Success with Online Education: Classroom Environment
Our last post shared some general findings about online learning from our 2022 Annual Results, Success with Online Education (pdf). In this post, we will share evidence that online classrooms appear to encourage a more diverse cross-section of students to participate in class discussions. We will also share reassuring signs that online law students are learning as much as their in-person counterparts.
Online discussions feature diverse voices
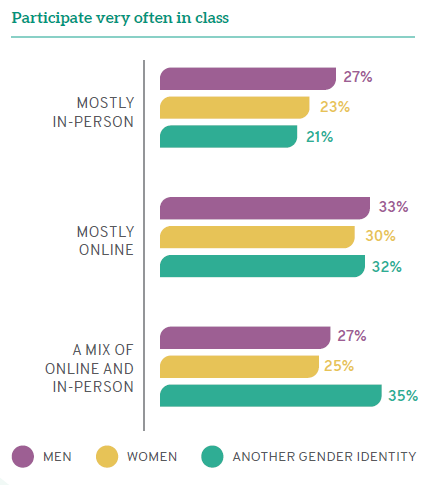
Online classes excel at inviting participation from a broader range of students than in-person classes. Men are equally likely to participate in class discussion and ask questions “often” or “very often” whether participating in person (60%) or online (61%). However, women taking mostly online courses are more likely to engage in class “often” or “very often” (58%) compared to women taking mostly in-person courses (53%). In fact, online courses appear to encourage all students to engage more intensely with class discussion. One quarter of students (25%) who take primarily in-person classes participate “very often” compared to 31% of students taking mostly online classes. There is a marked gender difference, with 23% of women participating “very often” in person but a full 30% participating “very often” online, and only 21% of those with another gender identity participating “very often” in person while 32% do so online. The online environment–perhaps because of the mechanisms for turn-taking or because it is more comfortable for students to volunteer– invites more voices to engage in the conversation.
Online students are learning as much as in-person students
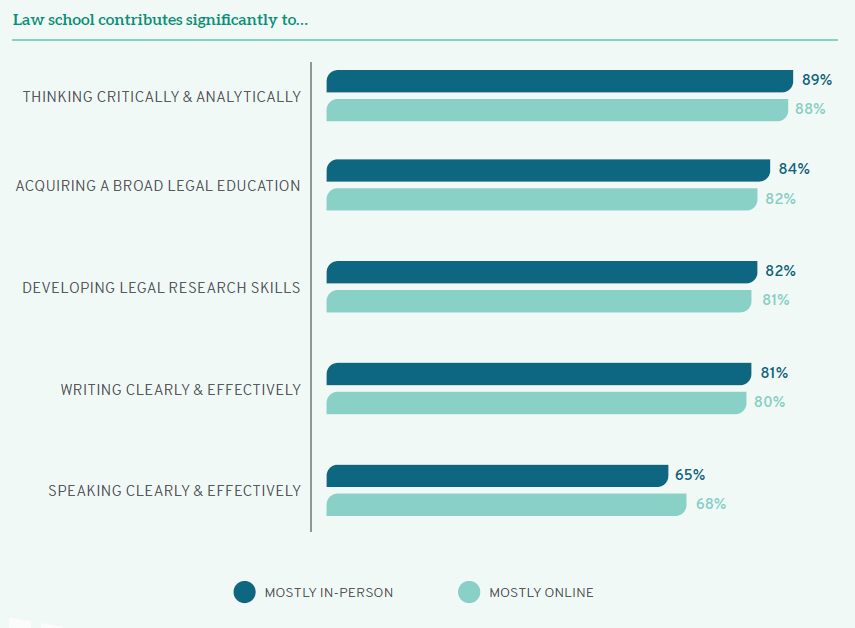
Regardless of how they attend classes, most students are confident that they are developing crucial legal skills. Nearly 90% of online and in-person students are learning to think critically and analytically. More than four out of five online and in-person students say they are acquiring a broad legal education (82% and 84%, respectively) and developing legal research skills (81% and 82%, respectively). Interestingly, online students are more likely to be developing the ability to speak clearly and effectively, perhaps because online courses invite more participation from a diverse range of students. Thus, law school classes do not lose their intellectual rigor when they are offered in an online format.
