Guest Post: The Normative and Legal Case For Affirmative Action Programs for the Descendants of Persons Enslaved In America

Guest Post: The Normative and Legal Case For Affirmative Action Programs for the Descendants of Persons Enslaved In America
Erika K. Wilson
Professor of Law, Wade Edwards Distinguished Scholar, and Director of the Critical Race Lawyering Civil Rights Clinic
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
The Supreme Court’s recent decision in Students for Fair Admissions, Inc. v. President & Fellows of Harvard Coll., 143 S. Ct. 2141 (2023) arguably ended race-conscious admissions policies as we know them. While the Court did not expressly overrule diversity as a compelling state interest, it did find that the way in which Harvard and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill were using race to achieve diversity was unconstitutional. The majority opinion observed that universities undermined their stated interest in obtaining a racially diverse class by relying upon “opaque racial categories.” It identified as particularly problematic categorizing all Asian applicants together with no distinctions made between South and East Asians; the arbitrariness of the Hispanic categorization; and the under inclusiveness of the Middle Eastern classification. Justice Gorsuch’s concurring opinion made a similar observation with respect to the categorization of Black students:
The “Black or African American” category covers everyone from a descendant of enslaved persons who grew up poor in the rural south, to a first-generation child of wealthy Nigerian immigrants, to a Black-identifying applicant with multi-racial ancestry whose family lives in a typical American suburb.
Gorsuch’s critique is salient because the original purpose of race-conscious affirmative action programs was to remediate the multi-generational effects of slavery and the afterlives of slavery. Yet, as documented by legal scholars like Angela Onwuachi-Willig, in the early 2000s Black students at elite universities were overwhelmingly mixed-race students, or first- or second-generation Black Americans, meaning their parents and/or grandparents were immigrants. Lani Guinier and Henry Gates raised concerns in 2004 because only one-third of Harvard’s Black undergraduate students were from families in which all four grandparents were born in America, descendants of persons enslaved in America.
Recent research by Kevin Brown and Kenneth Dau-Schmidt relying on LSSSE Survey data shows that not much has changed since the early 2000s. Similar patterns of disproportionate representation of what Brown and Dau-Schmidt call “ascendant Blacks” (those with two American-born Black (non-biracial) parents) exists in law school enrollment today. The data show three noteworthy trends:
First, while structural racism impacts all Black people in America, it impacts some groups more acutely. As they write in their article, ascendant Black law students have lower average family incomes, higher poverty rates, and are less likely to have parents with a college degree.
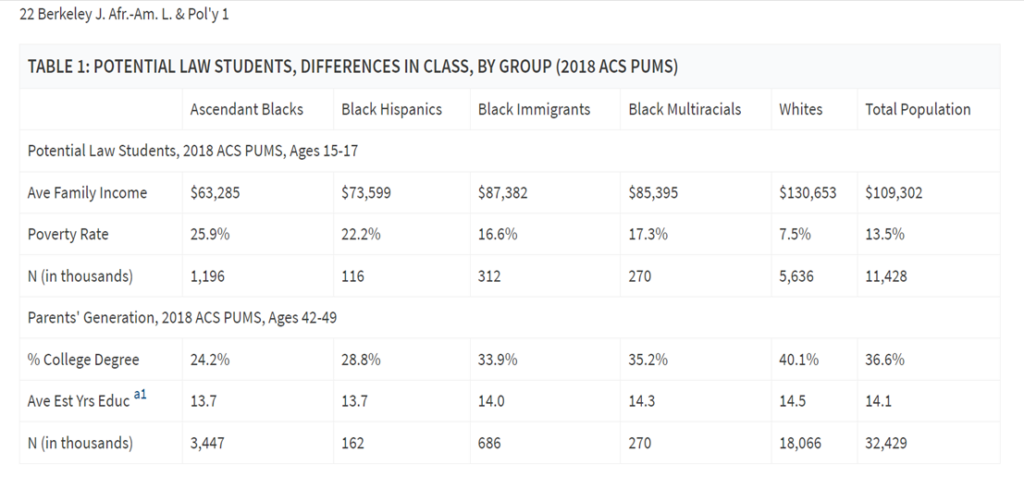
Second, all Black people, except Black Immigrants (defined as Black people with at least one parent not born in America), are underrepresented among law students; furthermore, the extent of underrepresentation is much worse for ascendant Black law students than for other Black law students.
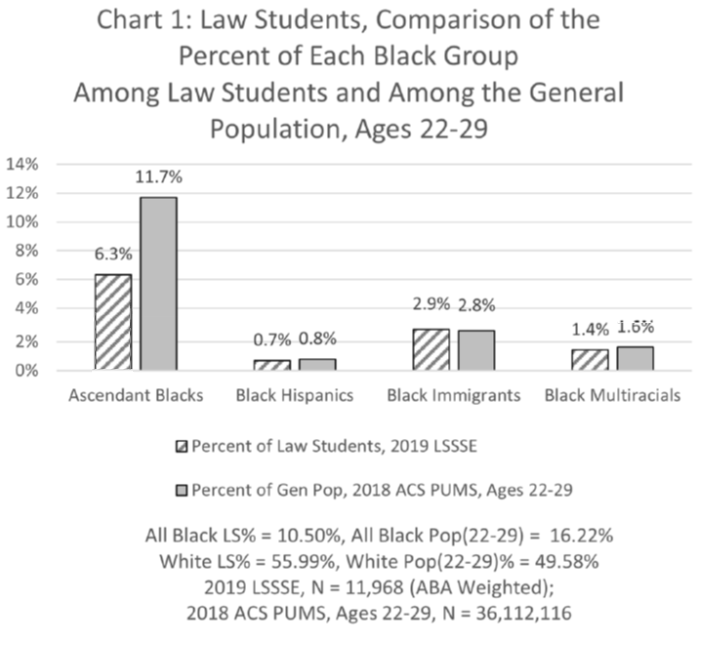
Third, ascendant Black law students are underrepresented at Top 50 law schools relative to their representation within the population of Black people in America, and relative to all other groups of Black law students.
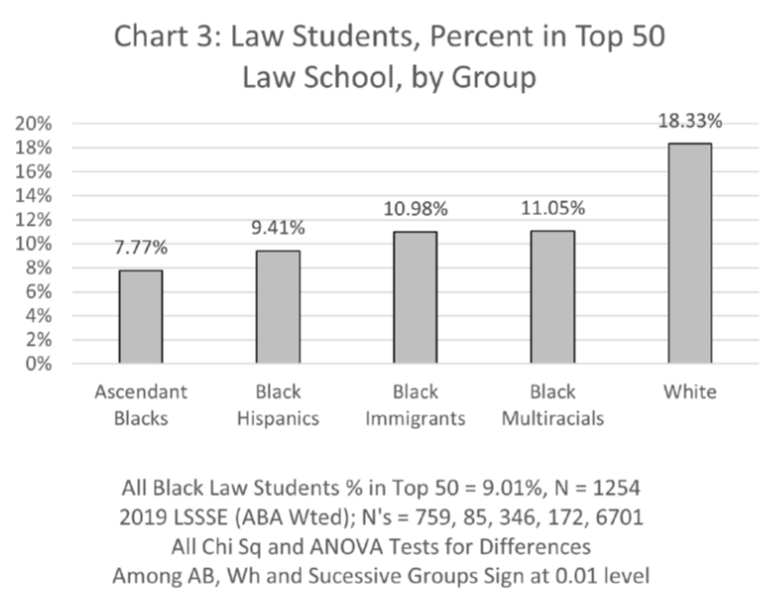
The data and their implications should inform the path universities take to reinvent their affirmative action programs. Diversity is still recognized as a compelling state interest. Universities can and should fashion admissions programs that seek to increase representation of Black students who are the descendants of persons enslaved in America. To be sure, they should also continue to make efforts to increase representation of all Black groups because race remains a salient and undeniable barrier for all Black people in America. Yet the unique burdens and history of subordination linked directly to American slavery imposes a special remedial obligation on universities to provide access to Black students who are the descendants of persons enslaved in America. This is especially true for elite universities such as Harvard and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill that directly benefited from slavery.
In Justice Clarence Thomas’ concurring opinion in Students for Fair Admissions, he offers a potential Constitutional path for doing so. He suggests that a classification consisting of descendants of persons enslaved in America is not a racial category. He contends that:
[The 1866 Freedmen’s Bureau Act ] applied to freedmen (and refugees), a formally race-neutral category, not [B]lacks writ large. And, because “not all [B]lacks in the United States were former slaves,” “ ‘freedman’ ” was a decidedly underinclusive proxy for race.
His comments, as other scholars have noted, raise questions as to the legality of an affirmative action program centered on descendants of persons formerly enslaved in America, as such a categorization may not be subject to the same level of heightened scrutiny as a race-based classification. Nonetheless, Thomas’ assertion that “freedmen” was not a racial categorization is admittedly dubious. But such a targeted program might also be justified under the remedial justification for race conscious policies. Thus, universities should take Thomas seriously. They should fashion admissions programs aimed at increasing the representation of Black students who are the descendants of persons enslaved in America. LSSSE data and history demonstrate the normative case for doing so.
A CRT Assessment of Law Student Needs
 Meera E Deo, JD, PhD
Meera E Deo, JD, PhD
The Honorable Vaino Spencer Professor of Law, Southwestern Law School
Director, Law School Survey of Student Engagement (LSSSE)
For over a century, American policy makers have recognized the need to provide personal support to students in primary and secondary school. Many states, including California, offer free or reduced lunch to students in need. Nurses and counselors are often available on campus to provide medical attention, academic guidance, and mental health support. Despite our clear understanding of the importance of these structures of support for children in the K-12 educational system, there are few mechanisms to support students in higher education. Yet many students in college, graduate school, and professional school also struggle to meet their basic needs.
In my new article, “A CRT Assessment of Law Student Needs,” and the accompanying Fact Sheet, I seek to convince policymakers that law students also need both administrative and legislative support to help them survive and thrive academically as well as professionally. LSSSE data show law students have been struggling to recover from the heightened challenges they endured during the early years of the pandemic. Struggles with food insecurity, financial anxiety, and emotional strain contribute to declining academic success, particularly for populations that were marginalized on law school campuses long before COVID. Legislative support is necessary to support students through this era so they can maximize their full potential.
Applying a CRT Framework
When we consider the CRT tenets of intersectionality and the compound effects resulting from those with devalued raceXgender characteristics specifically, it becomes evident that women of color law students are particularly at risk of falling behind or leaving law school altogether without greater support. The CRT concept of praxis further urges scholars to not only theorize about challenges and opportunities, but to put proposals into practice to achieve real change. Merging empirical methods with CRT, a new model of eCRT scholars “seek to rethink and change the premise of race scholarship in general by eschewing theoretical and methodological silos in pursuit of deepening our understanding of race and racism to advance racial justice.” Here, LSSSE data coupled with CRT theories are particularly instructive.
