Learning Effectively on Your Own
Working independently and working collaboratively are both important skills for budding legal professionals. In addition to learning through classroom experiences, law students must assume responsibility for learning large amounts of material in a relatively short period of time, often independently and sometimes in small groups. We examined the extent to which law students feel that their experiences in law school have contributed to their personal development in both learning effectively on their own and working effectively with others.
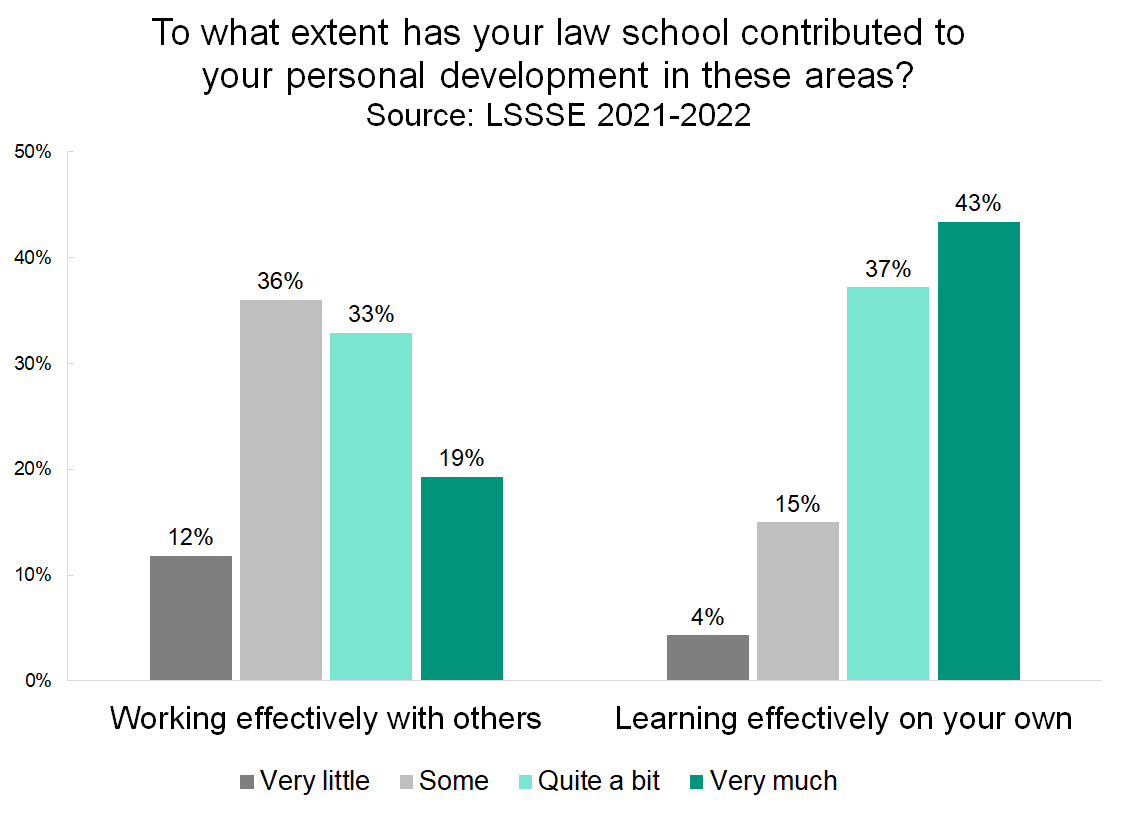
Four in five law students say that law school helped them “quite a bit” or “very much” in developing the ability to learn effectively on their own. Fifteen percent say that they developed “some” skills in this area, and only four percent said they developed “very little.” By comparison, only about half (52%) of law students learned “quite a bit” or “very much” about working effectively with others. A little more than a third (36%) developed “some” skills in this area, and more than one in ten (12%) learned very little about working effectively with others.
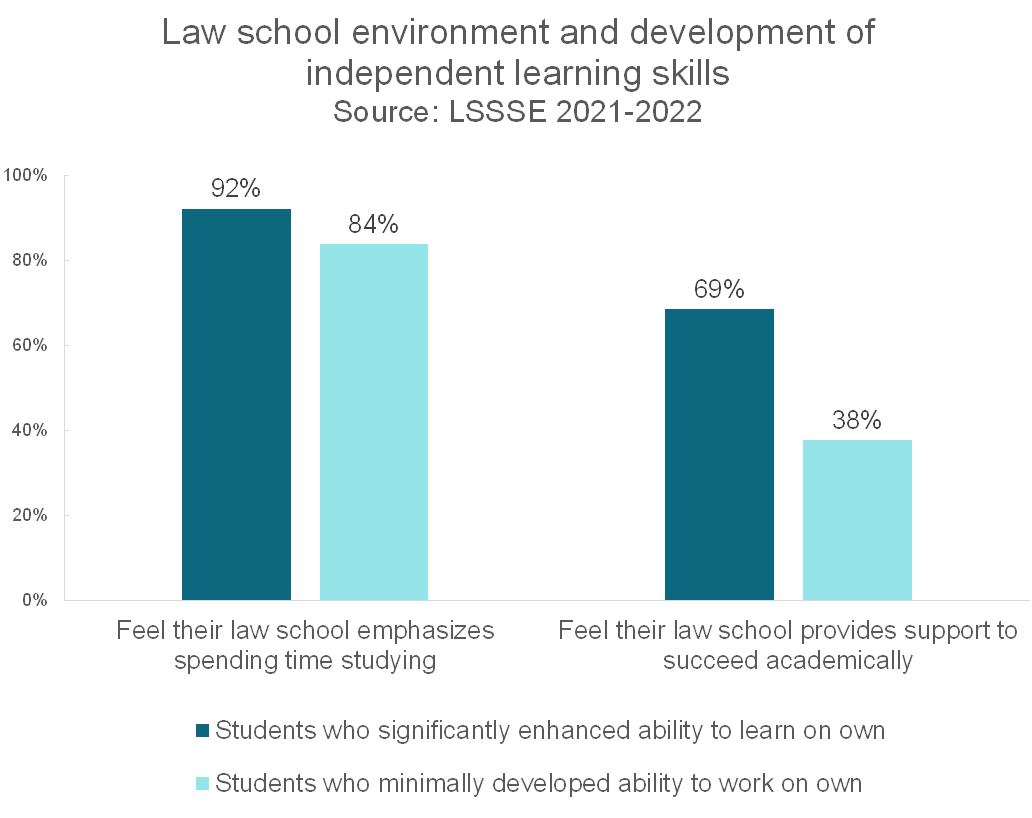
Students who greatly enhanced their ability to work on their own generally feel both that their law school has high standards and that their law school adequately supports their academic endeavors. Nearly all (92%) of students who significantly enhanced their independent learning skills felt that their law school emphasizes spending significant amounts of time studying and on academic work compared to 84% of their colleagues who developed fewer skills in this area. Additionally, over two-thirds (69%) of students who honed their ability to learn independently felt that their law school provides the support they need to succeed academically compared to only 38% of their peers. Rigor and institutional support work together to drive student achievement.
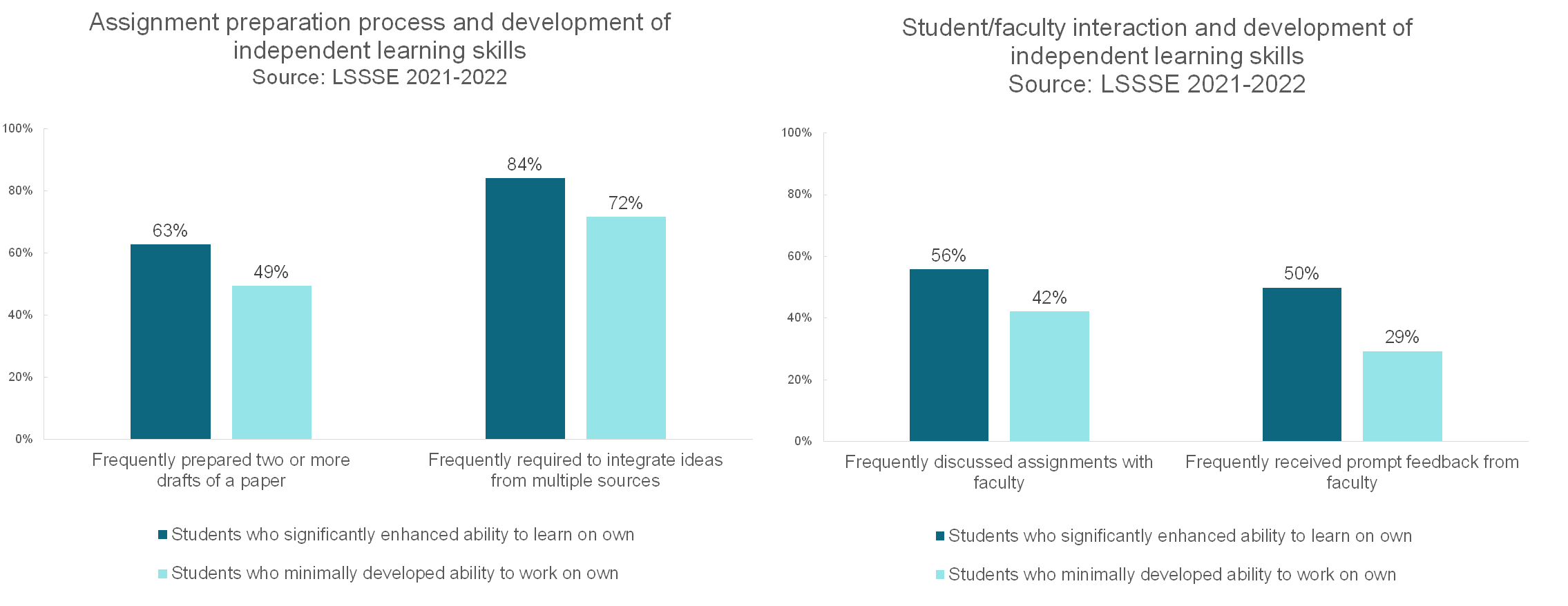
Students who substantially enhanced their ability to learn independently were more likely to revise course assignments at least once and to engage more deeply with course content. Sixty-three percent of independent learners frequently prepared two or more drafts of a paper or assignment and 84% were frequently required to integrate ideas from multiple sources in papers or course assignments. Students who developed independent learning skills were more likely to frequently discuss assignments with faculty compared to students who developed less of an ability to learn independently. Perhaps crucially, the independent learners were more likely to frequently receive prompt feedback from faculty (50% received prompt feedback "often" or "very often") compared to law students with less-developed independent learning skills (29% received prompt feedback "often" or "very often"). Deep, sustained learning is often an iterative process that requires feedback from experts, and this is borne out by the LSSSE data.