Online law school classes can be highly successful and well-received by students. Many students who take most of their classes online are as satisfied—and sometimes more satisfied—than their peers who attend classes primarily in person. Furthermore, law students who attend classes via either modality are equally likely to feel confident that they are learning important skills that will help them succeed as legal professionals. Although the law school experience is unlikely to be primarily online again, the accelerated transition to offering online courses that occurred due to COVID-19 shows that the online law school experience can be as successful, enriching, and satisfying as the traditional law school curriculum.
Success with Online Education: Relationships
The latest LSSSE Annual Results, Success with Online Education (pdf), focuses on the largely positive online learning experiment that law schools embarked upon due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This week and next week we will share selected snippets from the results. In this post we will describe how the switch to online learning impacted relationships among law students, law faculty, and administrators.
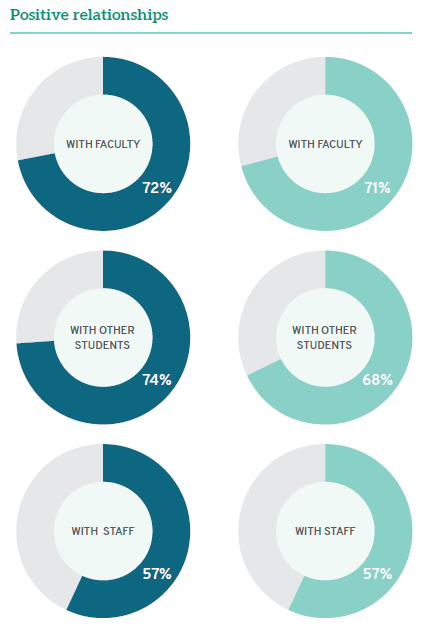
LSSSE data confirm other research showing how law school faculty have invested an enormous amount of energy and effort to connect with students, regardless of instructional modality. A full 72% of students taking mostly in-person classes have strong relationships with faculty (5 or higher on a 7-point scale), and 71% of mostly online students feel the same way. Students remain highly engaged with faculty in an online environment.
Online students and in-person students are equally likely to have positive relationships with administrative staff. A little over half (57%) of each group rate their relationships with their law school’s administrators a 5 or higher on a 7-point scale. Career services-oriented staff could consider using these relationships to bring more targeted career guidance to online students to narrow the gap in career preparedness between online students and in-person students. However, the relatively low percentage of both in-person and online students who have strong relationships with staff is a point of concern that should be addressed to better support law student development.
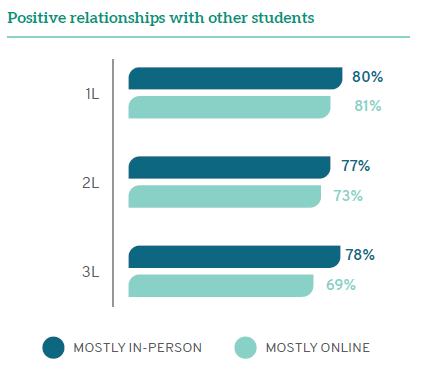
Despite similarly positive relationships with professors, students in mostly online classes are less likely than others to have strong relationships with each other. Only 68% of online students rate their relationships with their classmates positively, compared to nearly three-quarters (74%) of in-person students. There is again a disparity across class years, with 1Ls having similarly positive peer relationships regardless of mode of attendance and online 3Ls being much less likely to enjoy strong relationships with their peers than 3Ls attending in person. There may be a loss of social connections among online students because of a lack of the sort of incidental contact that builds relationships over time.
Next week we will discuss the learning experience in the virtual classroom. For the complete story, you can view the entire report on our website.
Online Learning and Law Student Age
The 2020-2021 academic year was unlike any other, forcing students and instructors to adapt to a different way of living and learning. Prior to the pandemic, law schools were less likely than other sectors of academia to embrace online learning. But when it became clear that COVID was not going away, many law schools shifted to primarily online interactions. The Online Learning module, which debuted with the spring 2021 LSSSE survey administration, was developed to capture students’ perceptions and experiences with online classes during this peculiar academic year and potentially beyond. Although the abruptness of the transition to online learning and the external stressors inherent to pandemic life may make these data unique in some ways, in other ways they are an excellent starting point for law schools to learn about how to structure their curriculum to leverage the strengths of the online environment, even as traditional in-person learning resumes.