LSSSE Findings on Law Student Needs
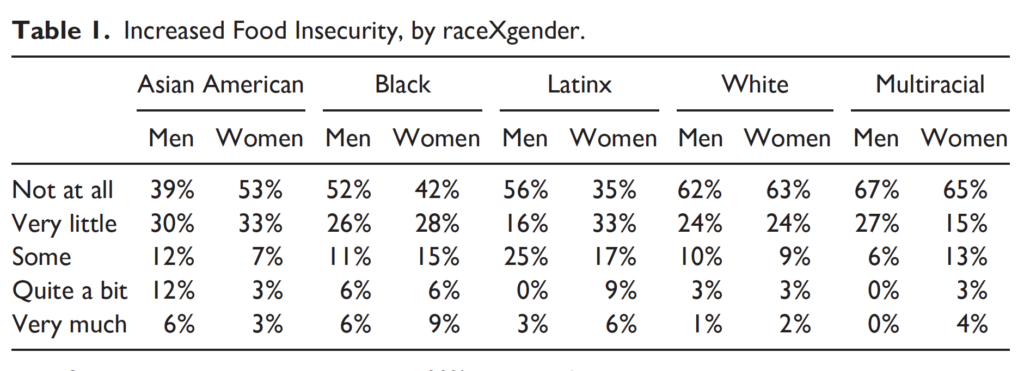
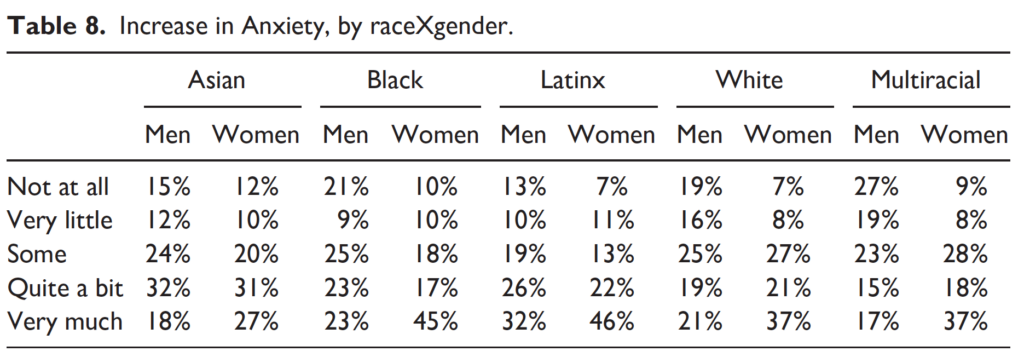
In 2021, LSSSE asked students about their experiences Coping with COVID. What they shared remains deeply disturbing, and even more so when we consider raceXgender effects. Women of color suffered with high levels of food insecurity—including 58% of Black women and 65% of Latinas who had increased concerns about whether they had enough food to eat.
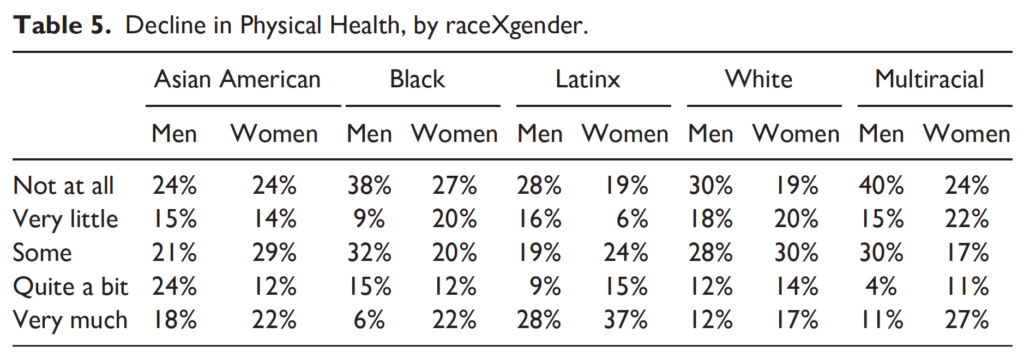
Students also reported declines in their physical health. For every racial group, higher percentages of women than men noted these declines—including 81% of Latinas (and 72% of Latino men).
Most students also managed depression (85%) and anxiety (87%) that interfered with daily functioning—again, with marked raceXgender effects that bear out the CRT literature. For instance, while 73%–81% of white men, Black men, and multiracial men reported increased anxiety, a full 93% of white women, 90% of Black women, and 91% of multiracial women experienced the same.
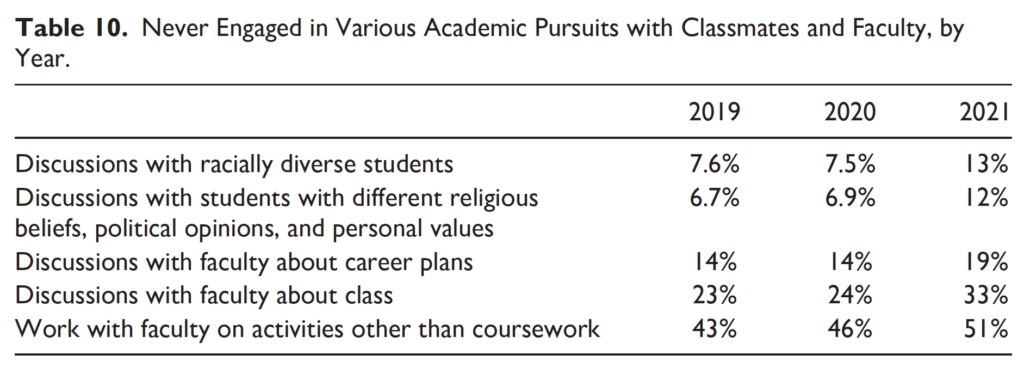
Struggles to meet their basic needs resulted in numerous missed opportunities for interaction with classmates and professors. One out of every five student respondents to the 2021 LSSSE survey (19%) never spoke with professors or other advisors about career plans or their job search. One third (33%) never discussed ideas from readings or classes with faculty members outside of class. There were also fewer opportunities for students to work with faculty on activities other than coursework (including committees, orientation, and student life activities); a full 51% of students never worked with faculty on these projects outside of class. Unsurprisingly, given all of these struggles, students also reported decreases in academic success, with women from most racial groups suffering more than men.

Institutional and Legislative Support
Most institutions already have a foundation to support students. But we can do better. In “A CRT Assessment of Law Student Needs,” I propose numerous options for administrators and policymakers to consider. For instance, while many campuses have food pantries to combat food insecurity, they should go beyond a locked room full of cans to prioritize accessibility by being open long hours or 24 hours, without an appointment or sign-in requirement, and on various parts of campus (not just one location that may be difficult for law students to access). Drawing from the CRT literature, food pantries should stock not only canned goods but also gift cards so students from varying backgrounds can purchase traditional or ethnic foods and fresh fruits and vegetables, and otherwise have agency over their food consumption.
Given increases in student anxiety and depression, law schools also should make mental health counseling available—with a focus on quality and accessibility for vulnerable populations. Counseling sessions should be free or low cost, with appointments scheduled via phone or through the click of a button, and meetings available both in person and online, as telehealth enables students of color—who rarely have on-site counseling available from professionals of their racial or cultural background—to connect online with counselors who work better for them.
Beyond institutional support, law students need legislative support. This is why the article includes an accompanying Fact Sheet—to make clear through brief bullet points and visualizations what the challenges are and how policymakers can help. Legislators could immediately reduce food insecurity by permanently expanding Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) benefits to law students—without requiring them to work 20 hours per week or prove they care for dependents. Both the EATS Act and the Student Food Security Act provide pathways for SNAP expansion and extension; they are currently pending before Congress and should be strongly supported. California recently passed legislation expanding CalFresh (the state SNAP program) to those enrolled in institutions of higher education at least half-time. Other states should follow suit. Similarly, legislation should ensure mental health care is covered in standard insurance policies that tend to focus on physical health. Legislation could also offer financial assistance to institutions providing integrated mental health counseling for free or low-cost to law students. Additional legislative support could offer rental assistance, loan forgiveness, emergency funds, and other resources to law students in need.
Conclusion
Together, administrators and legislators can work to combat barriers facing law students that have intensified as a result of COVID. Once their basic needs are met, students can turn to maximizing their academic and professional success. Part of student success involves effectively and enthusiastically engaging in the intangibles of legal education, drawing from their own experiences and backgrounds to share and learn from classmates and faculty. When students are overcome by anxiety, depression, and loneliness, it is impossible to perform at their best.
Better than BIPOC
 Meera E Deo, JD, PhD
Meera E Deo, JD, PhD
The Honorable Vaino Spencer Professor of Law, Southwestern Law School
Director, Law School Survey of Student Engagement (LSSSE)
We should be precise with our language, especially when talking about race. In “Better than BIPOC,” I argue that BIPOC is a flawed term for empirical scholars to use, one that prioritizes historical oppression over ongoing realities and relies on virtue signaling rather than working toward meaningful change. In my previous essay “Why BIPOC Fails,” I explain how BIPOC can be misleading, confusing, and contribute to the invisibility of the very groups that should be centered in particular contexts. Thus, without the deep investment of community engagement and review, new labels—like BIPOC—run the risk of causing more harm than good. Instead, we should continue to use the term “people of color” when referencing this group in comparison to whites, while “women of color” is useful when considering raceXgender intersectionality. Banding together for mutual support and action has been critical for people from marginalized identities as they have worked toward lasting social change. Additionally, it is often important to disaggregate data to report on individual groups that could otherwise get lost under these larger umbrella terms.
The experiences of various communities in law school help illustrate the point that academics, advocates, and allies should use be careful in their language usage—especially when dealing with data. Grouping populations together is often instructive. It can also be necessary to disaggregate the data to deal with separate communities individually. Law student debt and experiences with issues of diversity are particularly instructive in explaining both paths.
First, LSSSE data reveal that students of color carry more educational debt than white students. Here, it is appropriate and useful to group students of color together as a whole in comparing them with white students in terms of their overall debt loads. However, we can dig deeper to consider the intersectional experience of gender combined with race. If we ignore gender in this context, we run the risk of masking the distinct experiences of women of color compared with men of color as well as other groups. And there are differences. As I write in the article, “[H]igher percentages of Women of Color (23%) graduate with over $160,000 in law school debt, as compared with Men of Color (18%), white women (15%), and white men (12%).” While examining debt by raceXgender is thus more useful than considering race alone, being even more precise with the data and our language provides an opportunity to reveal more nuanced realities for communities within the women of color umbrella. As we share in our 2019 LSSSE Annual Report, The Cost of Women’s Success, the raceXgender groups most likely to carry the highest debt loads of over $200,000 are Latinas (16%) and Black women (14%), compared to lower percentages of Asian American women (7.7%), Black men (7.3%), Latino men (12%), and white men (4.3%). Thus, while it is correct to talk about the people of color and women of color carrying more debt than whites and those who are not women of color, it is more complete and sophisticated to explain how particular raceXgender groups—Black women and Latinas—have the highest debt loads of all. Precise racial language is instructive, particularly if we seek to craft solutions to ameliorate these challenges that are directly responsive to the needs of the populations affected.