Next month we will look at how students who feel law school has contributed substantially to their ability to work effectively with others differ from those students who do not feel this way. We will also consider how interpersonal effectiveness skills might affect attitudes toward diversity.
Law School Support for Non-Academic Responsibilities
Law students vary in their amount and type of non-academic responsibilities, and they also vary in the degree to which they feel that their law school helps them cope with these responsibilities. In addition to their studies, some law students work, care for children or other dependents, and engage in community activities. We wanted to examine the degree to which students feel supported in these endeavors by their law schools.
Time Spent Caring for Dependents
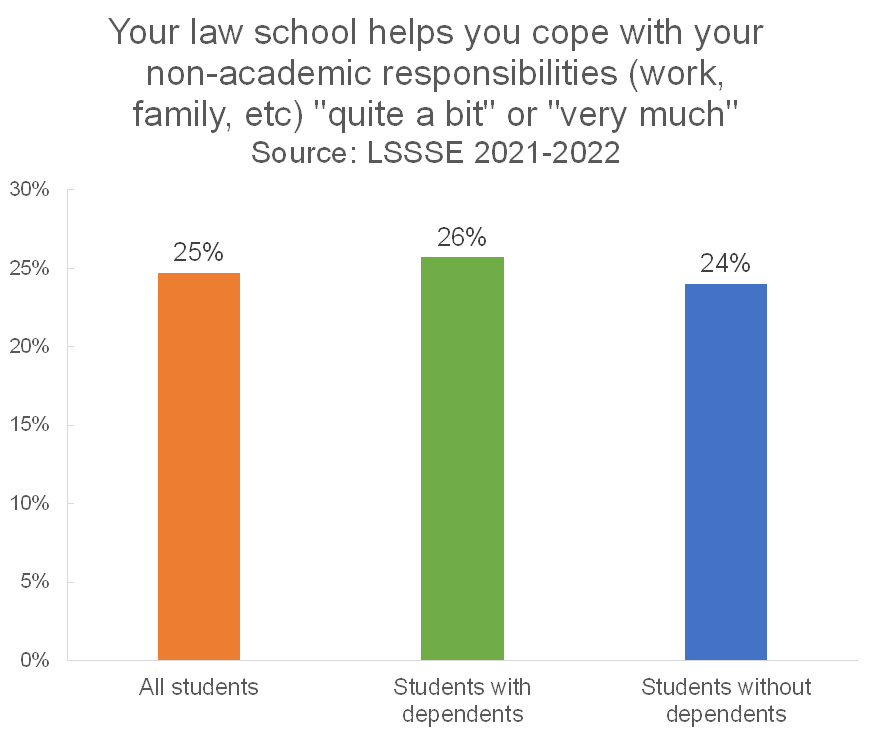
Thirty-eight percent of law students spend at least one hour per week caring for dependents living with them (parents, children, spouse, etc.). Interestingly, there is little difference in the percentage of students with and without dependent care duties who feel that their law school emphasizes helping them cope with their non-academic responsibilities. About a quarter of each group (26% of students with dependents and 24% of students without dependents) feel well-supported. However, students with dependents are slightly more likely to say that their law school does very little to help them cope with non-academic responsibilities. Two out of five (42%) of students with dependents feel this way compared to 38% of students without dependents.
Gender and Dependent Care
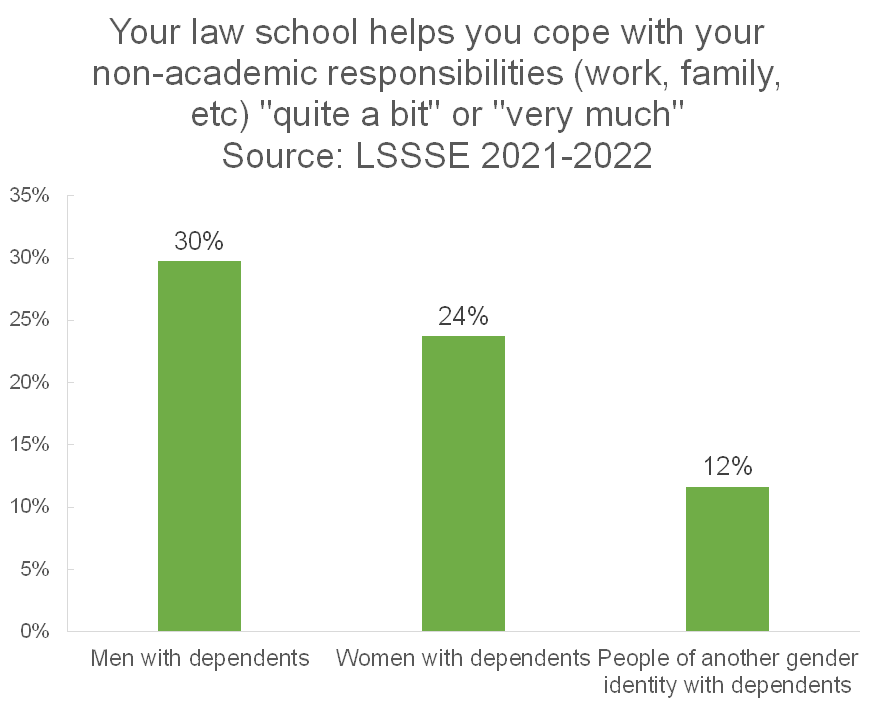
However, there are huge differences by gender. Men with dependent care responsibilities are much more likely to feel supported by their law schools than women with dependent care responsibilities, and both groups feel more supported than people of other gender identities with dependent care responsibilities.
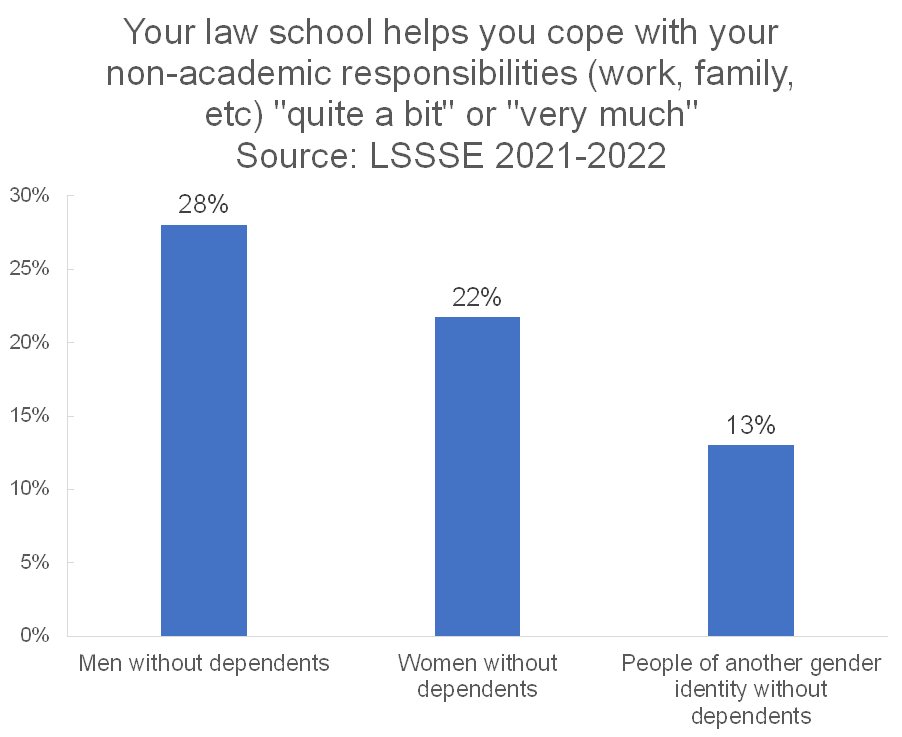
It appears, however, that this effect is more about gender and less about the dependent care responsibilities as we see this same disparity across gender among people without dependent care responsibilities.
Time Spent Working for Pay
Similar to the pattern we see with dependent care duties, there is minimal difference in the perceived level of support for non-academic responsibilities between students who have jobs and students who do not. Around one in four students in either category say that their law school emphasizes supporting their non-academic responsibilities.