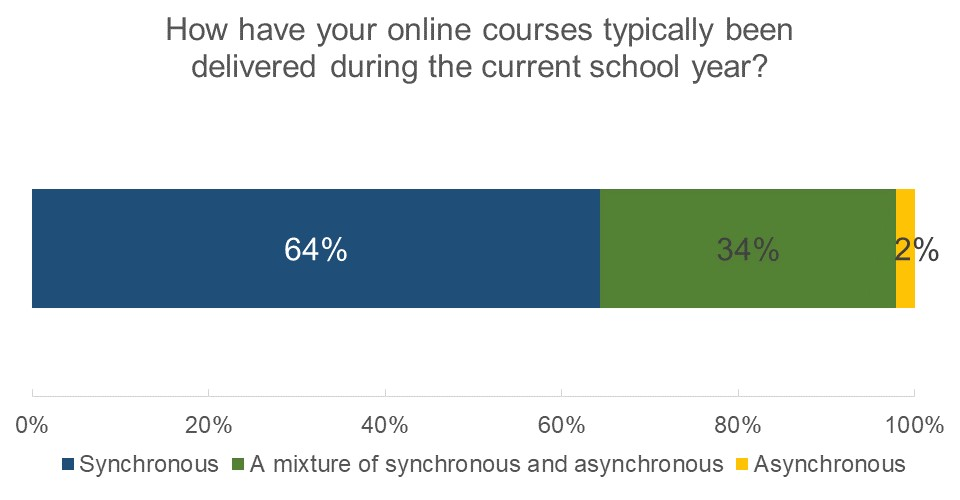
What types of online learning experiences were law students having in 2020-2021? Nearly all students who took online courses had at least some synchronous element in their courses. Nearly two-thirds of students typically had synchronous courses while another third experienced a mixture of synchronous and asynchronous content. Only about two percent of students typically received only asynchronous content.
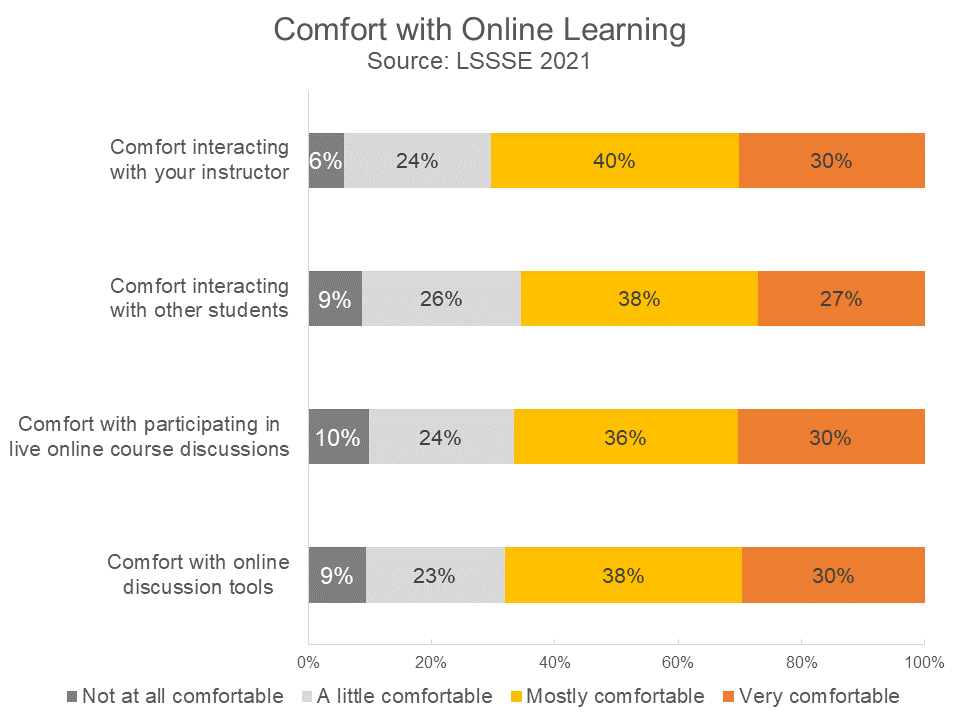
Most law students were fairly comfortable with online learning. Seventy percent of students were mostly comfortable or very comfortable interacting with the instructor of their online courses, and around 65% felt similarly about interacting with the other students. About two-thirds of students were comfortable with online discussion tools such as discussion boards and forums and about two-thirds of students were comfortable with live online course discussions.
