocate their time toward extracurricular activities. Which enriching activities had 1L students completed or planned to complete before graduation in 2019 and 2020? Check out our interactive visualization below to see.
** Note that non-binary students are included only when the population was large enough to ensure student anonymity in aggregate reporting.