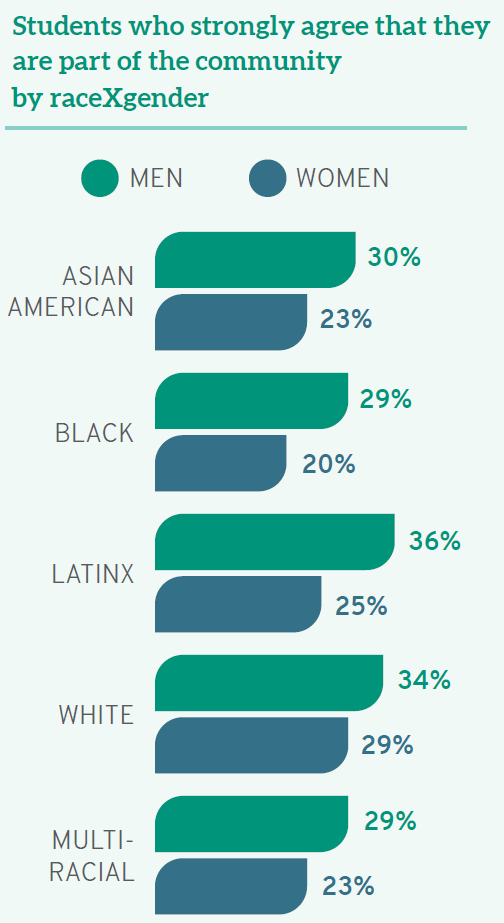
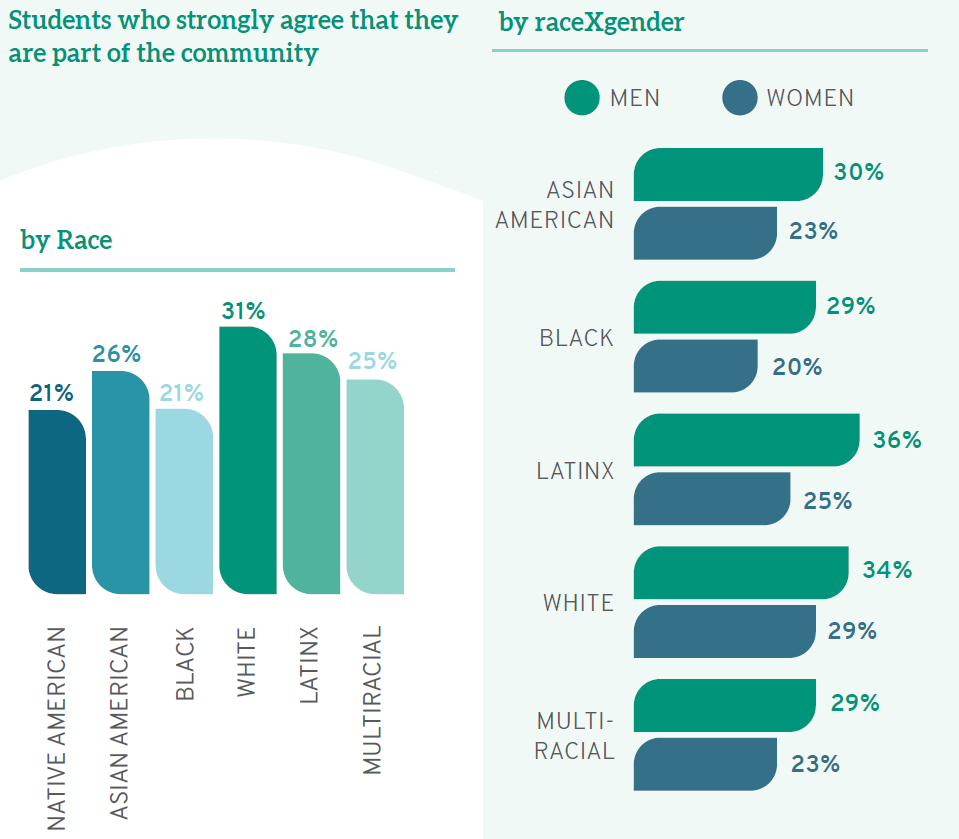
Student experiences with diversity provide another example of the benefits of careful language usage. Compared to their white peers, students of color have distinct opinions and experiences in law school when considering issues of diversity, equity, and inclusion. For example, although almost one-third (31%) of white law students “strongly agree” that they see themselves as part of the law school community, students of color are less likely to agree. As with debt levels, there are again additional distinctions based on raceXgender. In Better than BIPOC, I draw on data from the LSSSE 2020 Annual Report, Diversity & Exclusion, noting, “Fewer than one-quarter (23%) of women of color ‘strongly agree’ that they are part of the institutional community, compared to almost one-third (31%) of men of color.” Thus, distinctions based on race alone are not as precise as those disaggregating racial data by gender. In certain contexts, we also can—and should—go further still. By looking within the category of people of color, we can determine important differences between groups that administrators, faculty, and staff should consider in order to tailor solutions to the students who most need them. For instance, when we consider student belonging, “only 21% of Native American and Black law students see themselves as part of their law school community—compared to 31% of their white classmates, 25% of multiracial students, 26% of Asian Americans, and 28% of Latinx students.” Considering the student of color narrative as one group would tell an incomplete story as Black and Native law students are even more alienated nationally than even other students of color. Addressing their concerns will require us first to understand them, then to act.
Better than BIPOC also draws from the data behind my book project, Unequal Profession: Race and Gender in Legal Academia, to share examples from the law faculty context. I use findings on student evaluations and the challenges different populations face while navigating work/life balance to suggest when we should compare faculty of color as a whole to their white colleagues, when to disaggregate by race as well as gender to examine the experience of women of color faculty, and when to look more carefully within racial and gender-based categories to reveal important distinctions that could otherwise be hidden. Beyond the context of legal education, we can apply this thesis to frameworks as diverse as political engagement, workplace harassment, elementary school integration, diversity in corporate boards, and more. Different situations will naturally call for specific groups to be named and studied directly; that context, regardless of the terms currently en vogue, should drive the data used and arguments made in any endeavor. Working collectively serves a purpose, as does disaggregating the data. Through both efforts, we can understand the unique challenges facing different groups and work collectively to address them.
Guest Post: The Importance of Supporting First-Generation Law Students
 Melissa A. Hale
Melissa A. Hale
Director of Learning for Legal Education
Law School Admission Council
Today is First-Generation Student Day[1]! So, to celebrate, I want to talk about why we should support first-generation law students, and how we can do that.
Who are first-gen students? Although definitions vary and self-identification is important, a first-generation student is typically one whose parents or legal guardians have not completed bachelor’s degrees [2]. First-generation students are an important part of diversity, equity, and inclusion. However these students are often overlooked when discussing DEI goals. In fact, when I started law school[3], I’m not even sure the term “first-generation student” was being used, or if it was in some circles, students certainly weren’t recognizing the term or identifying as “first-gen” the way they are now.
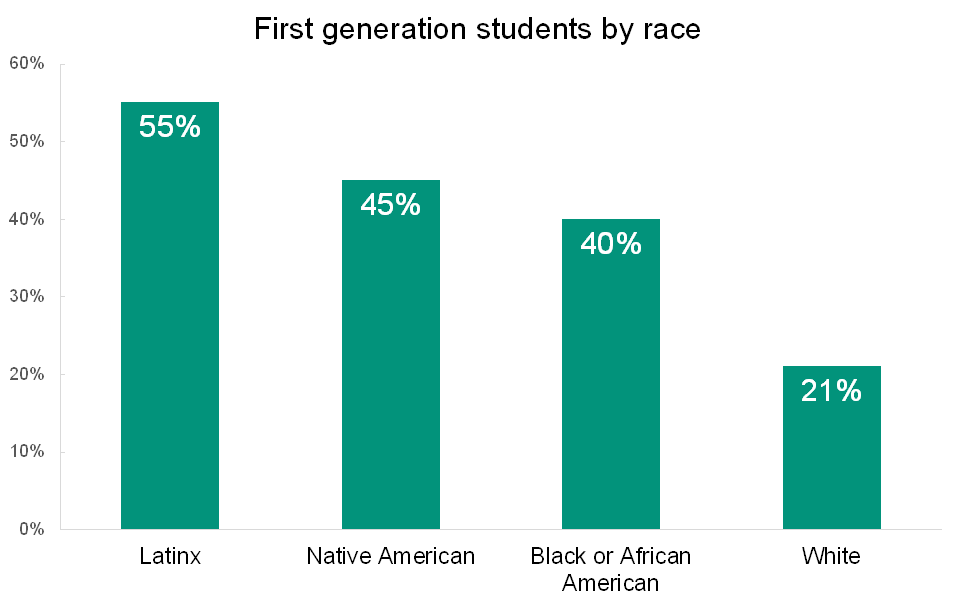
It’s certainly progress that we, as educators and researchers, are recognizing this group of students, but that’s not enough. We need to do more. Especially because there is significant intersectionality between first-generation students and historically underrepresented BIPOC students, including students of color and students from a lower socioeconomic status. According to the Law School Survey of Student Engagement (LSSSE), 29% of law students are first-generation. Students of color are more likely than their white classmates to be first-generation. More than half of all Latinx students, 45% of Native American students, and 40% of Black or African American students are first-generation.
What Makes First-Generation Students Different?
So why does this matter and why is this group different? Well, first-generation law students often come to law school with fewer resources than their peers, including a lack of social capital. Most importantly, they also come to law school bearing an “achievement gap.” The “achievement gap” refers to the disparity in academic performance – grades, standardized-test scores, dropout rates, college-completion rates, even course selection and long-term success– between groups of students. In this instance, we are referring to the gap between students who have had parents complete some form of higher education (“continuing-generation students”) and those that have not. The Close the Gap Foundation refers to this as “the opportunity gap” instead of the achievement gap, and specifically states that it is “the way that uncontrollable life factors like race, language, economic, and family situations can contribute to lower rates of success in educational achievement, career prospects, and other life aspirations.”[4]
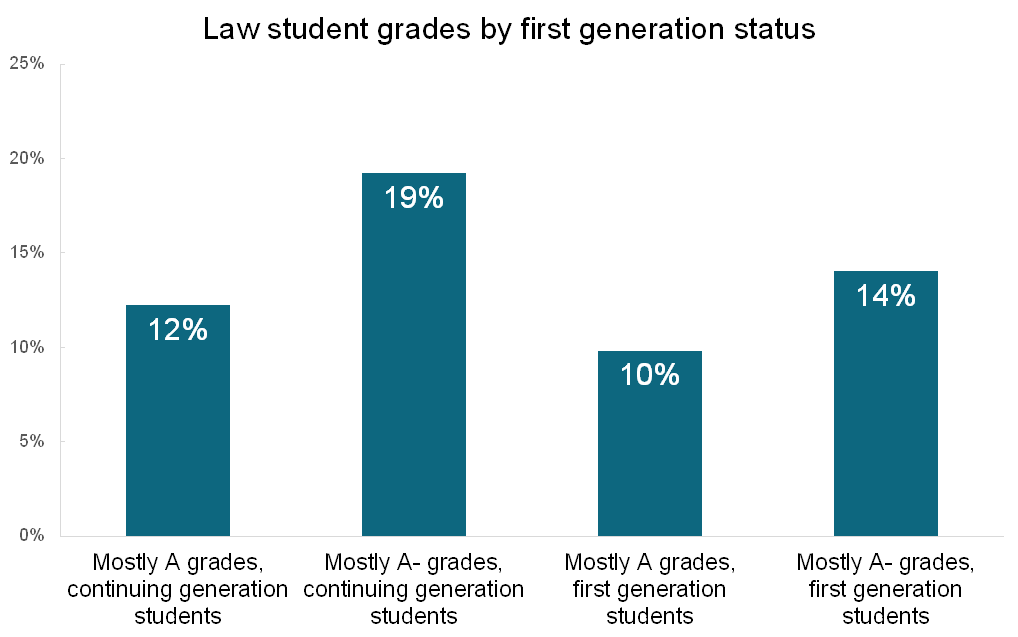
This gap becomes obvious when you look at the data. In the 2021 LSSSE survey, 31% of continuing generation students earned a A- or higher. For first-generation students that number was only 24%. While this might not seem like a staggering gap, without networking and family connections, first-generation students have to rely more heavily on grades for job prospects, so that gap can make a significant difference to their future.[5]
As for social capital, in all professions and cultures there are unwritten rules and norms, generally learned from observing others or knowing people in the culture or profession. Essentially these are not rules you learn about in any explicit way. There is no way for students to study up on these rules, no matter how diligent or well-prepared they are, because they are acquired only through experience. While incoming law students start to pick up on some of these rules during their undergraduate programs, there are still huge gaps where law school and the legal profession are concerned.
Finally, it is far more likely that first-generation students will be providing care for a dependent, either a parent or a child. In fact, 11.3% of first-generation students care for a dependent more than 35 hours per week, as compared to only 5.2% of continuing-generation students.[6] In addition, first-generation students typically end up working more hours, either in legal or non-legal jobs, than their continuing-generation counterparts.
Taken all together, this means that most first-generation students come to law school with considerable hurdles: lower access to finances, lower social capital (i.e., fewer networking connections), lack of exposure to professional norms, and finally, hurdles related to academic preparation, especially when so much of the language used in law school might be brand new to them. And first-generation students themselves know this, coming to law school with concerns surrounding academic success, their career path, building a professional network, finances and family obligations.[7]
What Can We Do?
As legal educators we can do so much. And this starts at the point of admissions. Today, I’m speaking on a panel at LexCon ’22[8] called "Empowering First-Gen Students Through Your Schools' 'Hidden Curriculum,'" along with Morgan Cutright of AccessLex, Teria Thornton, and Susan Landrum, Dean of Students at Illinois College of Law.