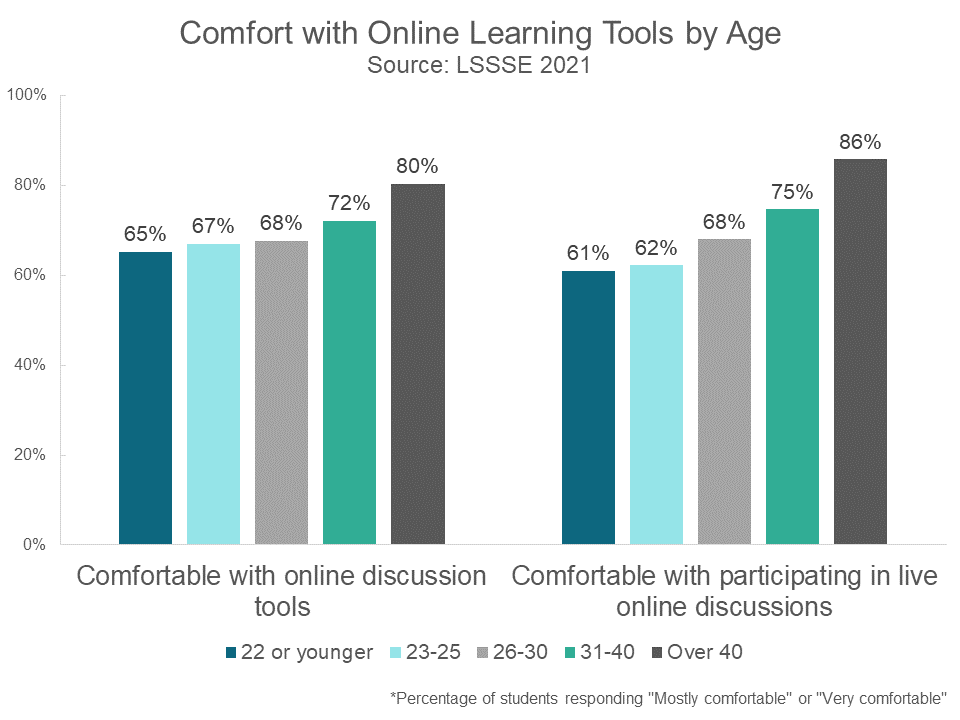
Interestingly, older students were more likely to be comfortable with virtually all aspects of online learning relative to their younger peers. In fact, comfort with online learning tools increased steadily across age brackets. The vast majority (86%) of students over 40 were comfortable participating in live online discussions compared to only around 62% of students 25 or younger.
This age discrepancy in participation exists in physical classrooms too. In 2019, before the widespread adoption of online law classes, 80% of students over age 40 often or very often asked questions in class or contributed to class discussions, compared to 48% of those 22 or younger and 54% of those between 23 and 25. In fact, students under age 30 may be somewhat more comfortable with online course discussions than in-person ones, even though their overall participation is less than that of their older classmates regardless of the class setting.