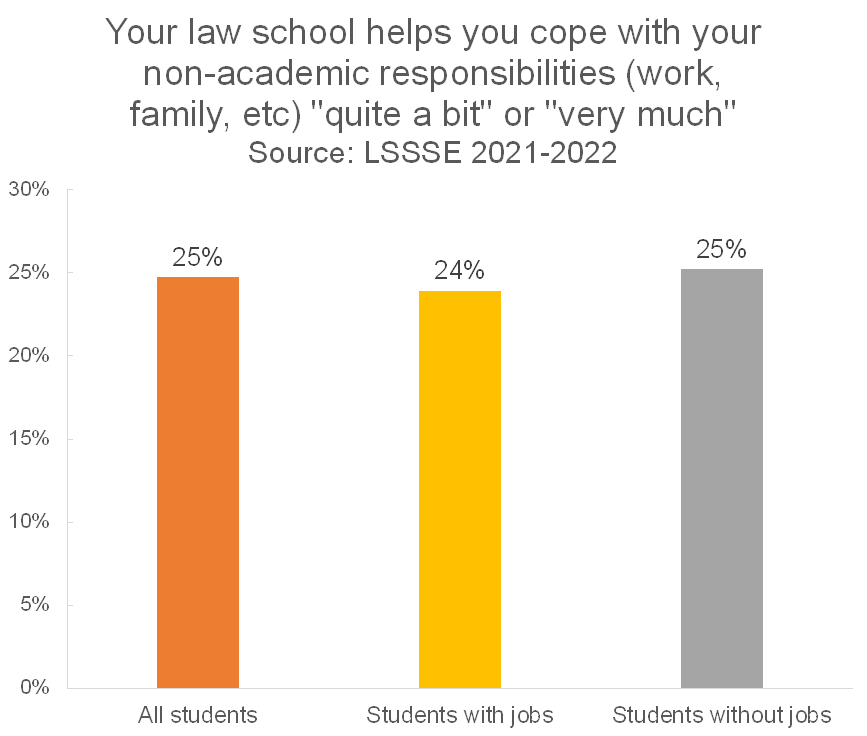
Gender and Employment
The gender pattern for perceived support is much the same for working/non-working students as it is for dependent care duties. Men are more likely to feel high levels of support than other students. However, people who identify as neither men nor women are actually more likely to feel highly supported in their non-academic responsibilities when they are employed (20% of students) relative to when they are not (6% of students).
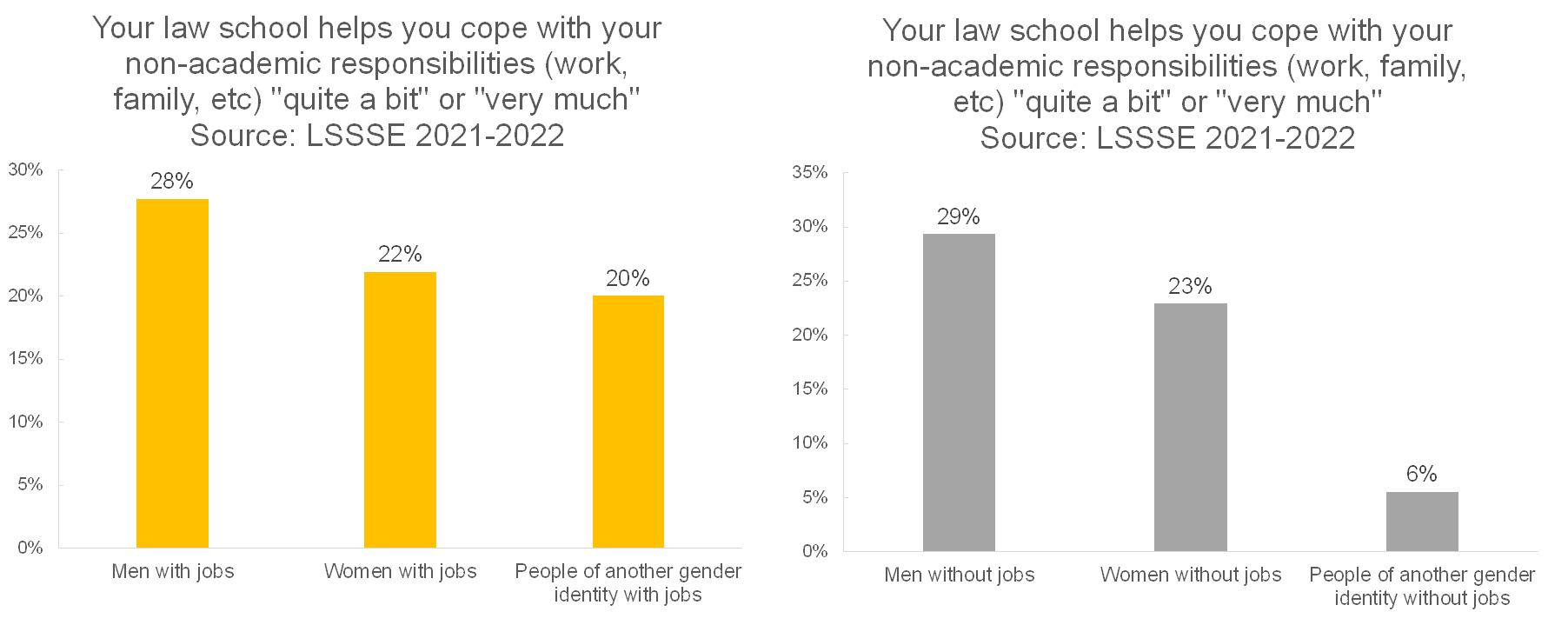
Regardless of how they spend their time outside of law school, men are much more likely to feel highly supported in their non-academic responsibilities, people of another gender identity are very unlikely to feel supported, and women generally fall somewhere in between. Adequate support for non-academic responsibilities clearly looks different for different people, and it appears that gender is a major factor. Rather than focusing on student populations based on which responsibilities they have and how they spend their time outside of the classroom, law schools may want to consider the unique needs of women and people of other gender identities to close the gap in the degree of support they feel about coping with their non-academic responsibilities.
Providing the support law students need to succeed academically
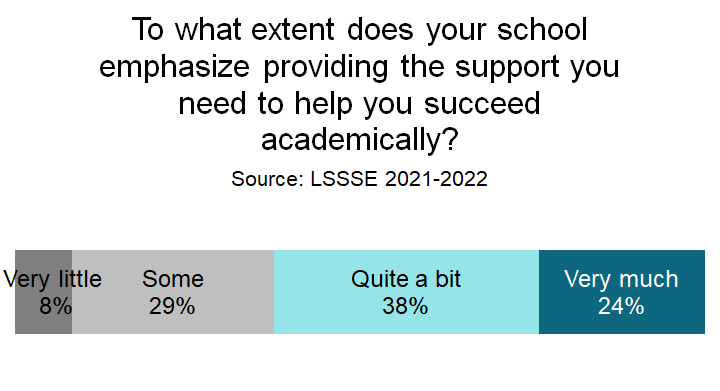
A strong academic program is the foundation of any law school. Equally important is that law schools provide the support services students need to meet the rigors of the curriculum. About two-thirds of law students feel that their law school places “quite a bit” or “very much” emphasis on providing the support they need to succeed academically.
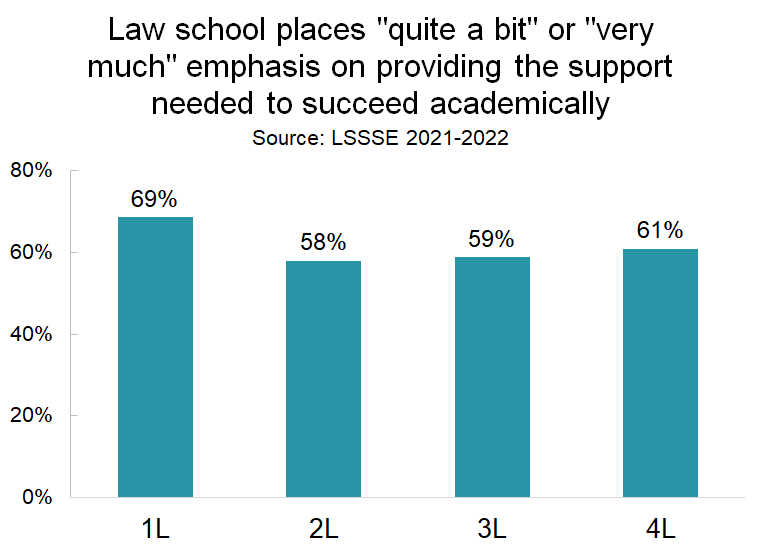
1L students are more likely to feel supported than their more advanced colleagues. Although the general optimism and positivity that 1L students feel toward their experience tends to steadily decline with advancing years for any measure of engagement, for the perception of academic support, satisfaction drops markedly among 2L students and then remains at that level during 3L and 4L years. This suggests that there is an initial sense of being supported that fades fairly quickly after students adjust to their new environment.
Two-thirds of men feel that their law schools places a strong emphasis on supporting academic success, which is slightly higher than the proportion of women who feel similarly (60%), but fewer than half of the people who have another gender identity feel that level of academic support.