Our panel is discussing ways to support first-generation students through the admissions process, navigating financial aid, and finally with academic support once they enter law school. The first step is having these discussions because we often don’t realize the challenges that first-generation students face or what resources they might lack. This is an opportunity for student facing law school professionals – student services, academic support, financial aid, admissions, career services and other administrators – to think through what information we take for granted and then how to make the transition for students a bit easier and more welcoming. For example, even recognizing that many choices they make might be based around financial considerations and scholarships, or staying close to family. Or that purchasing books so that they can read the first class assignment might prove difficult if financial aid checks aren’t distributed before classes begin. Another challenge might be career services assuming that all students have interview appropriate clothes to wear, or can afford such clothes. Some schools have set up interviewing closets where professors and alumni donate old suits for students.
Beyond conversation, at the point of admission, schools can also provide students with a wealth of resources that will help them feel like they belong in law school, and reinforce the message that law school is difficult for all -- not just them. We know that a sense of belonging is linked to positive academic outcomes, such as increased engagement, intent to persist, and achievement[9] However, first-generation students report less belonging, which then increases the achievement gap mentioned above. In addition, students who don’t feel they belong also find it much more difficult to persist in the face of struggle, or even reach out for assistance.
As an example of how we can address a sense of lack of belonging, I used to send incoming students a “law school glossary” upon admissions. It was fairly simple, only a few pages of common words that we tend to use. This was sent to all students, not just first-gen, because some of the terms we use on a daily basis are mystifying to anyone who is new to the study of law. For example, what is a “1L” or what on earth is “K” or “Civ pro”? Abbreviations and acronyms can be just as daunting, and alienating, as the Latin often used.
Because first-generation students often assume that everyone else knows things that they don’t, they might hesitate to ask what are perfectly reasonable questions. Providing them with a quick list of frequently used terms is a great way to decrease feelings of uncertainty. This glossary turned into a book – The First Generation’s Guide to Law School[10] – which was essentially the memo I wish I had received before I started law school. I couldn’t cover everything, but tried to cover most of the unwritten rules surrounding law school, as well as the core academic skills needed to thrive. I wanted to make sure that students could go into their first week of classes feeling confident.
In addition, there are many summer bridge programs that exist. I’m currently working on such a program for the Law School Admission Council (LSAC), and it will be available in the summer of 2023. We had a small bridge program in 2022, Law School Unmasked, and received positive feedback from students on how it increased their feelings of confidence and belonging, and generally increased their ability to succeed in their first semester.[11] For example, “It was very helpful for me as a first generation college and now law student since I do not have anyone I can turn to for help with these topics we went over. Figuring out how things work as a first generation student constantly seems like an uphill battle of asking lots of questions to lots of people who always seem to have vastly different answers and then finding out which answers are correct. This program helped to answer a lot of questions that would have made me feel lost for the first semester of law school.” This shows that programs designed for first-generation students can and do make a difference!
Finally, I encourage all schools to support the formation of a first-generation law student group. This can help ensure first-gen students feel connected, and in a very obvious way, realize they aren’t alone. When I was in law school, I assumed that I might be the only person in the building who didn’t have parents who went to college. However, when I started writing my book – and asking for stories and advice – I discovered that many of my friends and professors were, in fact, also first-generation students. This was shocking to me. So a student group, first and foremost, signals to students that they aren’t the only ones. LSAC is currently working on a National First-Generation Law Student Group, and meeting with already existing student groups to find the best ways to support and foster these types of student organizations.
If you have questions about how to support first-generation students, please feel free to reach out to me at mhale@lsac.org.
[1] Cite 3
[2] FAQ: First-Gen Definition, The Center for First-generation Success, https://firstgen.naspa.org/why-first-gen/students/are-you-a-first-generation-student.
[3] Way back in the dark ages in 2003.
[4] Close the Gap Foundation, last visited May 18th, 2022 https://www.closethegapfoundation.org/glossary/opportunity-gap?gclid=Cj0KCQjwspKUBhCvARIsAB2IYuscRgwXvBQgnHlxQtXJ34Bw4m8g4X_HdMdS_csWATPxgPN0dzuk6eUaAuwKEALw_wcB
[5] id.
[6] Law School Survey on Student Engagement, LSSSE Survey Tool 2021, https://lssse.indiana.edu/about-lssse-surveys/ 1 (Last visited Jan. 17, 2022).
[7] Id.
[8] https://web.cvent.com/event/e2323c1d-5bfb-4ab2-aad0-3cc606276ab1/summary
[9] Id.
[10] https://cali.org/books/first-generations-guide-law-school
[11] https://www.lsac.org/law-school-unmasked
Engagement with Law Student Organizations
Law student organizations are important venues for developing law students’ professional identities. Through networking, invited speakers, and events, these organizations foster a sense of community and provide students the opportunity to more intensely explore areas of law that interest them. [1]
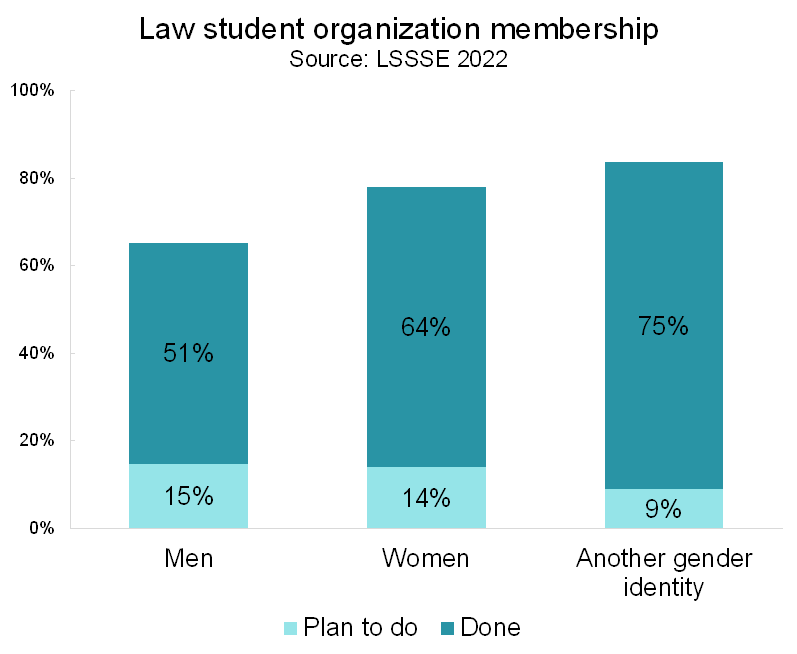
Law student organizations are among the most popular enriching activities at law schools. Nearly three-quarters (73%) of law students either plan to join a law student organization or have already done so. About 31% of students have served as law student organization leaders, and another 18% plan to take on a leadership role before they graduate. Men are less likely to join student organizations compared to women and those of another gender identity. In 2022, just 51% of men had already joined an organization compared to 64% of women and 75% of those with another gender identity.
Black students are particularly engaged as members of law student organizations, with 65% of Black students participating and another 20% planning to do so. Native Hawaiian students, American Indian students, and Alaska Native students have similarly high levels of engagement with law student organizations, while Asian and white students have the lowest participation rates.
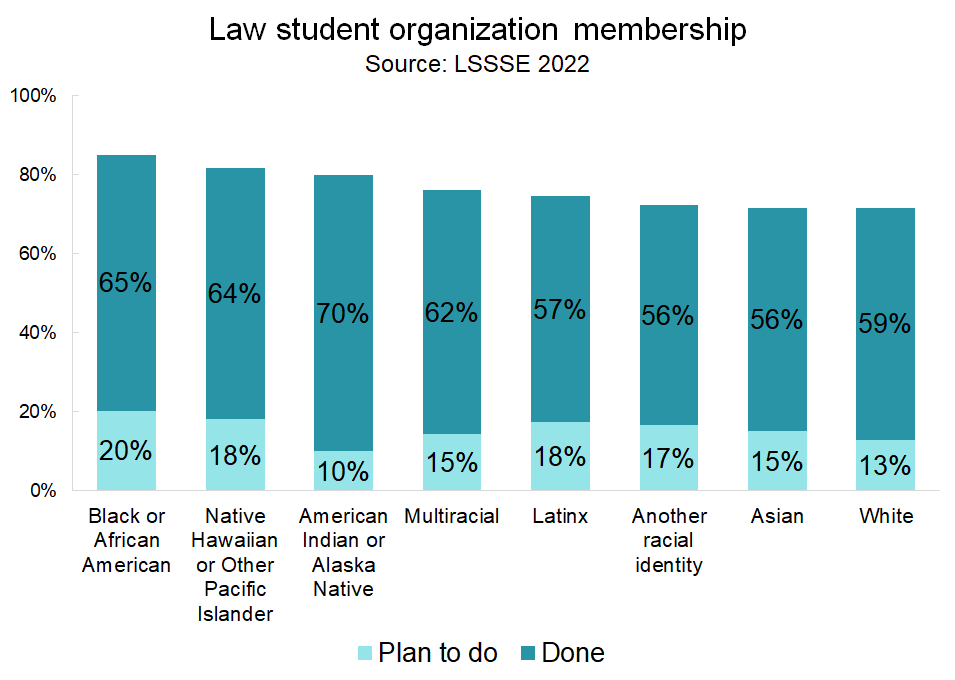
Women, gender-diverse people, and students of color are most likely to join student organizations. Thus, these organizations likely play a vital role in connecting law students who traditionally face higher barriers in accessing higher education and assimilating successfully into the legal profession. Law student organizations also given students the opportunity develop their leadership skills and to work with their professors and classmates in a non-classroom context.
____
[1] See Andrew Hitt, The importance of student organizations, (Aug. 27, 2009), https://law.marquette.edu/facultyblog/2009/08/the-importance-of-student-organizations/
Law Student Stress and Anxiety
Are today’s law students just as stressed as yesterday’s law students? LSSSE has been tracking student stress levels for the last eight years with our optional Student Stress module. In addition to overall law school-related stress and anxiety, the module asks about anxiety and stress caused by teaching methods, competition with peers, financial concerns, and more.