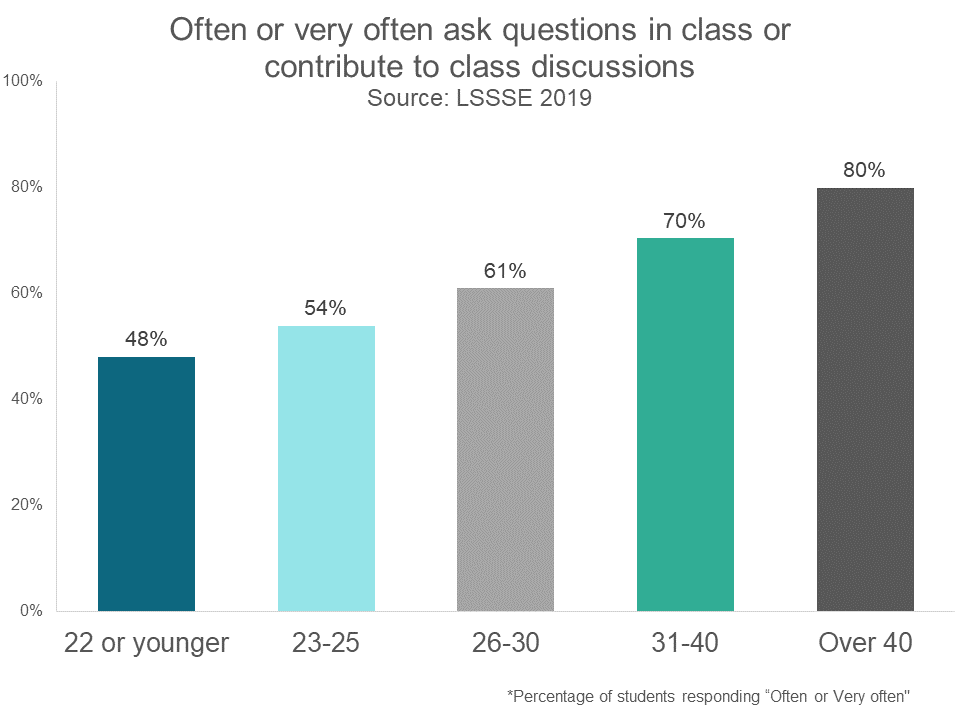
Older students were also more likely to be comfortable interacting with their peers and instructors online. Only 63% of students age 22 or younger were comfortable interacting with their instructors online, compared to a full 85% of students over 40. Among students between the ages of 23 and 25 (the most common age for a law student), less than two-thirds were comfortable interacting with other students in their online classes, compared to a full 78% of students over 40.
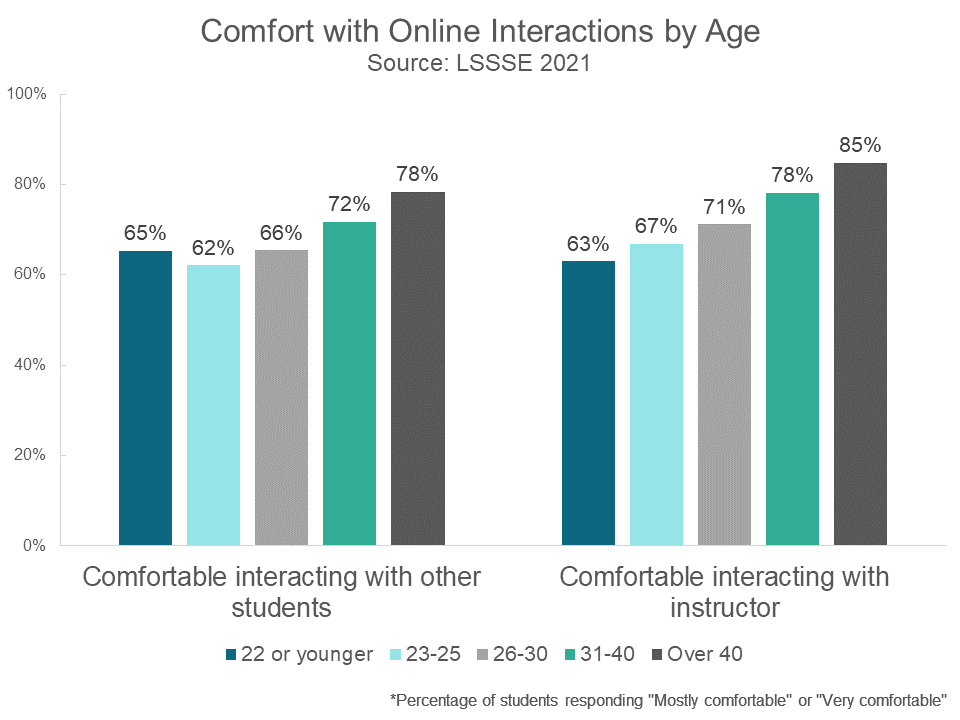
Although popular media tends to suggest that younger people are more adept with technology, the oldest Millennials – the first generation to live much of their lives online – are now in their forties. Perhaps these older students have adapted to so much online technology across their personal and professional lives that another pivot was not as disruptive as it was for their younger colleagues. Regardless of the reason, the LSSSE data show clearly that law schools should make a deliberate effort to support the technological skills and online engagement levels of their youngest students.