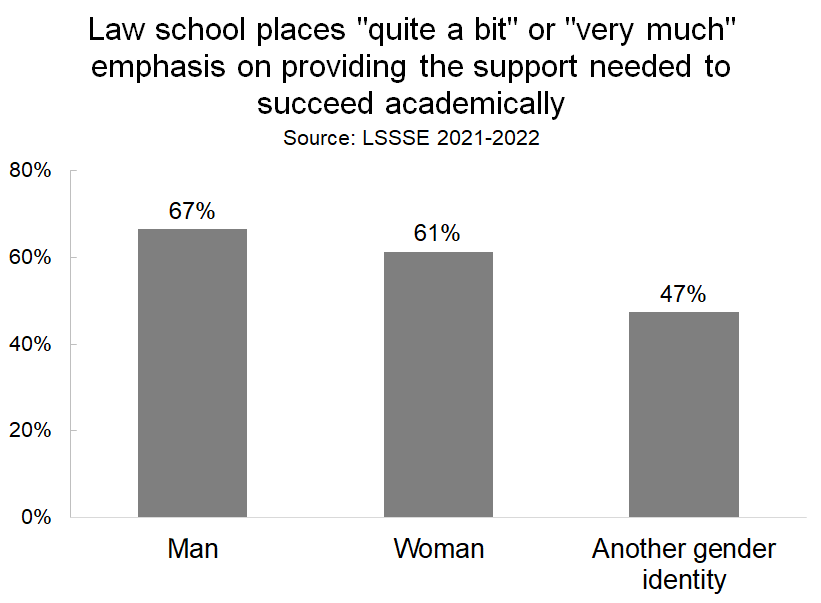
Importantly, the degree to which students feel academically supported is very strongly correlated with whether they are satisfied with their overall law school experience. A full 91% of students who rate their experience as “excellent” feel supported in their academic success compared to only 7% of students who have are having a “poor” experience.
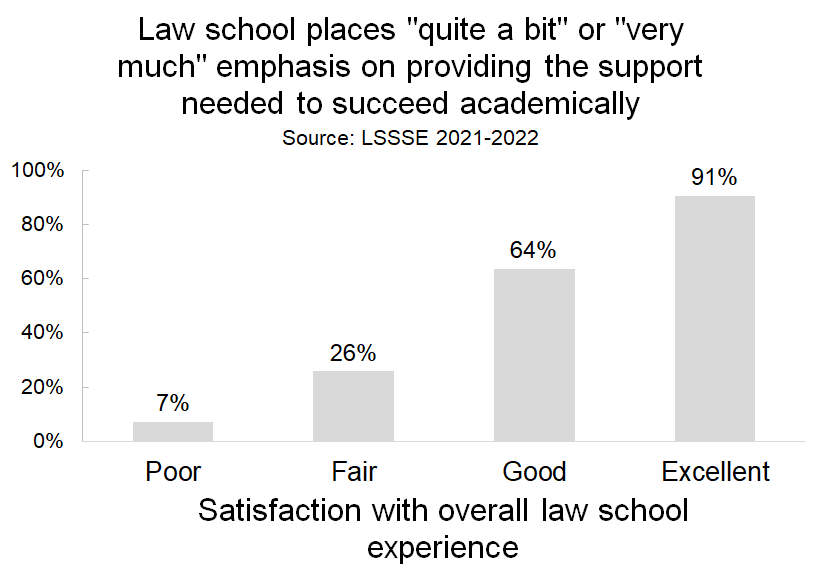
Perceived degree of academic support is also closely tied to whether a student would choose their law school again if they could start over, although the relationship is slightly less stark than for overall law school satisfaction. Among students who would either probably not or definitely not attend the same school, about 32% feel supported to succeed academically. But among students who would probably or definitely attend the same school, 70% feel academically supported.
Law students are driven to succeed in the face of the challenges presented by their academic program. Students who feel supported in their academic endeavors by their schools are more likely to be satisfied with their overall experience and to say that they would choose the same school if they could start over. Academic support is integral to a successful law school experience and likely impacts students’ long-term satisfaction and likelihood to become alumni who speak highly of their alma maters.
Law Student Stress and Anxiety
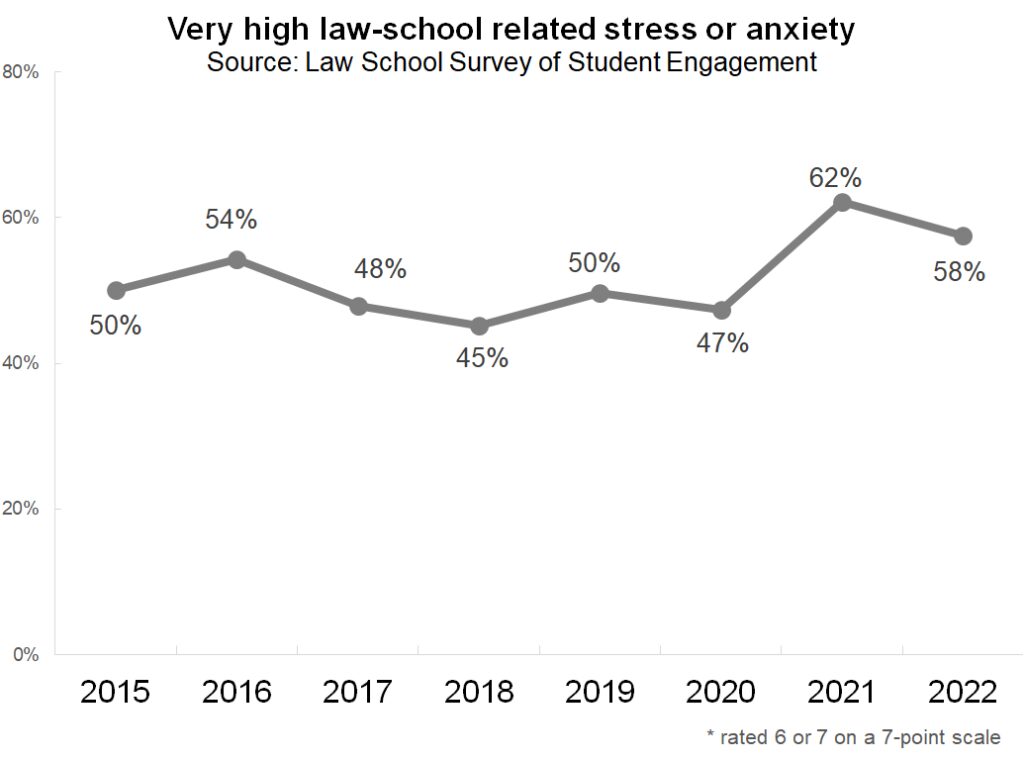
Are today’s law students just as stressed as yesterday’s law students? LSSSE has been tracking student stress levels for the last eight years with our optional Student Stress module. In addition to overall law school-related stress and anxiety, the module asks about anxiety and stress caused by teaching methods, competition with peers, financial concerns, and more.
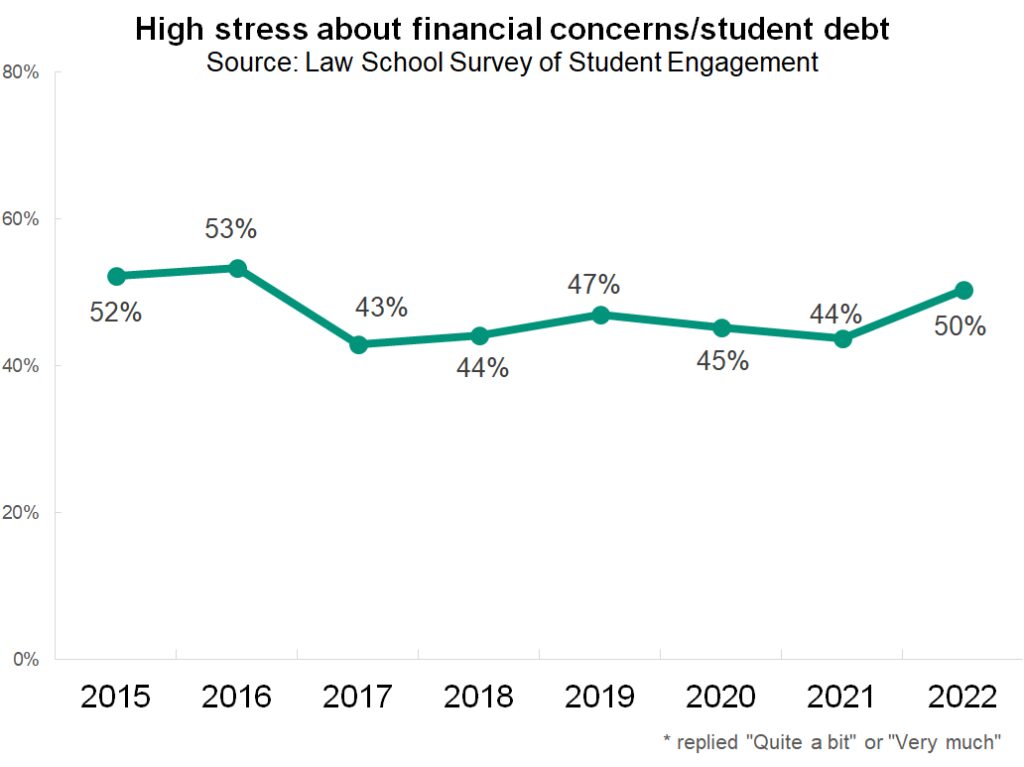
The percentage of students who report high levels of stress and anxiety (rated as a 6 or a 7 on a seven-point scale) has remained fairly stable over the last several years. About half of all law students feel very high levels of stress. There was a marked increase in highly stressed students between 2020 and 2021, which is likely a byproduct of living through a year of COVID-19.
Stress about financial concerns has remained mostly stable as well. A little less than half of all students feel that financial concerns and student debt cause them “quite a bit” or “very much” stress or anxiety.