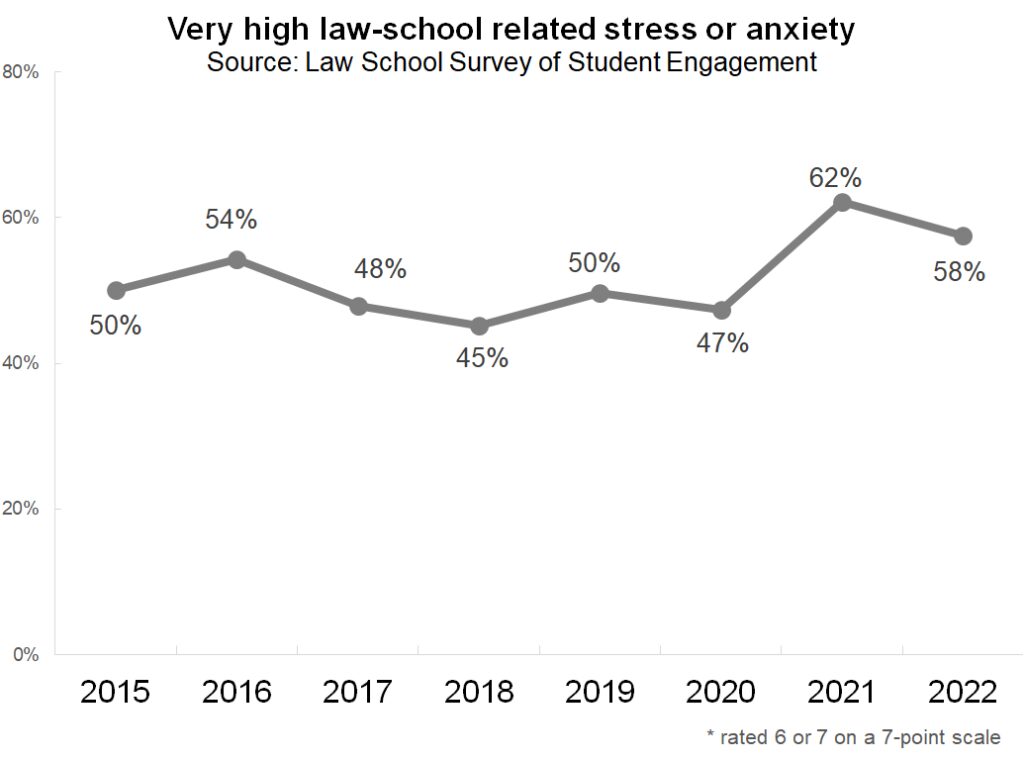
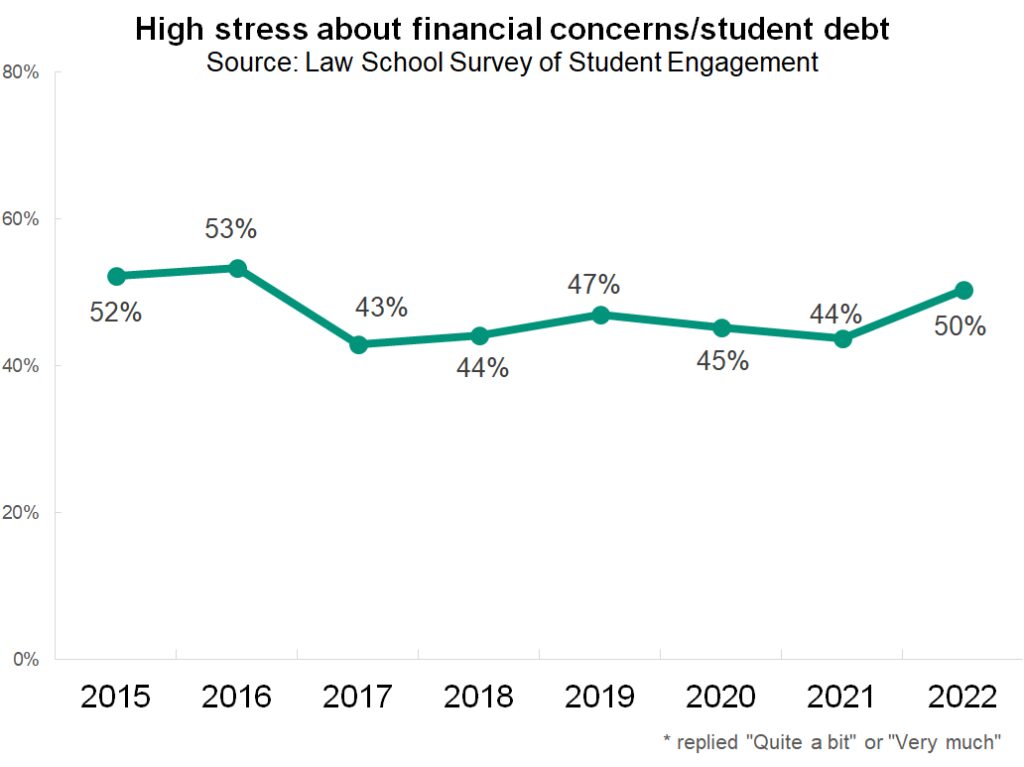
The percentage of students who report high levels of stress and anxiety (rated as a 6 or a 7 on a seven-point scale) has remained fairly stable over the last several years. About half of all law students feel very high levels of stress. There was a marked increase in highly stressed students between 2020 and 2021, which is likely a byproduct of living through a year of COVID-19.
Stress about financial concerns has remained mostly stable as well. A little less than half of all students feel that financial concerns and student debt cause them “quite a bit” or “very much” stress or anxiety.
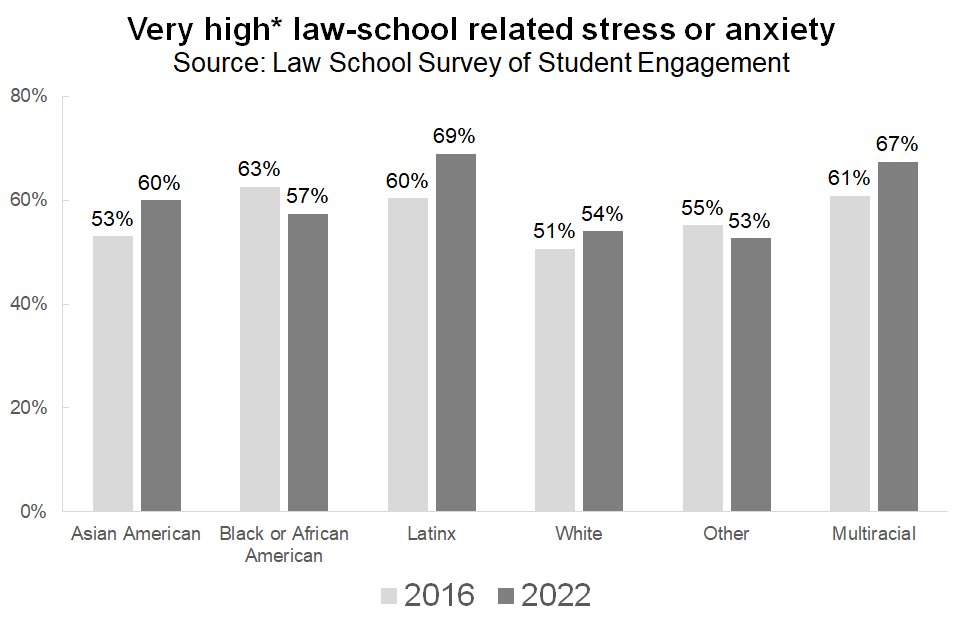
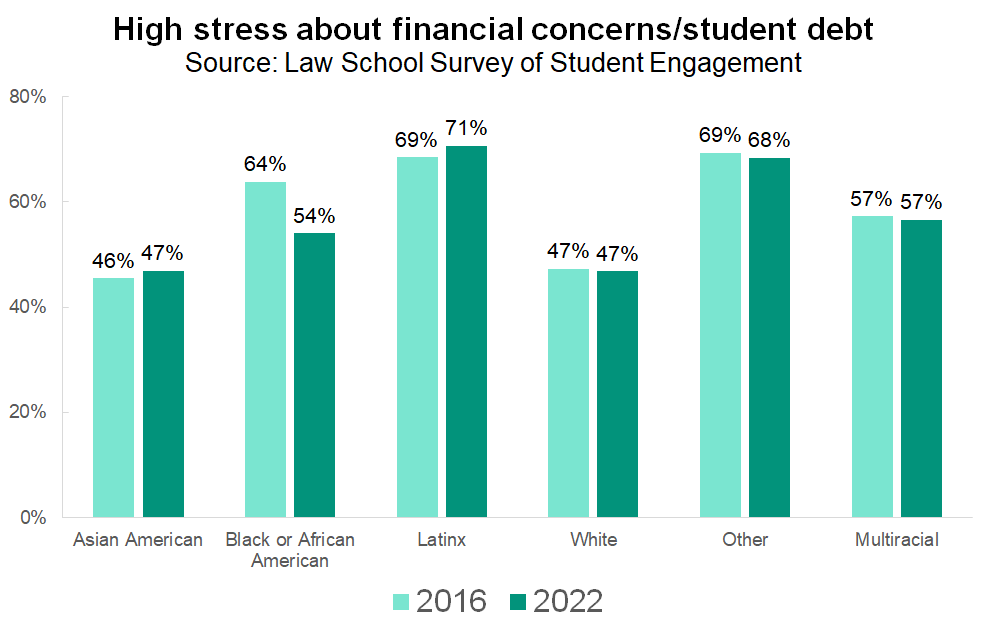
While stress levels have not changed considerably in the last several years, neither has the fact that some students are more likely to be stressed than others. Although African American and Latinx students experience only slightly higher levels of overall law school-related stress and anxiety relative to their white and Asian American peers, they are much more likely to be stressed about financial concerns. These fears are justified, given that the burden of student debt falls disproportionately on their shoulders.
Fortunately, most students do sense that their law school tries to help with stress management. In 2022, three-quarters of student said that their law school places at least some emphasis on ways to effectively manage stress and anxiety. Given high rates of substance misuse and mental health issues within the legal community, developing strong coping skills should remain a high priority for law schools and the future lawyers they serve.
Part 2: The COVID Crisis in Legal Education: Concern about Meeting Basic Needs
In our last post, we used LSSSE longitudinal data that was first reported in our 2021 Annuals Results, The COVID Crisis in Legal Education (pdf), to discuss the areas of law student engagement that were most impacted by the COVID-related challenges of the 2020-2021 academic year. In addition to the intangible losses, COVID also deepened ongoing disparities and inequities in legal education, as it did in society more generally. Student populations that were especially vulnerable pre-pandemic faced even greater challenges over the past year. The crisis has been perhaps most critical when considering basic necessities, though every level of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs has been affected—from the essentials of food, rest, physical safety, and financial security to the desire for belonging, appreciation, and ultimately achieving one’s full potential.
In 2021, many students struggled to meet their basic needs. In their responses to the LSSSE survey module Coping with COVID, 43% of all law students reported increased concern about having enough food due to COVID-19. This already troubling finding about students as a whole masks significant racial disparities with food insecurity: over half of all Black (55%), Latinx (57%), and Asian American (52%) students acknowledged that the past year brought increased concerns about whether they had enough food to eat.
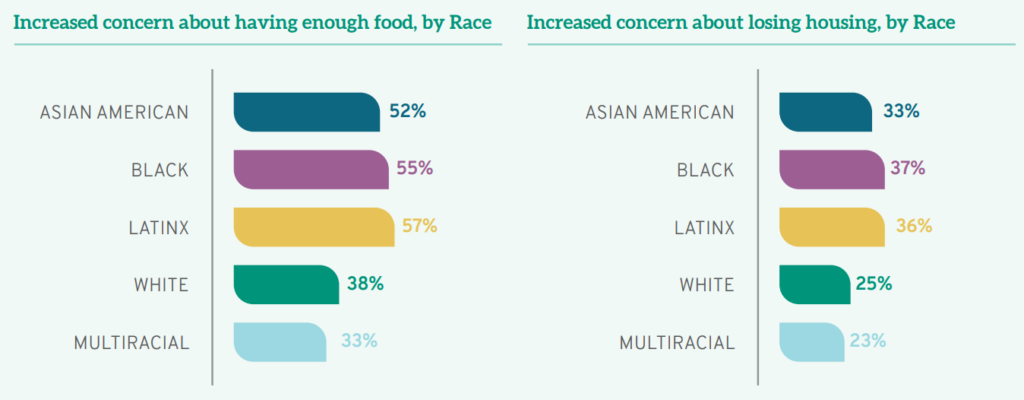
Financial concerns weighed heavily on students’ minds. Almost two-thirds (63%) of all student respondents had increased concerns about their ability to pay their bills, with both gender and race-based disparities increasing challenges for already vulnerable populations. For instance, among those who had elevated concerns about their financial security were 71% of Latinx students, 68% of Black students, 67% of multiracial students, and 64% of Asian Americans, compared to 60% of White students. Additionally, while over half of the men (57%) worried that the pandemic would affect their ability to pay their bills, over two-thirds of the women respondents (67%) faced similar financial uncertainty; a full 14% of women students reported that their financial fears had increased “very much,” compared to only 6% of men reporting that same high level of concern.