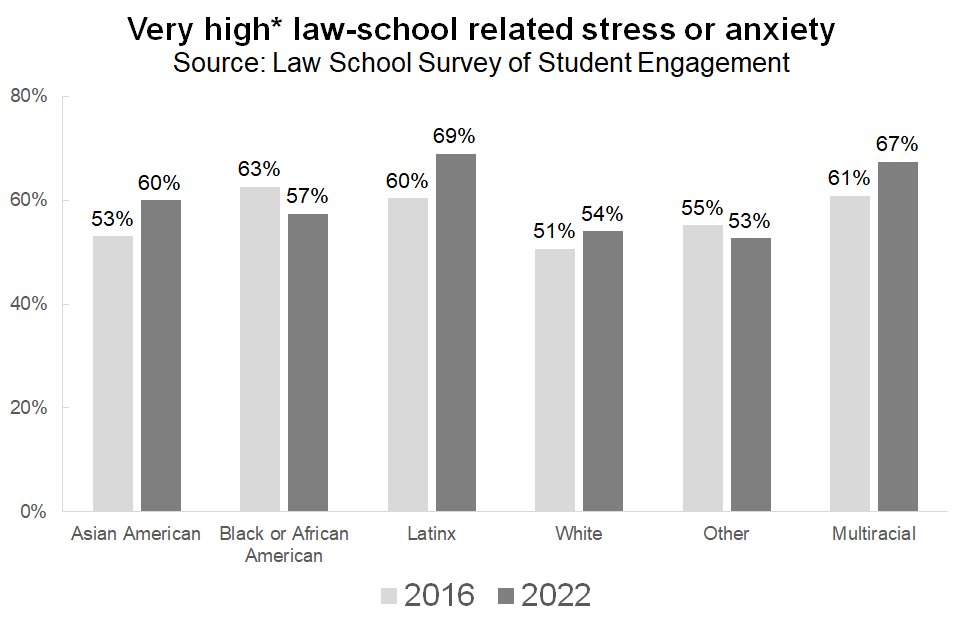
While stress levels have not changed considerably in the last several years, neither has the fact that some students are more likely to be stressed than others. Although African American and Latinx students experience only slightly higher levels of overall law school-related stress and anxiety relative to their white and Asian American peers, they are much more likely to be stressed about financial concerns. These fears are justified, given that the burden of student debt falls disproportionately on their shoulders.
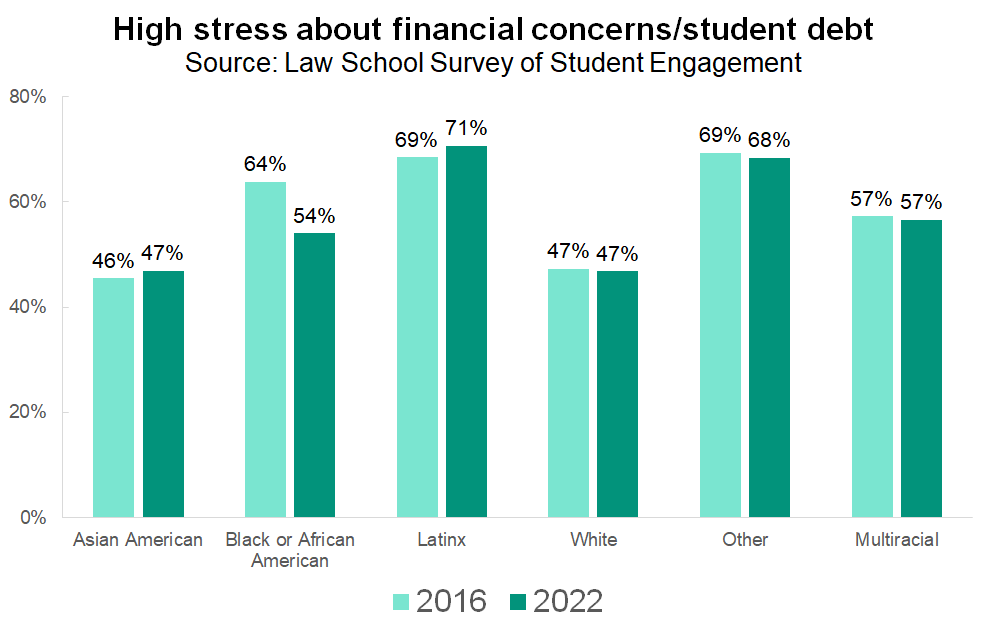
Fortunately, most students do sense that their law school tries to help with stress management. In 2022, three-quarters of student said that their law school places at least some emphasis on ways to effectively manage stress and anxiety. Given high rates of substance misuse and mental health issues within the legal community, developing strong coping skills should remain a high priority for law schools and the future lawyers they serve.
The Changing Landscape of Legal Education: High Levels of Satisfaction
In spite of many challenges, law students report relatively constant positive levels of satisfaction with legal education over the last decade and a half. Our 2020 special report The Changing Landscape of Legal Education: A 15-Year LSSSE Retrospective shares longitudinal findings on select metrics as well as demographic differences within variables to catalog how legal education has changed over time. In this blog post, we highlight the remarkably high levels of satisfaction that students have expressed about their law school experience since LSSSE’s inception.
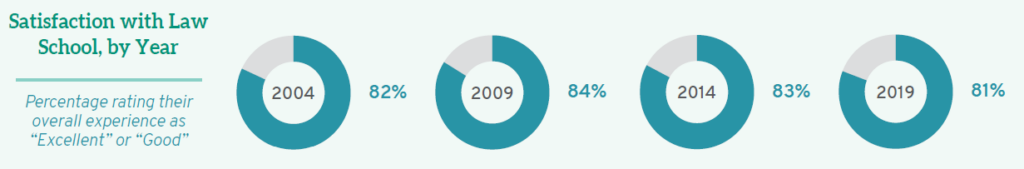
When students were asked, “How would you evaluate your entire educational experience at your law school?” over eighty percent of all law students rated their experience as at least “good” with roughly one-third of all students saying they have enjoyed an “excellent” law school experience.
If we consider student satisfaction with a number of different encounters—including academic advising, career counseling, personal counseling, and job search help—we see a consistent pattern of improvement over fifteen years. While over half (53%) of students who sought out academic support were “satisfied” or “very satisfied” with advising and planning in 2004, that number grew to almost three quarters (71%) of all students by 2019. Interestingly, there are also more students using academic advising and planning today than in years past: a full 94% of students used those services last year.
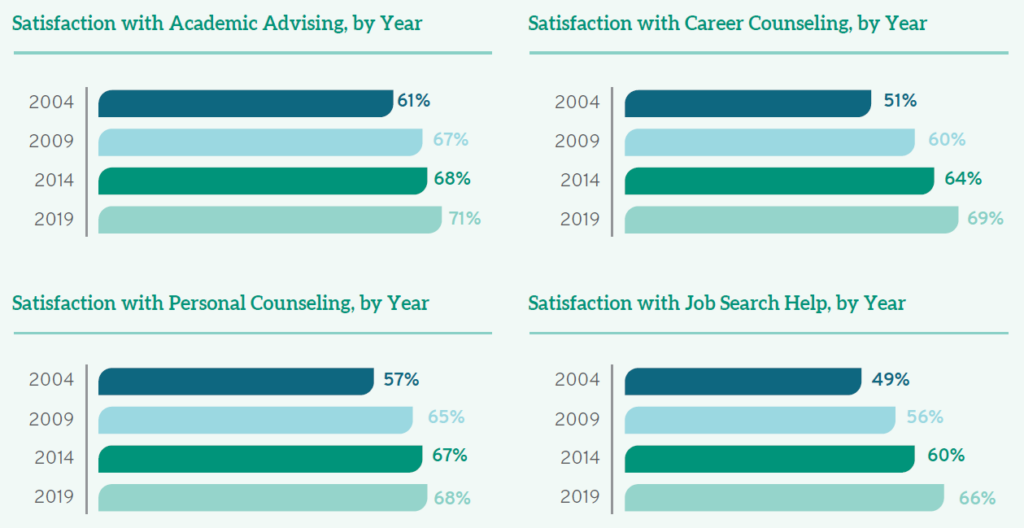
Students also appreciate how the significant investment of career counselors improves their professional prospects. While fifteen years ago, 51% of students were satisfied with career counseling (and 9.9% of these were “very satisfied), satisfaction has grown steadily over time with 60% satisfied in 2009, 64% in 2014, and a remarkable 69% satisfied in 2019 (with 22% of those noting they are “very satisfied”). As with academic advising, higher percentages of students are taking advantage of career counseling—only 8.0% of students in 2019 did not use this service (compared to 15% in 2004).
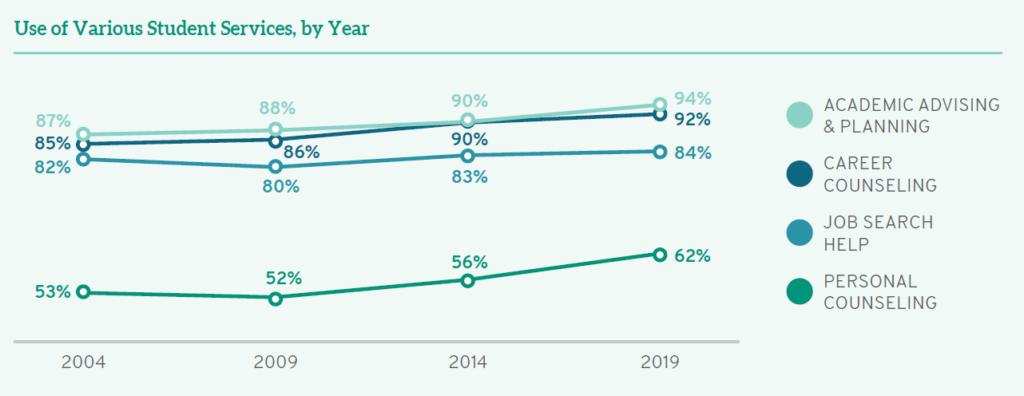
The vast majority of students sought assistance with the job search in 2004 and in subsequent years. While almost half (49%) of students were satisfied with staff efforts to provide job search help in 2004, those numbers have increased over time to 56% in 2009, 60% in 2014, and now to 66%. Although there is room for improvement, students are noticing and appreciating improvement over time.