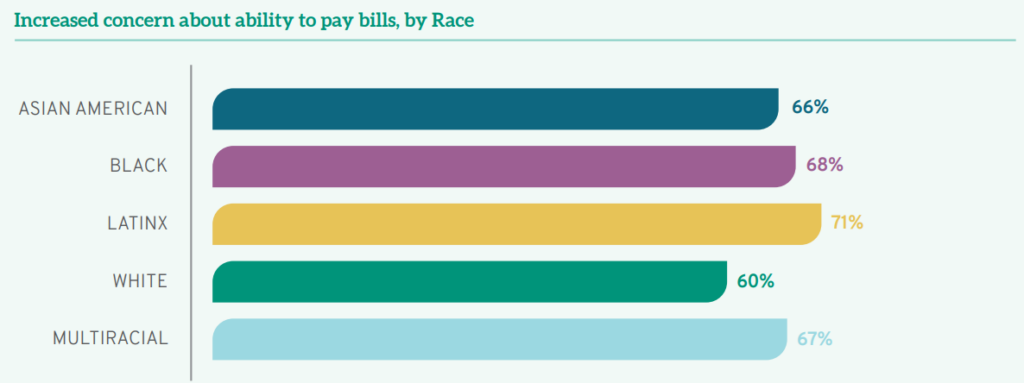
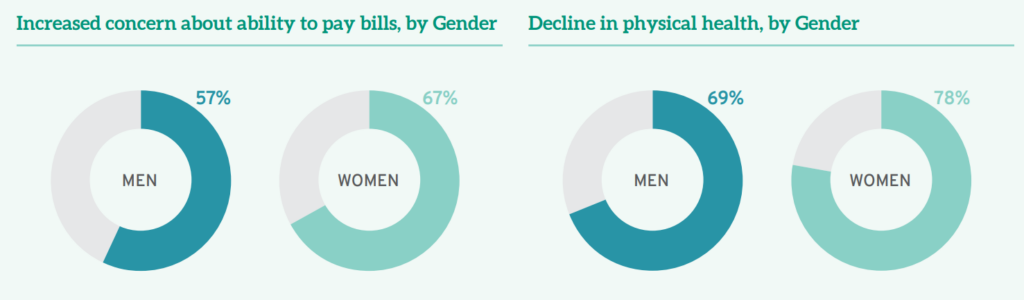
Perhaps unsurprisingly, given elevated attention to satisfying basic needs like food, shelter, and financial security, as well as the realities of the pandemic, 75% of all law student respondents also reported increased concerns about their own health and safety, while 84% were also more worried about the health and safety of friends or family. A full 75% reported a decline in their own physical health over the past year, though men fared better in this regard: two-thirds (69%) of all men surveyed noted a decline in their physical health compared to over three-quarters (78%) of women law students.
Legal education has survived what were hopefully the deepest lows of the COVID-19 pandemic. But we did not emerge unscathed. The core of legal education continued as before—the basics of teaching and learning pivoted from in-person to online, professors successfully conveyed care and concern along with doctrinal analyses, and student satisfaction levels remained remarkably high. Yet just as in other aspects of our lives this past year, legal education lost much of its depth and flavor. It has been less fulfilling, less comprehensive, less effective at imparting the intangible skills our students will need to employ in their future careers. Most critically, the Coping with COVID Report (pdf) reveals that our students have been struggling beyond anything they have experienced collectively before.
Guest Post: Legal Education and the Illusion of Inclusion
Guest Post: Legal Education and the Illusion of Inclusion
 Shaun Ossei-Owusu
Shaun Ossei-Owusu
Presidential Assistant Professor of Law
University of Pennsylvania Carey Law School
A new semester and a potentially new political landscape are upon us. Last month law students around the country resumed coursework. Their educational pursuits are virtual, in-person, or some mix of both. No matter the format, law students continue their educational journey in an ideologically polarized pandemic society where race, class, and gender disparities are on sharp display.
Students will also be learning in a context where changes in our legal system may have direct relevance to their legal education. As is typically the case, a newly constituted Supreme Court has a diverse docket this term that might shape substantive areas of law that students take courses in, chiefly constitutional law. There will be regulatory shifts that come with new administrations. These kinds of changes will have meaning for administrative law and related areas of law: health law, environmental law, employment law, and civil rights, to name a few. COVID-19 has upended state and federal judiciary systems in ways that have still-undetermined implications for procedural courses law students take (e.g., evidence, civil procedure, criminal procedure) and access to justice issues more generally. And we know from the late Deborah Rhode’s work which communities access to justice issues tend to devastate—racial minorities, women, and other marginalized populations.
Notwithstanding future uncertainty, one thing can be said with some measure of confidence: issues of race and gender—amongst other social categories—will remain relevant inside and outside the sometimes intellectually-cordoned off walls of law schools. How these issues are integrated in the classroom, if they are at all, will affect the substantive learning of law and will either include or exclude historically marginalized groups.
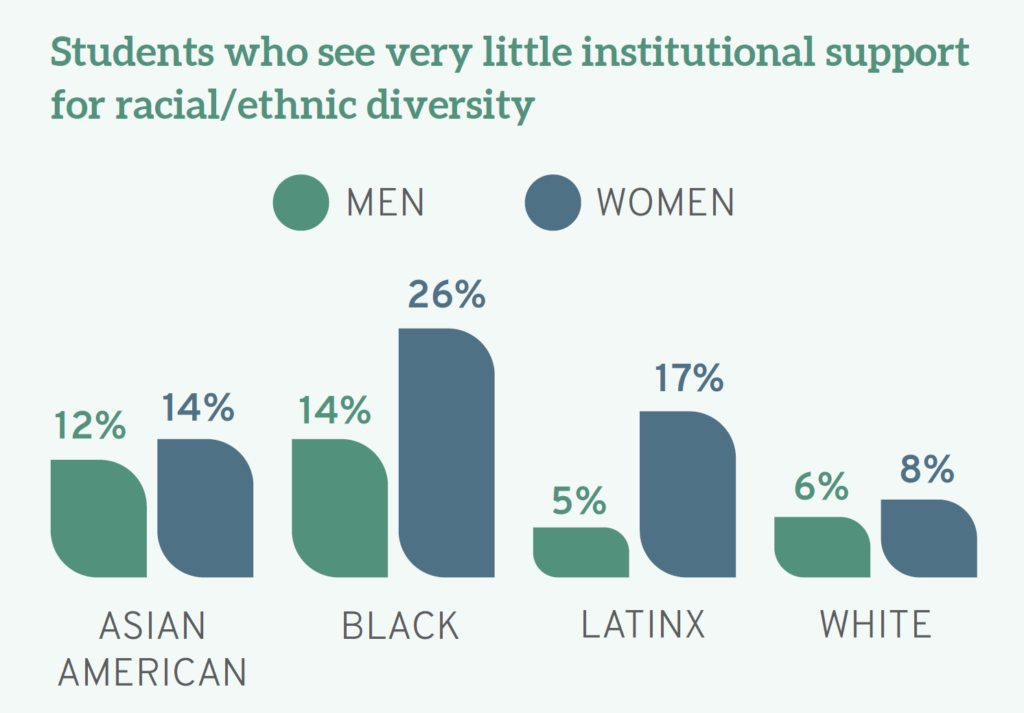
In the specific context of legal education, the results of Law School Survey of Student Engagement’s (LSSSE) Annual Survey illuminate. The Report provides a glimpse into how law schools fail to meet the aspirational goal of inclusion that often takes up primetime real estate on their websites and promotional materials. From my own read, the most jaw-dropping finding is intersectional in nature and about Black and Latinx women law students—aspiring attorneys who are often told that they do not look like lawyers when they transition to practice. 26% of Black women respondents and 17% of Latinx women respondents reported that their schools do “very little” to support racial and ethnic diversity.
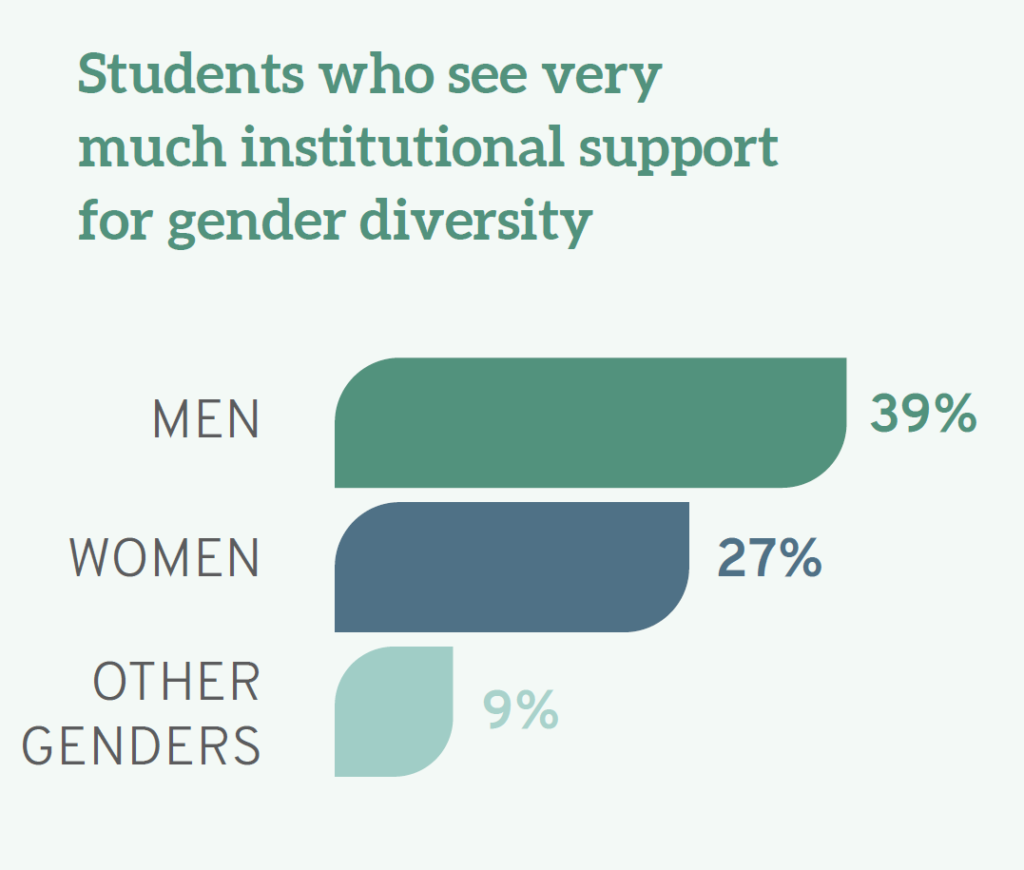
Disenchantment with the lack of support for diversity can be distilled even further. The Report notes that men varied on the issue of gender inclusivity, with 39% “very much” believing that their schools support gender diversity compared to 27% of women and 9% of individuals who identified with the “other gender” category.
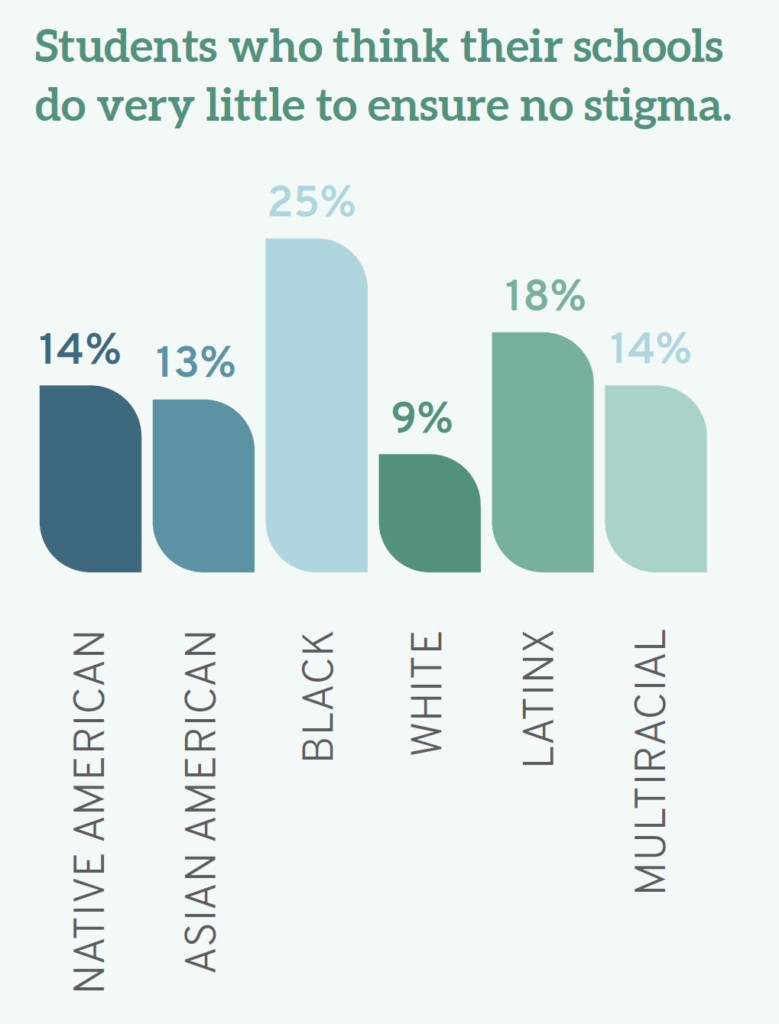
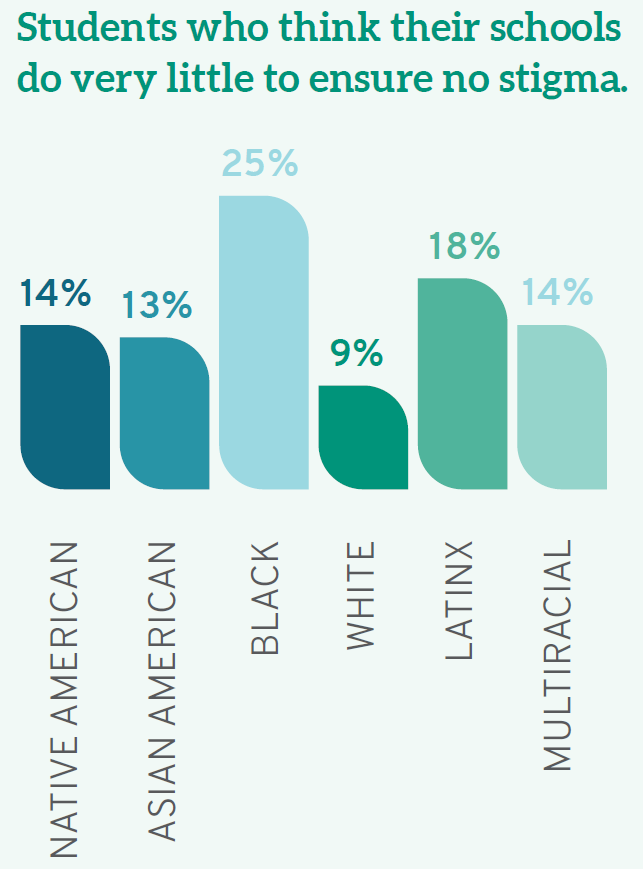
In the context of race, student views also differed, with 9% of White students, 14% of Native American students, 18% of Latinx students, and 25% of Black students believing that their schools do “very little” to ensure that students are not stigmatized based on identity.
Where sexuality and sexual orientation are concerned, 11% of heterosexual students think their schools do only “very little” to avoid identity-based stigma; conversely, 20% of gay students, 16% of lesbian students, 15% of bisexual students, and 19% of those who identify as another sexual orientation see their schools as doing “very little” in this regard. What do these findings mean for legal education and the political moment I gestured to in the beginning?
LSSSE’s data suggest that some students are dissatisfied with the six-figure education they are receiving. Put plainly, law students from backgrounds that the profession has historically excluded—women, racial minorities, LGBTQ communities, and people with disabilities in particular—do not feel part of the academic community and believe law schools are relatively disinterested in their stigmatization. In some ways, this is unsurprising, as there is a deep scholarly literature and genre of books on student disappointment with law school. Moreover, student disenchantment with legal education—which has a history of exclusion that traces back to the nativism and anti-Semitism of the early twentieth century—may in some ways be pre-determined.
The confines of the classroom, which is one of the many areas the LSSSE survey discusses, provides more insight into the inclusion-exclusion dyad. From the vantage point of some educators, law school is simply about training people to be lawyers. The most generous reading of this position suggests that social justice-like ideas like “inclusion” are too ideologically weighty to meaningfully bring in the classroom. For people who subscribe to this view, attempts at inclusion can create impossible-to-navigate landmines for professors. More skeptically, some see inclusion as an ancillary. Read in this light, the primary goal is to inculcate legal knowledge. For these professors, some things are not relevant to the practice of law and are therefore not relevant to legal education.
Such professional school-based views of legal education, vary in their reasonableness, but are held by swaths of the professoriate. Yet, there is a two-fold problem, and this is where the LSSSE survey is especially useful. First, this vision of legal education rubs up quite abrasively against the representations of law schools as bastions of inclusion. Second, this version of education, in some ways, undermines the well-touted “diversity rationale” in affirmative action jurisprudence. What does diversity mean when the subjects of diversity feel alienated?
Considering the mismatch between some students’ experiences and the stricter professional school model of legal education that some professors are beholden to, there are some options. Educators can simply be more intellectually honest about the reality that law school is a site of professionalization where inclusion principles can be trivialized. Alternatively, law schools can continue to disingenuously hitch the law school wagon to social justice rhetoric while failing to actualize inclusion as a practice. Or, in the most courageous and imaginative versions of themselves, law schools can refashion their curriculum and use developments in the legal world as opportunities to offer more inclusive learning environments.
For law schools committed to the third way, resources abound. Complaints about the need to diversify the content of law school courses have existed for decades. Scholars such as Derrick Bell and Dorothy Brown have authored casebooks that describe how race intersects with different areas of the legal curriculum, whereas feminist legal theorists, poverty researchers, scholars of law and sexuality have penned their own books, supplements, and articles that all give educational guidance on how to bring these issues into core courses, and do so in ways that are doctrinally sound. Still, some professors—many of whom have the most analytically sharp minds on their university campuses—throw their hands up in despair or continue with the same regularly scheduled program. For some of these instructors, these conversations were absent in their legal education, and they were likely not trained to incorporate these issues. Some may think it would be better to leave this work of thematic inclusion to their more expert colleagues (e.g., scholars of race, sex, class, disability) rather than wade into territory where they are sure to mess up. But throwing one's hands up in despair is increasingly a less credible course of action. The pandemic, along with the protests of 2020, have forced some people to rethink how they deliver course content, and more importantly, have made inequality a more prominent theme in our public discourse. The current socio-political moment, and the reality of pandemic pedagogy, call for curricular redesign.
Fortunately, the tools to make the classroom more inclusive are available and they are not limited to the usual courses. To be sure, law professors have written about how first-year courses like criminal law and property are inattentive to inequality in ways that produce the responses found in the LSSSE survey and have offered suggestions on how those same courses could easily be improved. But attempts to diversify and create a more inclusive curriculum are not confined to these foreseeable areas of law but can be found in more unsuspecting places like evidence, corporate law, trust and estates, and intellectual property, to name a few.
Law professors have also identified space in the curriculum for trans-substantive engagement with the kinds of questions and perspectives that demonstrate an awareness of inequality, both in legal education and in law more generally. Indeed, I, along with my colleague Karen Tani, have taken on the task of trying to simultaneously create an inclusive learning environment that rigorously addresses inequality by creating a 50-person Law and Inequality course at Penn Law. This endeavor and more meaningful engagements with diversity need not be limited to women, racial minorities, and sexual minorities. Inclusion also implicates and has meaning for the larger law student population. One of the most understated findings in the LSSSE Report is that 16 percent of white students believed law schools placed “very little” emphasis on issues of equity and privilege and do not prioritize providing students with the skills necessary to confront discrimination and harassment.
My purpose here is not to proselytize teaching a course like the one we are offering. Instead, I want to highlight how student dissatisfaction with inclusion, which the Report highlights in detailed and accessible fashion, can be situated within this critical juncture. 2021 is a unique moment where law schools can reimagine legal education in real time, and for a post-pandemic world. This will not be easy, as this is a stressful time for faculty—some of whom are in high-risk groups during the pandemic and/or have a variety of care obligations. COVID-19 has upended a lot of assumptions and forced people to change longstanding pedagogical practices. Institutions could do a lot of good by encouraging faculty reflection and supporting creative reorganization of current courses.
The LSSSE Report tells us that in many ways, law schools are failing to provide the inclusive educational spaces that they, I believe in good faith, want to offer and that students of various backgrounds actively desire. Ultimately, the teaching tools are available, the moment is ripe, and the only outstanding question is whether legal educators will make the changes necessary so that the next LSSSE survey offers more optimistic findings.
Annual Results 2020 Diversity & Exclusion: Diversity Skills
This year for the first time, LSSSE introduced a set of questions focused on diversity and inclusion that supplement related questions from the primary survey. The Diversity and Inclusiveness Module examines environments, processes, and activities that reflect the engagement and validation of cultural diversity and promote greater understanding of societal differences. The 2020 LSSSE Annual Results Diversity & Exclusion report presents data about how diversity in law school can prepare students for the effective practice of law upon graduation. In our final post in this series, we will explore how law schools can teach skills to equip students to interact with people from different backgrounds.
Schools have a responsibility to not only admit and provide the resources to enroll a diverse class of students, but to impart the skills these students will need to be effective lawyers. Increasingly, the practice of law requires sensitivity to issues of race/ethnicity, gender, sexual orientation, and socioeconomic status. Law schools can empower students first by encouraging them to reflect on their own identities, and then supplying coursework on issues of privilege, diversity, and equity; while it is important for students to learn about anti-discrimination and anti-harassment, law schools should also equip them with the tools they will need to fight these social problems as attorneys and civic leaders.
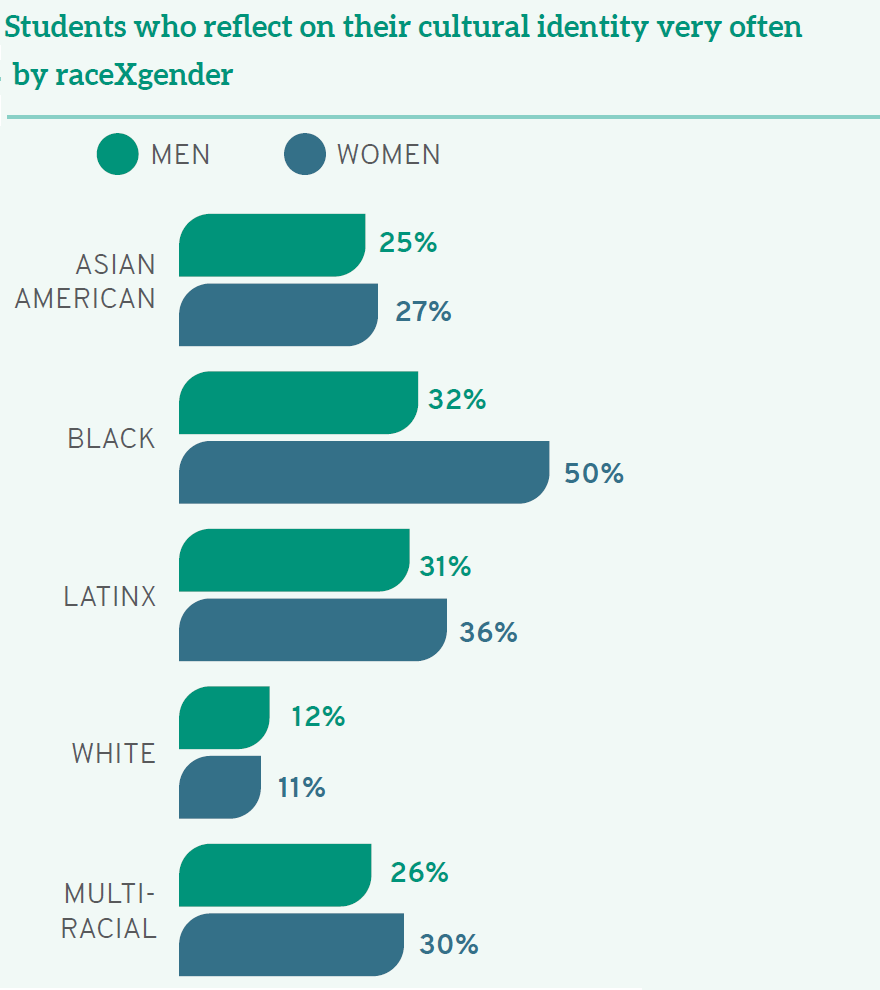
Yet schools are, by and large, not preparing law students to meet these challenges and succeed as leaders. When students were asked how frequently they reflect on their own cultural identity, only 12% of White students do so "very often," compared to 50% of Native American students, 44% of Black students, and 34% of Latinx students. Even more alarming, over a quarter (26%) of White students never reflect on their cultural identity during law school. When we consider the intersection of raceXgender, an even more troubling picture emerges. A full 28% of White men and 25% of White women in law school never reflect on their cultural identity, compared to the 50% of Black women who do so "very often."