Guest Post: Legal Education and the Illusion of Inclusion
Guest Post: Legal Education and the Illusion of Inclusion
 Shaun Ossei-Owusu
Shaun Ossei-Owusu
Presidential Assistant Professor of Law
University of Pennsylvania Carey Law School
A new semester and a potentially new political landscape are upon us. Last month law students around the country resumed coursework. Their educational pursuits are virtual, in-person, or some mix of both. No matter the format, law students continue their educational journey in an ideologically polarized pandemic society where race, class, and gender disparities are on sharp display.
Students will also be learning in a context where changes in our legal system may have direct relevance to their legal education. As is typically the case, a newly constituted Supreme Court has a diverse docket this term that might shape substantive areas of law that students take courses in, chiefly constitutional law. There will be regulatory shifts that come with new administrations. These kinds of changes will have meaning for administrative law and related areas of law: health law, environmental law, employment law, and civil rights, to name a few. COVID-19 has upended state and federal judiciary systems in ways that have still-undetermined implications for procedural courses law students take (e.g., evidence, civil procedure, criminal procedure) and access to justice issues more generally. And we know from the late Deborah Rhode’s work which communities access to justice issues tend to devastate—racial minorities, women, and other marginalized populations.
Notwithstanding future uncertainty, one thing can be said with some measure of confidence: issues of race and gender—amongst other social categories—will remain relevant inside and outside the sometimes intellectually-cordoned off walls of law schools. How these issues are integrated in the classroom, if they are at all, will affect the substantive learning of law and will either include or exclude historically marginalized groups.
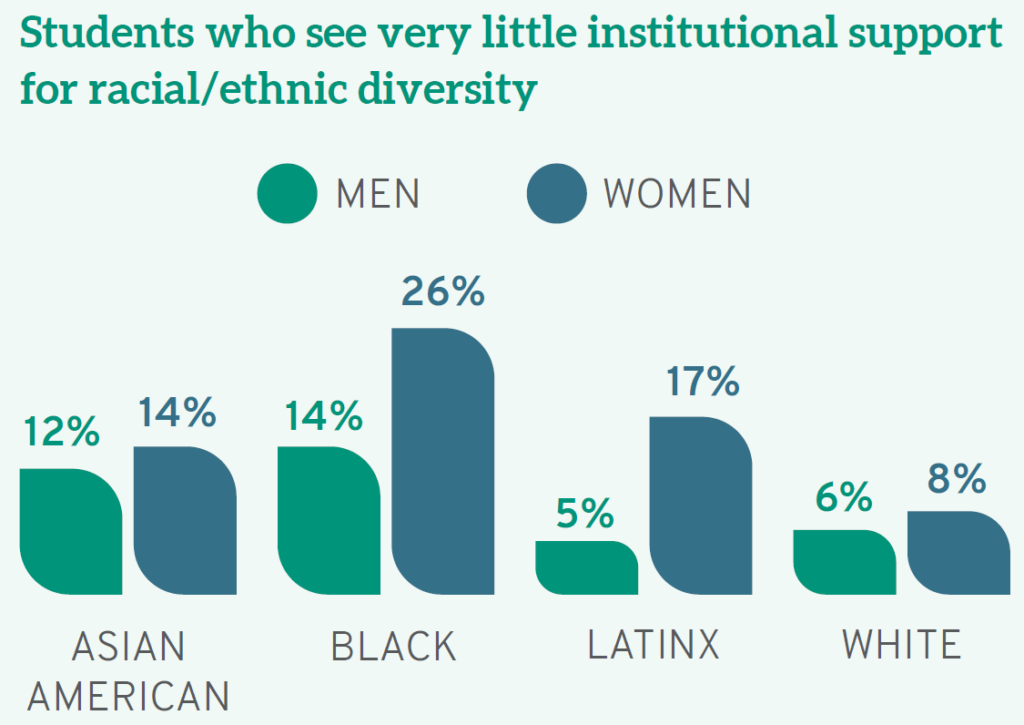
In the specific context of legal education, the results of Law School Survey of Student Engagement’s (LSSSE) Annual Survey illuminate. The Report provides a glimpse into how law schools fail to meet the aspirational goal of inclusion that often takes up primetime real estate on their websites and promotional materials. From my own read, the most jaw-dropping finding is intersectional in nature and about Black and Latinx women law students—aspiring attorneys who are often told that they do not look like lawyers when they transition to practice. 26% of Black women respondents and 17% of Latinx women respondents reported that their schools do “very little” to support racial and ethnic diversity.
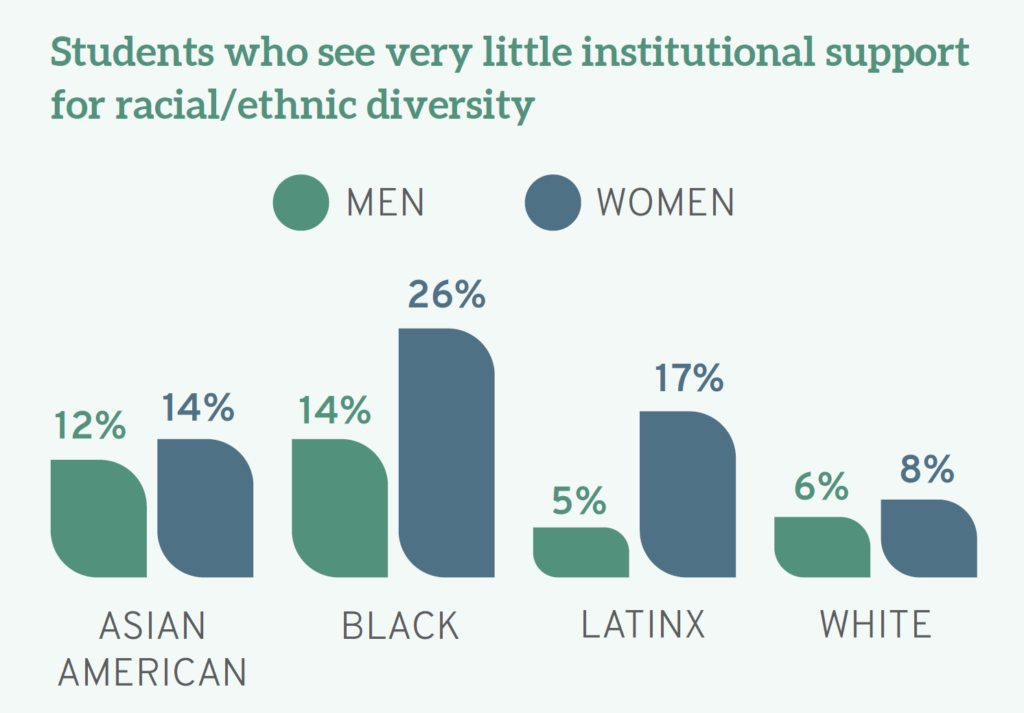
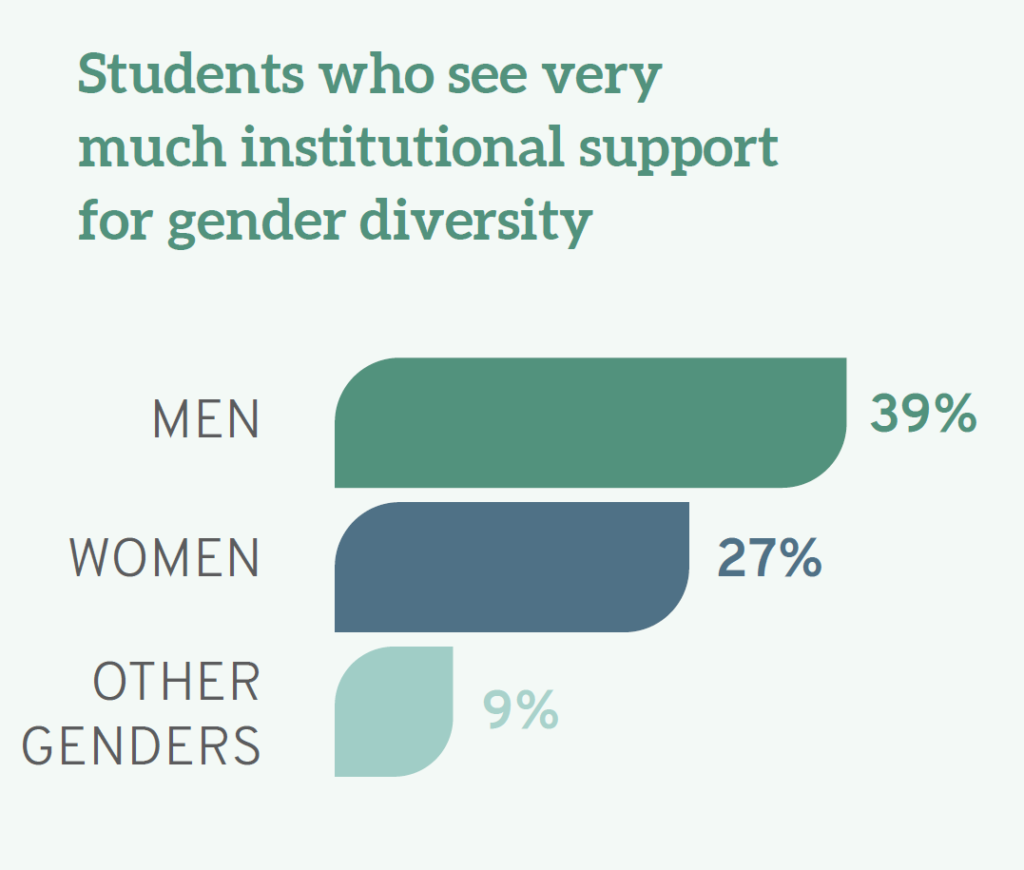
Disenchantment with the lack of support for diversity can be distilled even further. The Report notes that men varied on the issue of gender inclusivity, with 39% “very much” believing that their schools support gender diversity compared to 27% of women and 9% of individuals who identified with the “other gender” category.
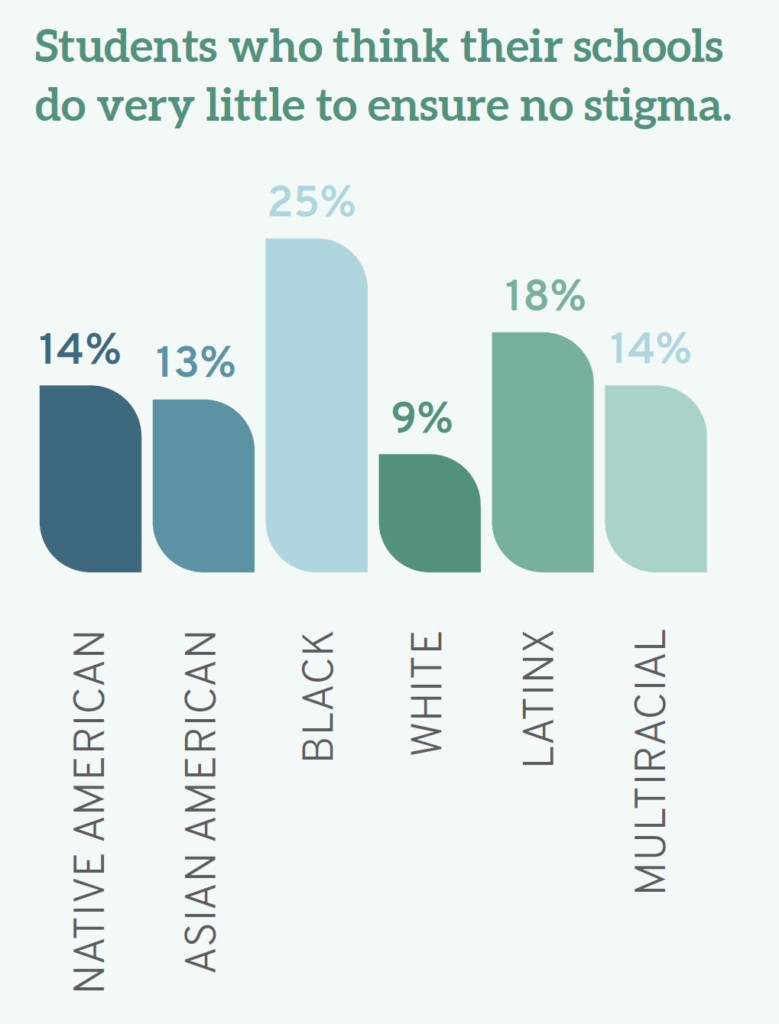
In the context of race, student views also differed, with 9% of White students, 14% of Native American students, 18% of Latinx students, and 25% of Black students believing that their schools do “very little” to ensure that students are not stigmatized based on identity.
Where sexuality and sexual orientation are concerned, 11% of heterosexual students think their schools do only “very little” to avoid identity-based stigma; conversely, 20% of gay students, 16% of lesbian students, 15% of bisexual students, and 19% of those who identify as another sexual orientation see their schools as doing “very little” in this regard. What do these findings mean for legal education and the political moment I gestured to in the beginning?
LSSSE’s data suggest that some students are dissatisfied with the six-figure education they are receiving. Put plainly, law students from backgrounds that the profession has historically excluded—women, racial minorities, LGBTQ communities, and people with disabilities in particular—do not feel part of the academic community and believe law schools are relatively disinterested in their stigmatization. In some ways, this is unsurprising, as there is a deep scholarly literature and genre of books on student disappointment with law school. Moreover, student disenchantment with legal education—which has a history of exclusion that traces back to the nativism and anti-Semitism of the early twentieth century—may in some ways be pre-determined.
The confines of the classroom, which is one of the many areas the LSSSE survey discusses, provides more insight into the inclusion-exclusion dyad. From the vantage point of some educators, law school is simply about training people to be lawyers. The most generous reading of this position suggests that social justice-like ideas like “inclusion” are too ideologically weighty to meaningfully bring in the classroom. For people who subscribe to this view, attempts at inclusion can create impossible-to-navigate landmines for professors. More skeptically, some see inclusion as an ancillary. Read in this light, the primary goal is to inculcate legal knowledge. For these professors, some things are not relevant to the practice of law and are therefore not relevant to legal education.
Such professional school-based views of legal education, vary in their reasonableness, but are held by swaths of the professoriate. Yet, there is a two-fold problem, and this is where the LSSSE survey is especially useful. First, this vision of legal education rubs up quite abrasively against the representations of law schools as bastions of inclusion. Second, this version of education, in some ways, undermines the well-touted “diversity rationale” in affirmative action jurisprudence. What does diversity mean when the subjects of diversity feel alienated?
Considering the mismatch between some students’ experiences and the stricter professional school model of legal education that some professors are beholden to, there are some options. Educators can simply be more intellectually honest about the reality that law school is a site of professionalization where inclusion principles can be trivialized. Alternatively, law schools can continue to disingenuously hitch the law school wagon to social justice rhetoric while failing to actualize inclusion as a practice. Or, in the most courageous and imaginative versions of themselves, law schools can refashion their curriculum and use developments in the legal world as opportunities to offer more inclusive learning environments.
For law schools committed to the third way, resources abound. Complaints about the need to diversify the content of law school courses have existed for decades. Scholars such as Derrick Bell and Dorothy Brown have authored casebooks that describe how race intersects with different areas of the legal curriculum, whereas feminist legal theorists, poverty researchers, scholars of law and sexuality have penned their own books, supplements, and articles that all give educational guidance on how to bring these issues into core courses, and do so in ways that are doctrinally sound. Still, some professors—many of whom have the most analytically sharp minds on their university campuses—throw their hands up in despair or continue with the same regularly scheduled program. For some of these instructors, these conversations were absent in their legal education, and they were likely not trained to incorporate these issues. Some may think it would be better to leave this work of thematic inclusion to their more expert colleagues (e.g., scholars of race, sex, class, disability) rather than wade into territory where they are sure to mess up. But throwing one's hands up in despair is increasingly a less credible course of action. The pandemic, along with the protests of 2020, have forced some people to rethink how they deliver course content, and more importantly, have made inequality a more prominent theme in our public discourse. The current socio-political moment, and the reality of pandemic pedagogy, call for curricular redesign.
Fortunately, the tools to make the classroom more inclusive are available and they are not limited to the usual courses. To be sure, law professors have written about how first-year courses like criminal law and property are inattentive to inequality in ways that produce the responses found in the LSSSE survey and have offered suggestions on how those same courses could easily be improved. But attempts to diversify and create a more inclusive curriculum are not confined to these foreseeable areas of law but can be found in more unsuspecting places like evidence, corporate law, trust and estates, and intellectual property, to name a few.
Law professors have also identified space in the curriculum for trans-substantive engagement with the kinds of questions and perspectives that demonstrate an awareness of inequality, both in legal education and in law more generally. Indeed, I, along with my colleague Karen Tani, have taken on the task of trying to simultaneously create an inclusive learning environment that rigorously addresses inequality by creating a 50-person Law and Inequality course at Penn Law. This endeavor and more meaningful engagements with diversity need not be limited to women, racial minorities, and sexual minorities. Inclusion also implicates and has meaning for the larger law student population. One of the most understated findings in the LSSSE Report is that 16 percent of white students believed law schools placed “very little” emphasis on issues of equity and privilege and do not prioritize providing students with the skills necessary to confront discrimination and harassment.
My purpose here is not to proselytize teaching a course like the one we are offering. Instead, I want to highlight how student dissatisfaction with inclusion, which the Report highlights in detailed and accessible fashion, can be situated within this critical juncture. 2021 is a unique moment where law schools can reimagine legal education in real time, and for a post-pandemic world. This will not be easy, as this is a stressful time for faculty—some of whom are in high-risk groups during the pandemic and/or have a variety of care obligations. COVID-19 has upended a lot of assumptions and forced people to change longstanding pedagogical practices. Institutions could do a lot of good by encouraging faculty reflection and supporting creative reorganization of current courses.
The LSSSE Report tells us that in many ways, law schools are failing to provide the inclusive educational spaces that they, I believe in good faith, want to offer and that students of various backgrounds actively desire. Ultimately, the teaching tools are available, the moment is ripe, and the only outstanding question is whether legal educators will make the changes necessary so that the next LSSSE survey offers more optimistic findings.
Annual Results 2020 Diversity & Exclusion: Institutional Support for Diversity
This year for the first time, LSSSE introduced a set of questions focused on diversity and inclusion that supplement related questions from the primary survey. The Diversity and Inclusiveness Module examines environments, processes, and activities that reflect the engagement and validation of cultural diversity and promote greater understanding of societal differences. The 2020 LSSSE Annual Results Diversity & Exclusion report presents data about how diversity in law school can prepare students for the effective practice of law upon graduation. In our next three posts, we will highlight key findings from the report and suggest some areas for improvement.