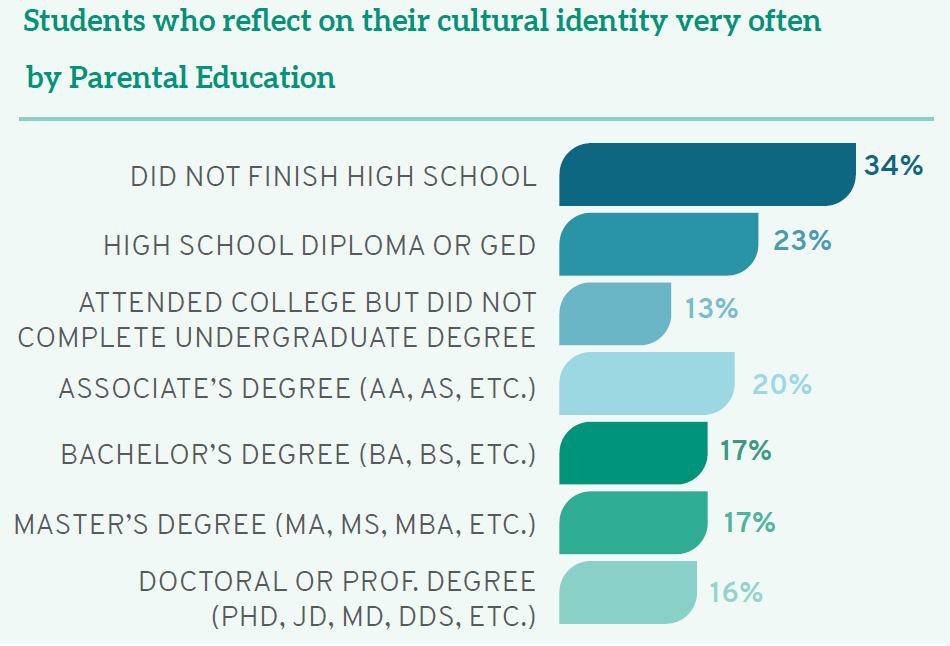
Students whose parents have less formal education are also more likely to reflect on their cultural identity, including 34% of those whose parents did not finish high school as compared to 16% of those who have a parent with a doctoral or professional degree. In sum, students with racial, gender, or class privilege are less likely to reflect on the benefits associated with their identity.
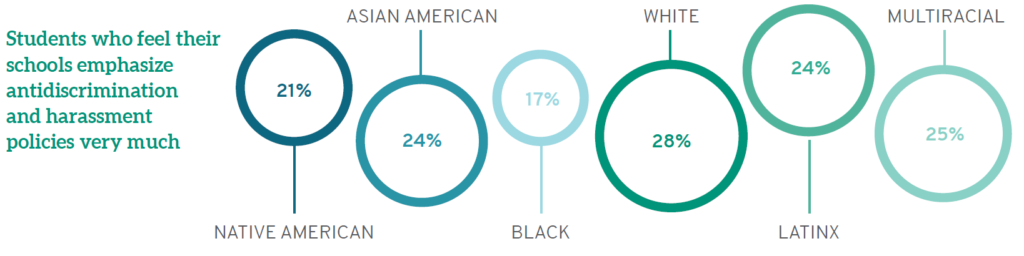
Even without self-reflection, students can nevertheless gather information about anti-discrimination and harassment policies. LSSSE data show that while White students see their schools as prioritizing this information, students of color do not agree at the same high levels. Similarly, men (31%) are more likely than women (23%) and those with another gender identity (11%) to believe their schools strongly emphasize information about anti-discrimination and harassment. Considering raceXgender, a full 27% of Black women see their schools as doing "very little" to share information on anti-discrimination and harassment, while 32% of White men believe their schools do "very much" in this regard.
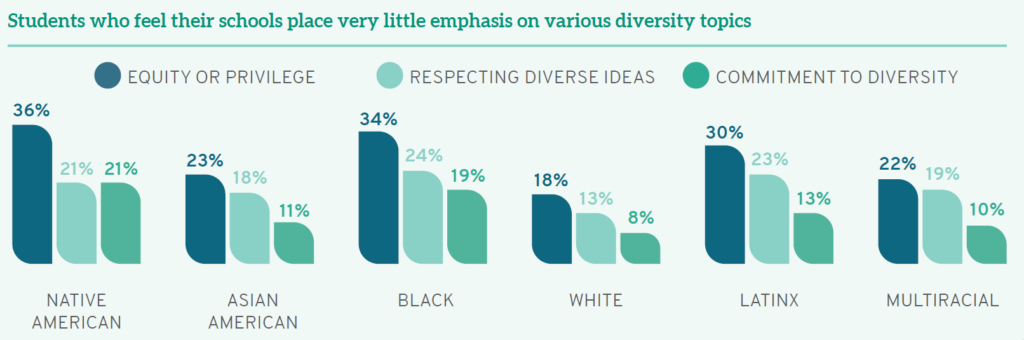
Equally troubling, students from different backgrounds perceive institutional emphasis of various diversity-related topics in starkly divergent ways. Although White students believe that their schools emphasize issues of equity or privilege, respecting the expression of diverse ideas, and a broad commitment to diversity, students of color are less likely to agree. Students of color—including those who are Black, Latinx, Asian American, Native American, and multiracial—frequently note and appreciate assignments or discussions of race/ ethnicity and other identity-related topics in the classroom; yet they are more likely than their White peers to report that schools place “very little” emphasis on diversity issues. Women are similarly more likely than men to believe their schools do “very little” to emphasize diversity in coursework. Furthermore, higher percentages of Black women report “very little” emphasis on equity or privilege (36%), respecting diverse perspectives (27%), and an institutional commitment to diversity (21%)— compared to high percentages of White men who believe their schools are doing “very much” in all three arenas (20%, 24%, and 34%, respectively). First-gen students are also more likely than their classmates whose parents completed college to note “very little” diversity coursework. Synthesizing these data, students who are traditionally underrepresented and marginalized—arguably the students who have the most personal experience with issues of diversity—see their schools as doing less to promote diversity and inclusion than those who are privileged in terms of their race/ethnicity, gender, and parental education.
As part of a broad curriculum that sets up students for their future practice, law schools should teach students diversity skills—a set of skills that facilitate success in our increasingly globalized society, ranging from personal reflection to the tangible tools lawyers can use to combat discrimination. Law schools that succeed at these diversity-related endeavors will be preparing our nation’s newest lawyers to meet the full range of challenges ahead.
Annual Results 2020 Diversity & Exclusion: Sense of Belonging
This year for the first time, LSSSE introduced a set of questions focused on diversity and inclusion that supplement related questions from the primary survey. The Diversity and Inclusiveness Module examines environments, processes, and activities that reflect the engagement and validation of cultural diversity and promote greater understanding of societal differences. The 2020 LSSSE Annual Results Diversity & Exclusion report presents data about how diversity in law school can prepare students for the effective practice of law upon graduation. In this post, we explore how sense of belonging at law school varies among students from different backgrounds.
Scholarly research indicates that students who have a strong sense of belonging at their schools are more likely to succeed.1 Generally, belonging refers to feeling like part of the institutional community, fitting in, and being comfortable on campus.2 Using a number of separate indicators, LSSSE data on diversity and inclusiveness show that White students are more likely to have a strong sense of belonging than their classmates of color. For instance, when asked whether they feel they are "part of the community at this institution," a full 31% of White students strongly agree—though lower percentages of students of color do, including only 21% of Native American and Black students. Even more problematic when considering the importance of building an inclusive community: women of color are more likely than men from their same racial/ethnic backgrounds to feel that they are not part of the campus community—including a whopping 34% of Black women law students nationwide. First-gen students also deserve greater support, as only 23% "strongly agree" that they feel like part of the community at their law school, compared to 31% of students whose parents have at least a bachelor’s degree.
Students of color are also more likely than their White classmates to think their schools do "very little" to ensure students are not stigmatized based on various identity characteristics, including race/ethnicity, gender, religion, and sexual orientation. While only 9.3% of White students agree, 14% of Native Americans, 18% of Latinx students, and a full quarter (25%) of Black students believe their schools do "very little" to emphasize that students are not stigmatized based on identity. Similarly, 11% of heterosexual students think their schools do only "very little" to avoid identity-based stigma; conversely, 20% of gay students, 16% of lesbians, 15% of bisexual students, and 19% of those who identify as another sexual orientation see their schools as doing "very little" in this regard. Taken together, these findings suggest that those most likely to suffer stigma are also those most likely to think their schools do very little to protect them.
White students are also more likely than those from other backgrounds to be comfortable being themselves on campus, with only 12% noting they are not. Yet one out of every five (21%) law students who is Native American, Black, or Latinx notes that they do not "feel comfortable being myself at this institution."
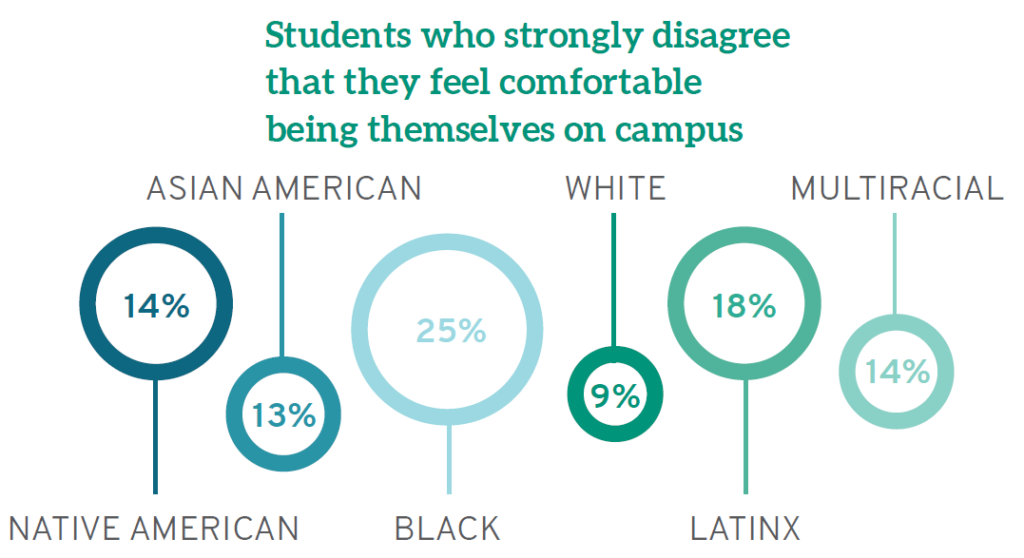
There are also disturbing disparities when considering parental education—a strong proxy for family socioeconomic status. Being comfortable on campus increases almost in lockstep with increases in parental education; a full 32% of law students whose parents did not finish high school are uncomfortable being themselves on campus, compared to just 12% of those who have a parent with a doctoral or professional degree.
The overarching theme from this report is that those who are most affected by policies involving diversity—the very students who are underrepresented, marginalized, and non-traditional participants in legal education—are the least satisfied with diversity efforts on campuses nationwide. Nontraditional students remain marginalized on campus, left out of the community, devalued, and underappreciated. The solution is clear: institutions should place greater emphasis on valuing students from all backgrounds, creating an inclusive community, and integrating diversity into the curriculum. With that foundation, law schools can prepare students to interact in meaningful ways with diverse clientele, to first recognize and then resist instances of discrimination or harassment, and to meet the many challenges they will confront in their roles as lawyers and leaders.
1 Kuh, G. D., Kinzie, J., Buckley, J. A., Bridges, B. K., & Hayek, J. C. (2006). What matters to student success: A review of the literature (ASHE Higher Education Report). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
2 Strayhorn, T. L. (2018). College students’ sense of belonging: A key to educational success for all students. New York, NY: Routledge.