Support for diversity in law school must begin with the institution. Yet many students of color do not see their campus as supportive of racial/ethnic differences. Almost a quarter (23%) of Black law students nationwide say their schools do "very little" to create a supportive environment for race/ethnicity, compared to just 6.8% of White students. At the opposite end of the spectrum, 32% of White students believe their schools do "very much" to support racial/ethnic diversity, compared to only 18% of their Black classmates. Men (37%) are also more likely than women (26%) and those of another gender identity (7.5%) to believe their campus is very supportive of racial/ethnic diversity. Even more dramatic are intersectional identity findings, as a full 26% of Black women— more than any other raceXgender group—see their schools doing "very little" to create an environment that is supportive of different racial/ethnic identities, as compared to just 5.5% of White men (while 72% of White men believe their schools do "quite a bit" or "very much" in this arena).
Men are also more likely to see their campus as a "supportive environment for gender diversity," with 39% believing this "very much" as opposed to 27% of women students, and only 9% of students who identify as another gender identity. Furthermore, White students as a whole (33%) see the campus as very supportive of people of different genders, compared to 21% of Native Americans and Black students. Again, the views of White male students differ significantly from most others with a full 40% seeing their campus as very supportive of gender difference. In short, women as well as others from less privileged groups do not see their schools as particularly supportive of gender inclusivity.
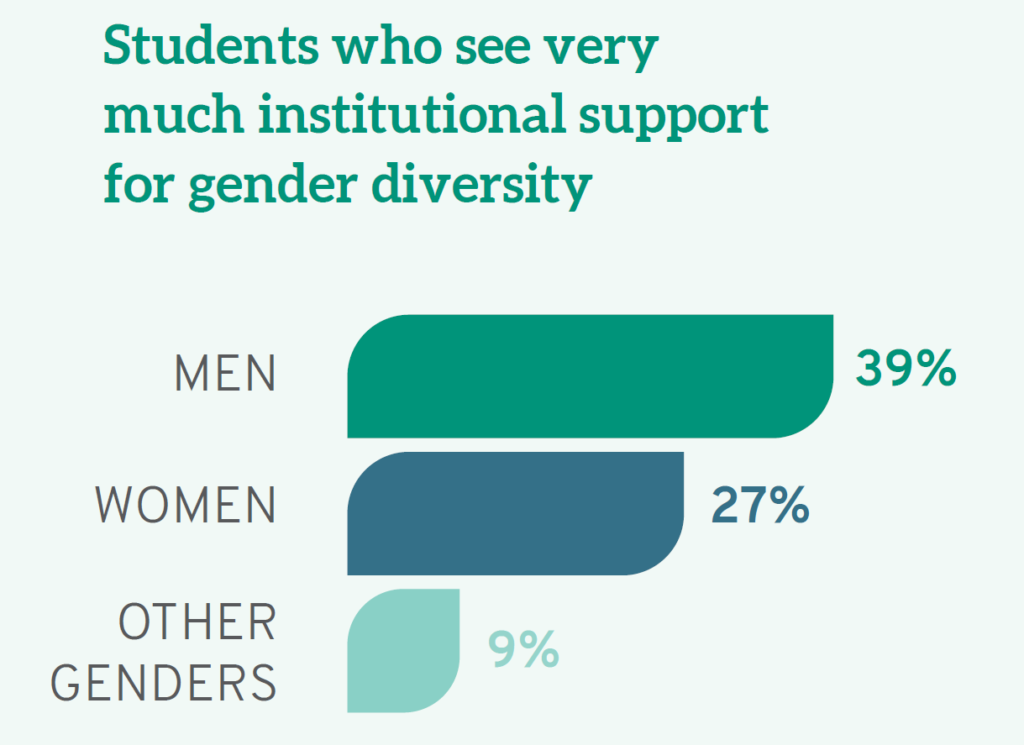
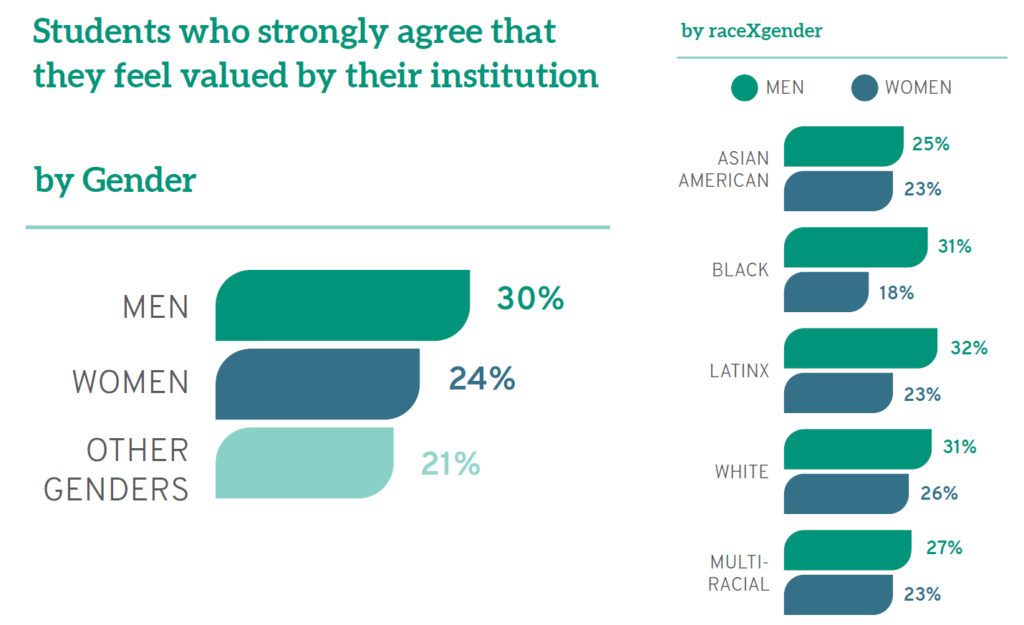
Not surprisingly, given the relative lack of support they see for racial/ethnic and gender diversity on campus, women and students of color also believe their schools are less invested in them as individuals. When asked whether they "feel valued" by their law school, a full 30% of men "strongly agree" compared to only 24% of women and 21% of those who identify as neither male or female. Similarly, the racial/ethnic group most likely to "strongly agree" is Whites (28%). In fact, while Latinos, White men, and Black men "strongly agree" that they are valued at roughly equal rates, men feeling more valued than women is consistent across every racial/ethnic group. Furthermore, students who are the first in their families to earn a college degree, often called "first-gen" students, feel less valued by their institution: a full third (33%) note they do not feel valued, compared to a quarter (25%) of others, which is also a significant proportion of law students overall.
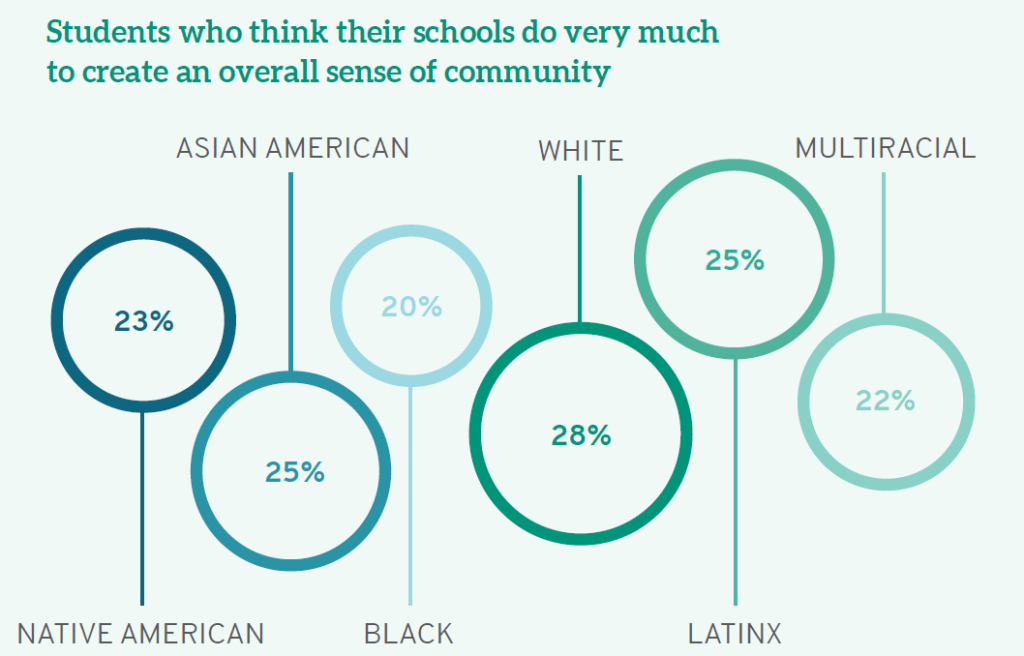
Institutions can put mechanisms in place to foster community among those on campus, regardless of their background or experiences. Finding this common ground helps all students understand that they belong and that others who may be different should be equally welcome. Again, White students are most likely to believe their institution emphasizes the importance of "creating an overall sense of community among students." While 28% of White students think their schools do this "very much," smaller percentages of students of color feel similarly. Even more disheartening, 18% of Black students and 14% of Latinx students think their schools do "very little" to foster community.
Many law schools have made concerted efforts to add student diversity to their campuses. But once students enroll, we owe it to them to provide a safe and welcoming environment, one where they feel valued, where they can be themselves, where they acquire the tools they need to succeed in the workplace, and where they can thrive. Admitting and even enrolling more students of color, first-gen students, students who identify as LGBTQ, and women is not enough unless that diversity is accompanied by inclusion. Law schools that want their students to succeed as future lawyers and leaders must commit to fostering a campus community where the most vulnerable and non-traditional are encouraged to reach their full potential, where faculty are expected to train students not only for the global marketplace but for the realities of American life, and where all students appreciate their own backgrounds, biases, and responsibilities to the profession.